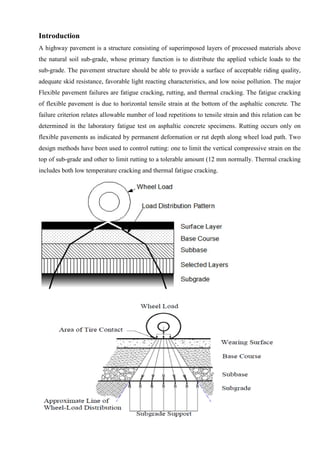
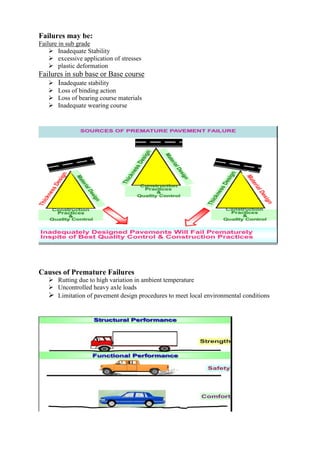
This document provides information about failures in flexible pavements. It discusses the major types of failures such as fatigue cracking, rutting, and thermal cracking. It then describes different types of failures that can occur in the subgrade, subbase, and base course layers. Finally, it defines and describes common flexible pavement distresses including various types of cracking, deformation, deterioration, and problems associated with seal coats. The distresses and failures are defined in detail.