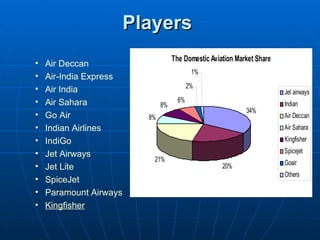
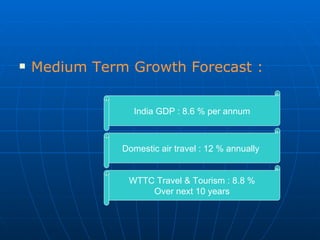
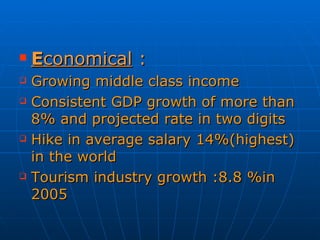
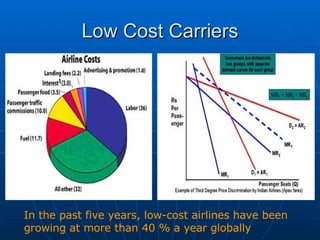
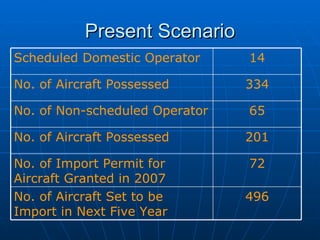
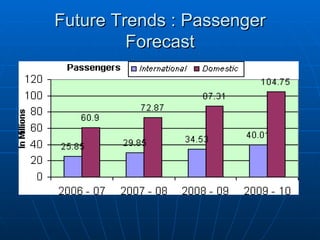
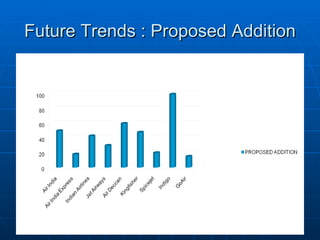
The document summarizes the domestic aviation industry in India. It discusses the history and key players in the industry. Some of the major players mentioned are Air India, Jet Airways, IndiGo, SpiceJet and Go Air. It also analyzes the macro environment factors like growing economy, middle class and potential for future growth. Low cost carriers have been gaining popularity in India and the business models of these carriers are also summarized. The document concludes with future trends of increasing passenger traffic and challenges around infrastructure constraints.