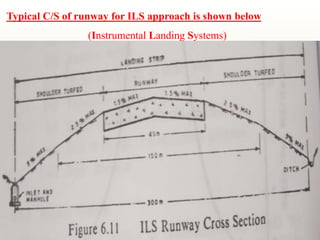
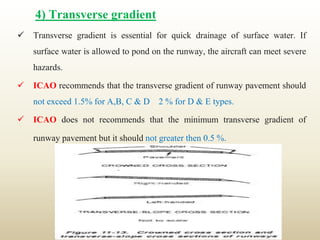
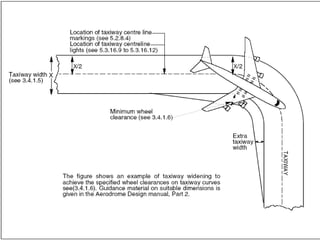
The document discusses runway and taxiway design standards. It covers topics like basic runway length determination, corrections for elevation, temperature, and gradients. It provides geometric design standards for runway length, width, safety areas, gradients, and sight distances. For taxiways, it discusses design considerations like length, width, safety areas, gradients, sight distances, and turning radii. It also covers visual aids like airport markings and lighting for runways, taxiways, and other areas to assist pilots.