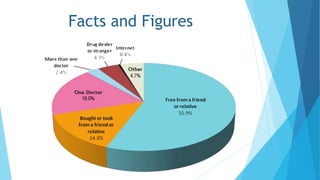
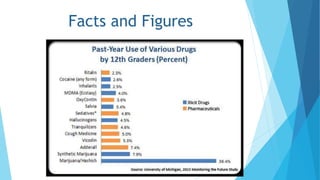
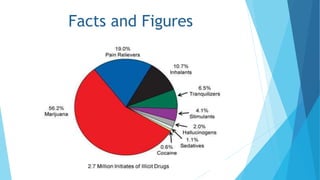
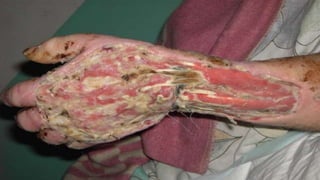
This document discusses drug abuse and addiction. It defines drugs and the differences between drug abuse and addiction. It describes various types of drugs like stimulants, depressants, opiates, and hallucinogens. It discusses reasons why people take drugs and provides statistics on drug use worldwide. The document also covers the effects of specific drugs like marijuana, cocaine, and krokodil. It discusses prevention of drug abuse and treatments for drug addiction. Finally, it highlights the severe drug problem in the state of Punjab, India.