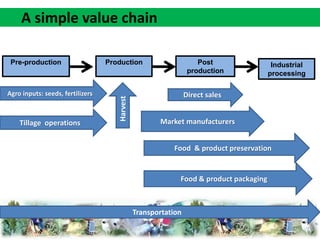
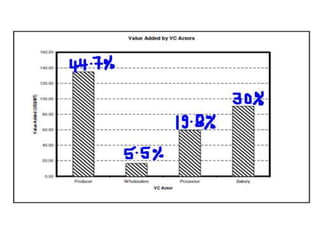
The document discusses agricultural value chains. A value chain describes the range of activities and actors involved in bringing an agricultural product from production to final consumption, with value added at each stage. It analyzes the factors that influence performance at each stage, from input suppliers to final buyers. Value chain analysis is a useful tool to understand trends, identify problems and opportunities for improvement, and inform policy interventions.