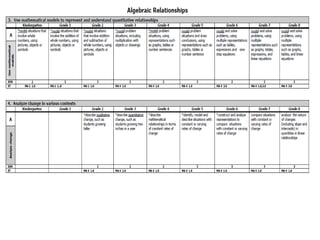
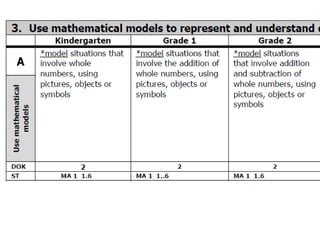
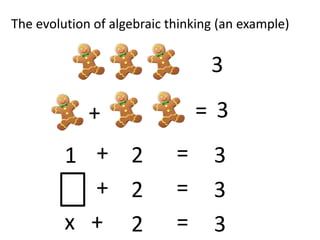
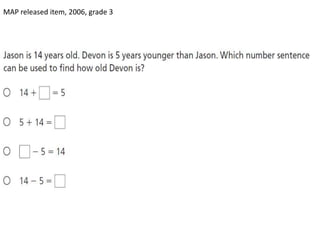
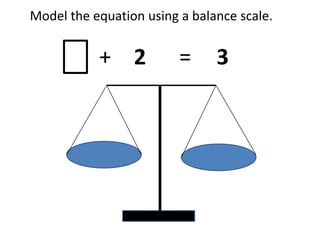
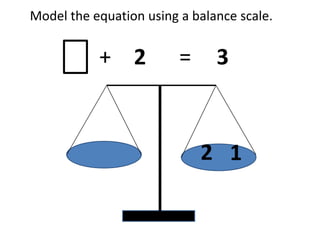
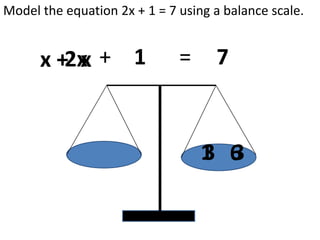
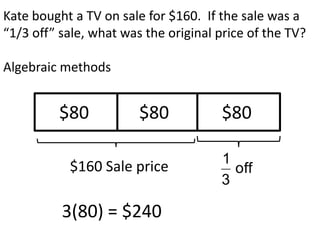
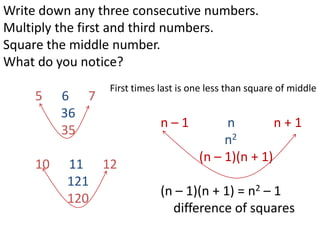
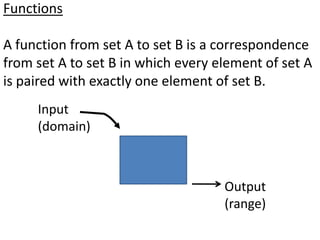
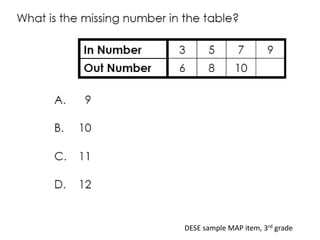
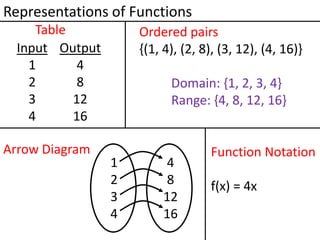
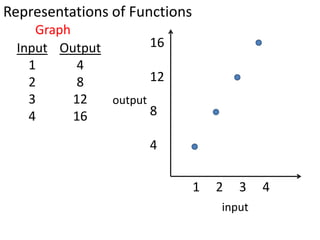
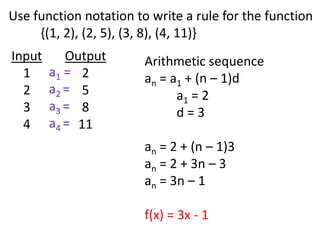
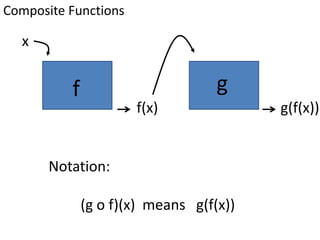
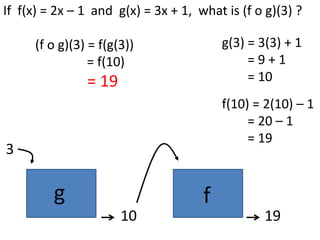
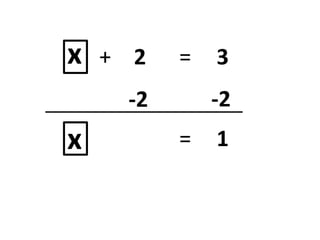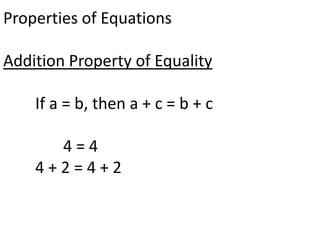Algebraic thinking involves recognizing patterns, modeling situations with symbols, and analyzing change. It relies on understanding variables to represent unknown quantities. The document traces the evolution of algebraic thinking from simple equations to more complex concepts like functions, composite functions, and properties of equations. It provides examples of how algebraic reasoning and symbols can be used to represent and solve real-world problems.