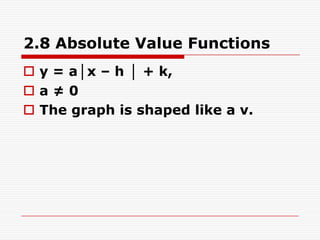
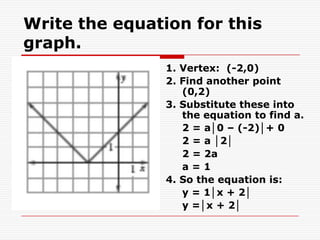
1. The document discusses absolute value functions of the form y = a|x - h| + k, where a ≠ 0.
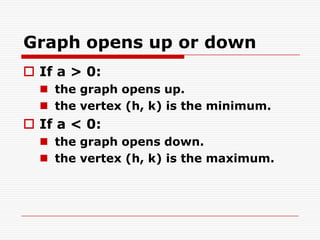
2. It explains how to find the vertex (h, k) and line of symmetry x = h of an absolute value function graph.
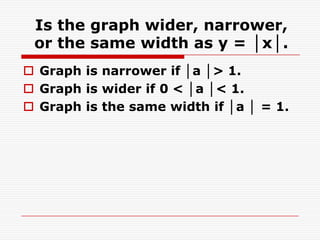
3. It also describes how the graph opens up or down depending on whether a is positive or negative, and how the width compares to y = |x| depending on the value of |a|.