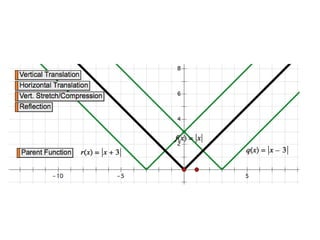
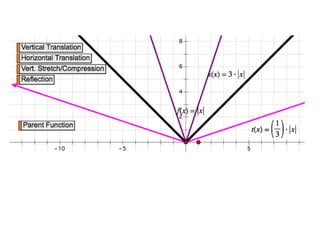
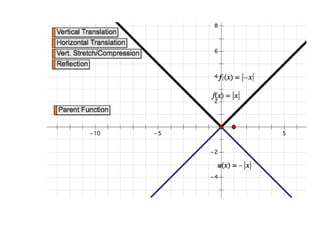
This document provides an overview of key concepts for graphing and understanding absolute value functions in Algebra II Chapter 2. It defines absolute value functions and their key features, including that the absolute value of f(x) gives the distance from the y-axis. Students will learn to graph absolute value functions by hand and using technology. The general form of an absolute value function is given as y = a|x - h| + k and examples are provided to show transformations from the standard form. Practice problems are assigned from the textbook.