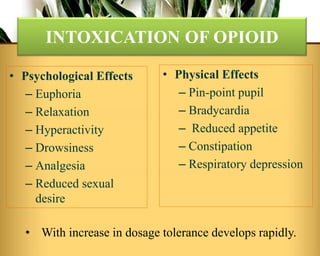
This document discusses opioid use disorder and its effects. It notes that opioids like opium, heroin, and morphine are highly addictive substances. Long term opioid use can lead to dependence and addiction through binding to mu opioid receptors in the brain. Withdrawal symptoms include flu-like symptoms like nausea and craving for the drug. Diagnosis involves examining pupils, testing urine for opioids, and observing for withdrawal symptoms. Treatment involves medication-assisted therapy with drugs like methadone or buprenorphine, counseling, and psychosocial support to prevent relapse.