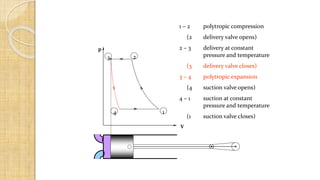
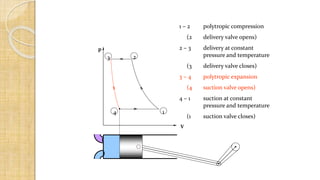
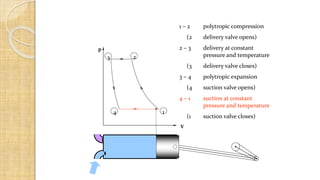
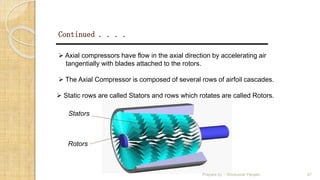
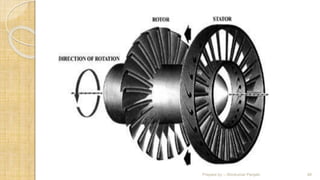
The document discusses different types of compressors and their applications. It begins by explaining that a compressor takes in atmospheric air, compresses it, and delivers high-pressure air to a storage vessel. It then describes two basic compressor types - positive displacement compressors that mechanically reduce air volume to increase pressure, and dynamic compressors that impart velocity energy to continuously flowing air. Specific compressor types are then outlined, including reciprocating compressors that use pistons, rotary vane compressors with rotating blades, and screw compressors that employ two rotating helical screws to compress air. Applications of compressed air in tools, spraying, mining, and pneumatic systems are also summarized.