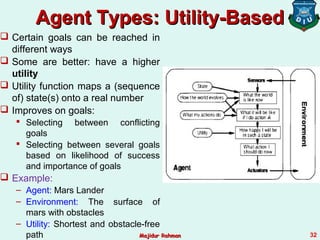
This document discusses intelligent agents and their environments. It covers:
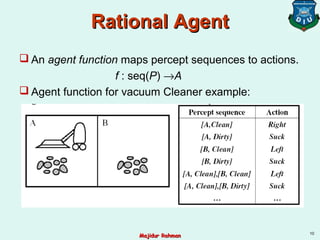
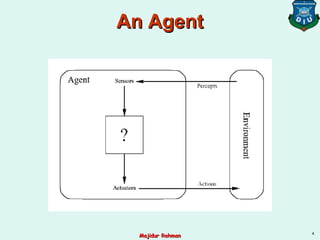
1) Intelligent agents are entities that perceive their environment through sensors and act upon the environment through actuators. They map percept sequences to actions.
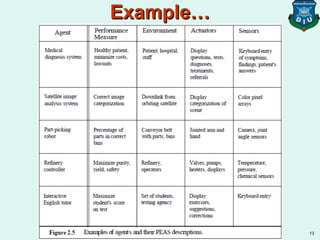
2) A rational agent should select actions that are expected to maximize its performance measure given the percept sequence and its prior knowledge. Performance measures evaluate how well the agent solves its task.
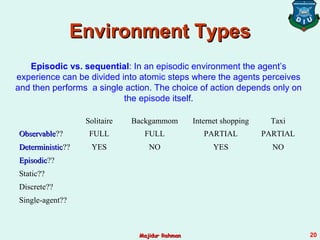
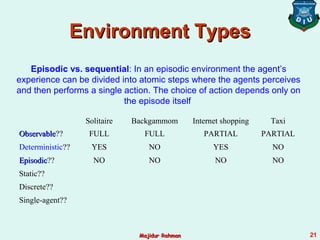
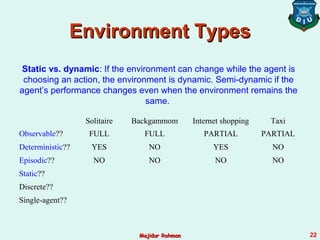
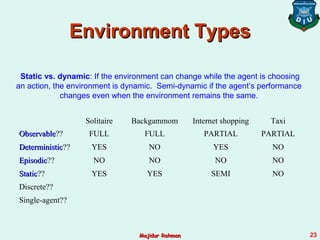
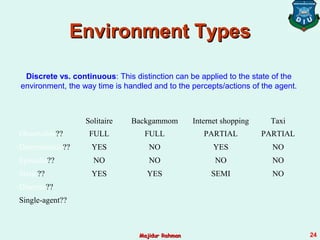
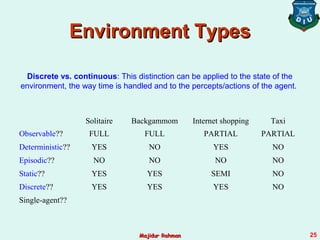
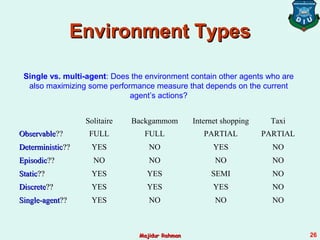
3) Agent environments can have different properties such as being fully or partially observable, deterministic or stochastic, episodic or sequential, static or dynamic, discrete or continuous, and single-agent or multi-agent. The simplest is fully observable, deterministic, etc. but most real environments are more complex.




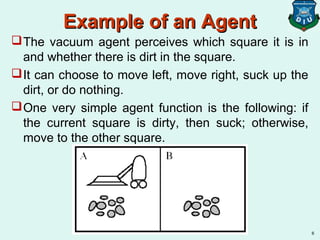
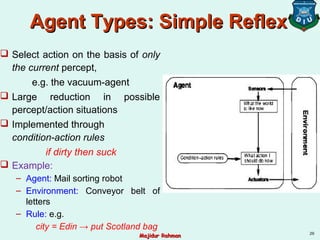
![Example of an AgentExample of an Agent
Environment: squares A and B
Percepts: [location, status], e.g. [A, Dirty]
Actions: left, right, suck, and no-op
7
Majidur RahmanMajidur Rahman](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic-2intelligentagents-190426041219/85/AI-Lecture-2-intelligent-agents-7-320.jpg)
![function REFLEX-VACUUM-AGENT ([location, status]) return an action
if status == Dirty then return Suck
else if location == A then return Right
else if location == B then return Left
Example of an AgentExample of an Agent
Majidur RahmanMajidur Rahman](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic-2intelligentagents-190426041219/85/AI-Lecture-2-intelligent-agents-8-320.jpg)