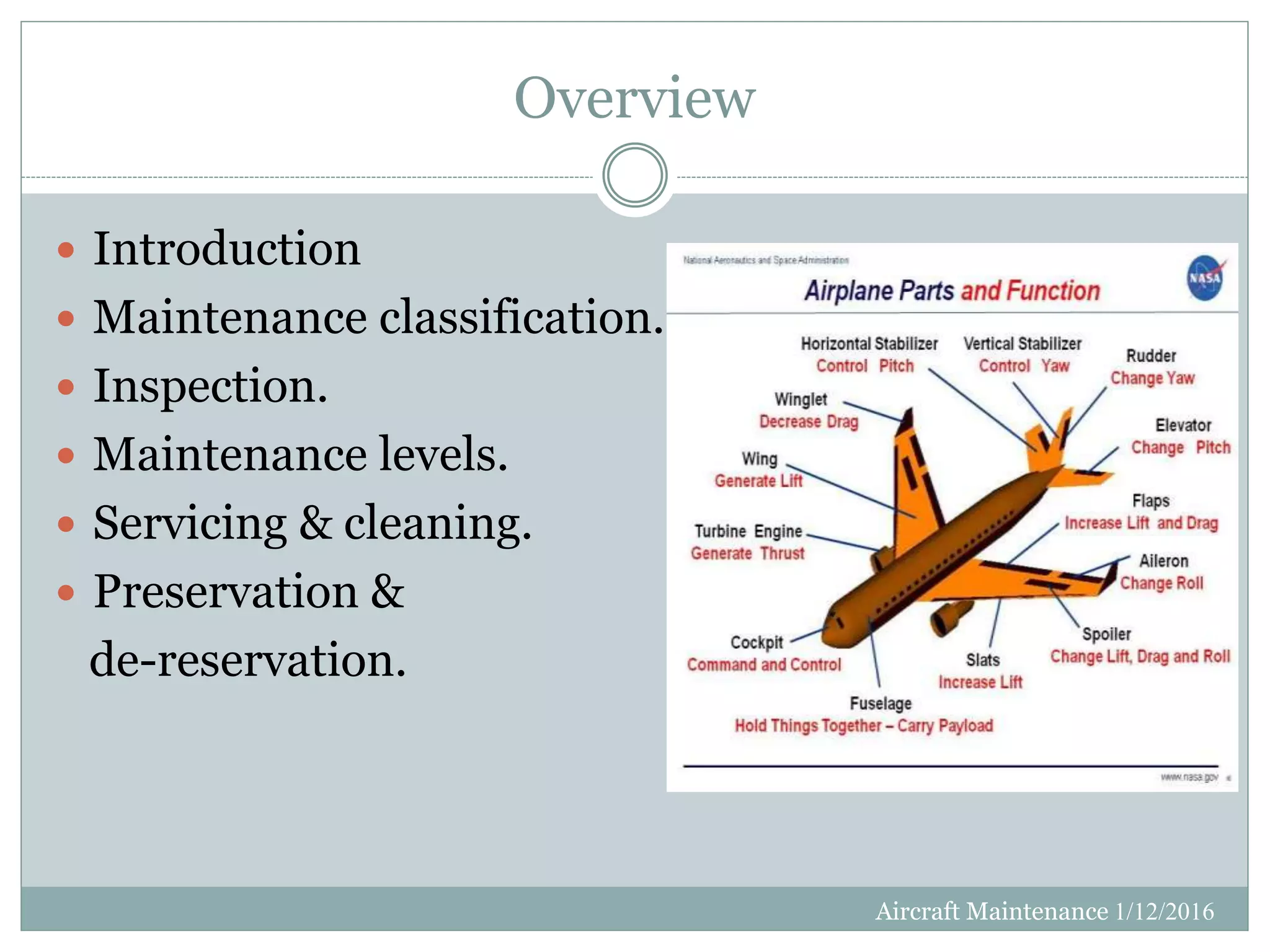
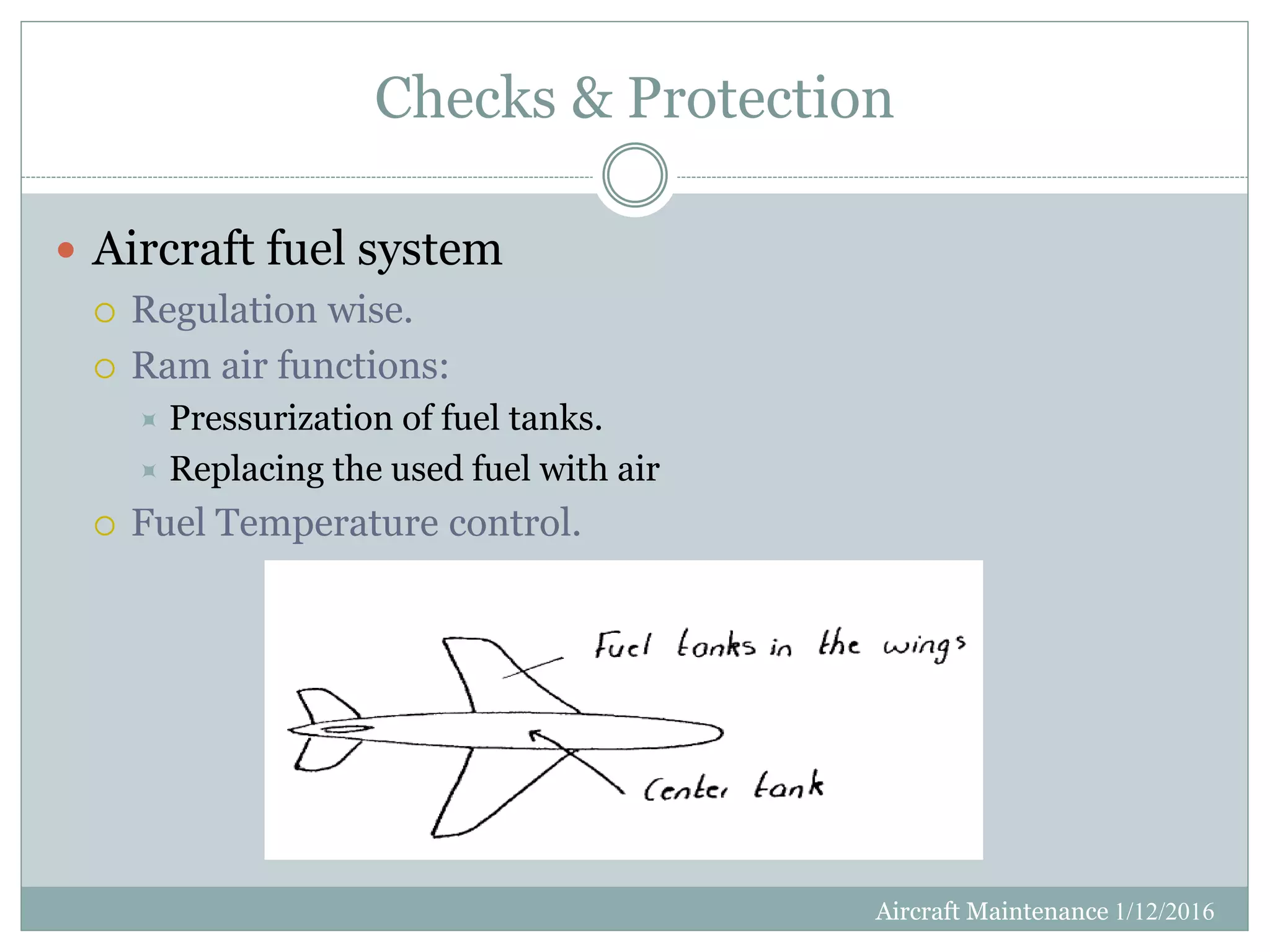
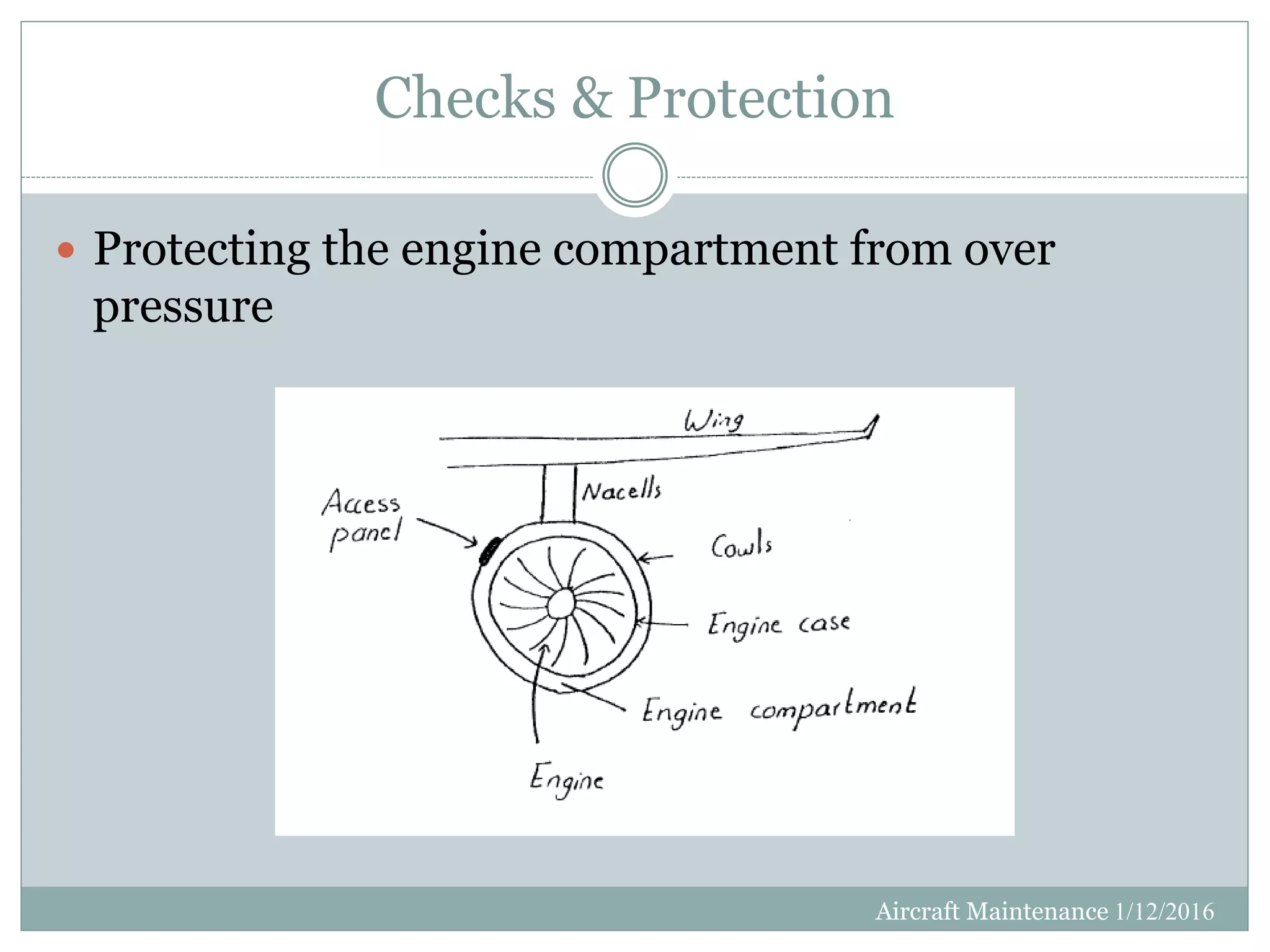
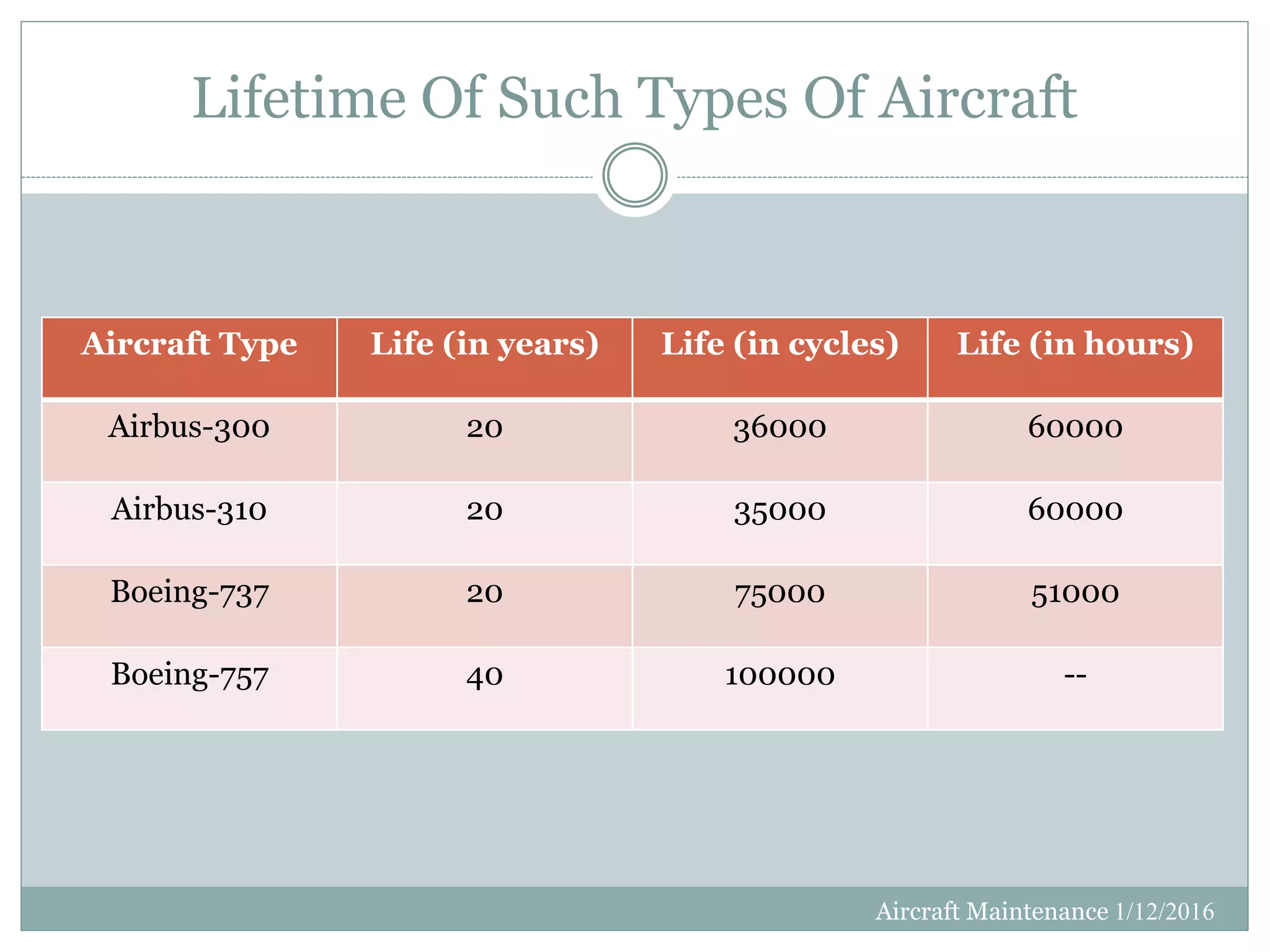
