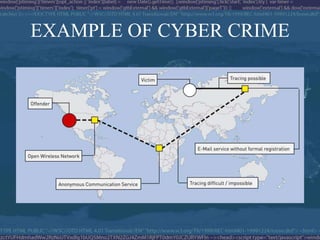
The document discusses the history and development of the Internet. It explains that the Internet originated from the ARPANET system developed by the U.S. Department of Defense in the 1960s to link computers. It grew significantly in the 1980s and beyond as more computers and networks were connected. The document also outlines some of the basic services of the Internet like email, file transfer, and the World Wide Web. It notes the rapid growth in the number of devices connected to the Internet over time. Finally, it briefly discusses cybercrime and the need for cyber laws to address illegal activities online.