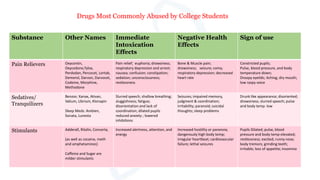
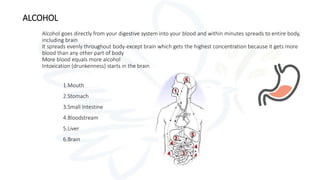
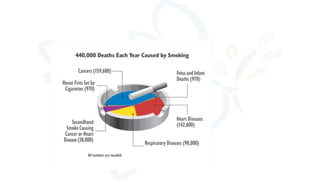
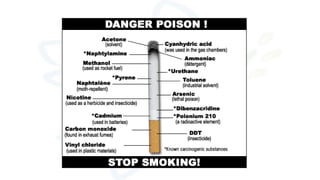
The document discusses alcohol and substance abuse, defining it as harmful patterns of using drugs that can lead to serious health and psychological complications. It highlights the risks associated with various substances, including alcohol, nicotine, and marijuana, while detailing their effects on health and behavior. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of prevention strategies and educating individuals about the dangers of substance misuse.