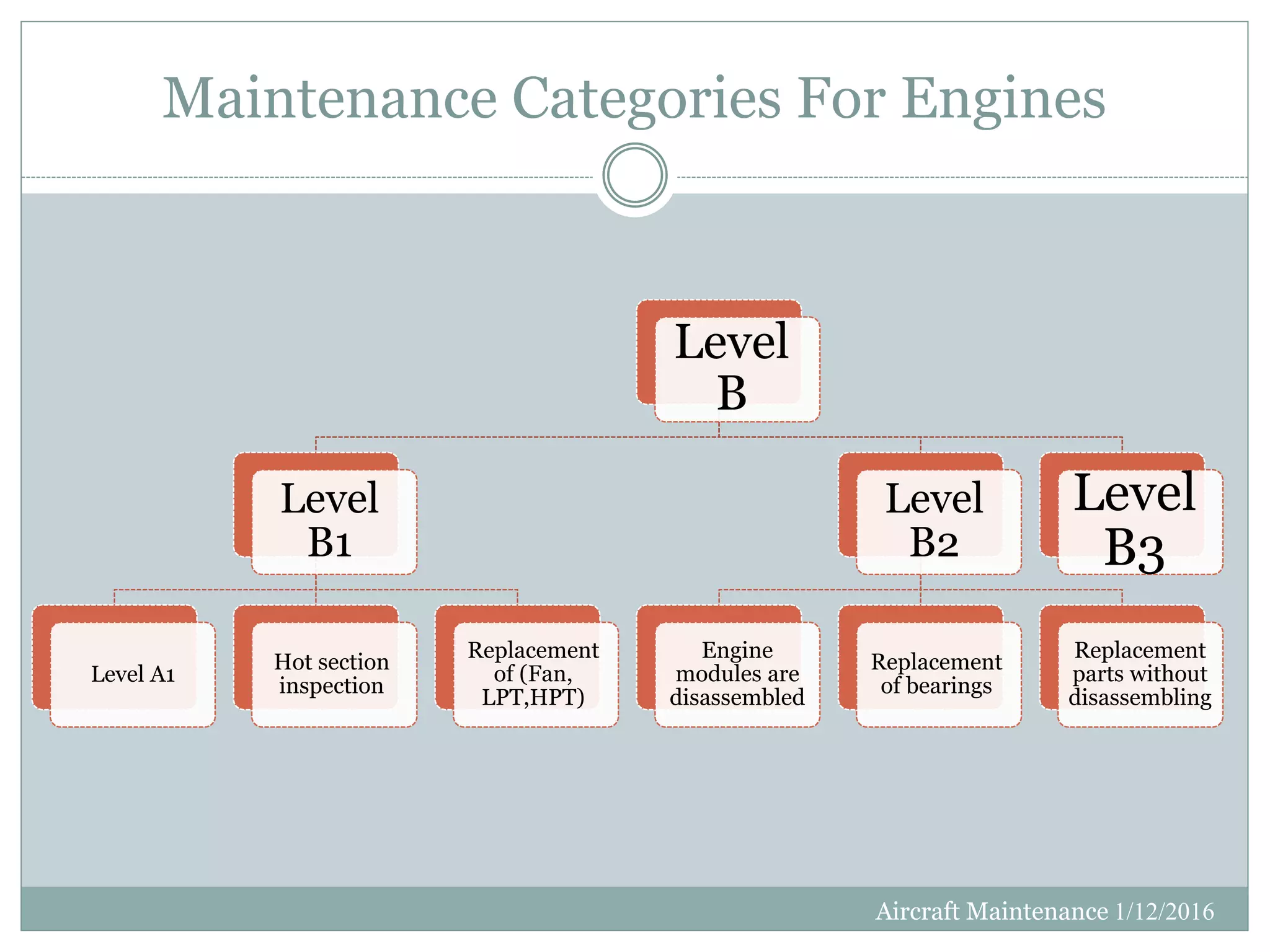
This document discusses aircraft maintenance practices. It covers maintenance classification including inspection, servicing, preservation, and different maintenance levels. It also addresses aircraft systems checks, engine lifetime determination based on hours and cycles, and engine condition monitoring. Maintenance categories for engines including on-wing, modular, and parts-level repair are defined. Finally, the document outlines engine cleaning, preservation routines for short and long-term storage, and depreservation routines when putting an aircraft back into service.