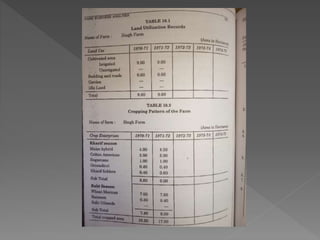
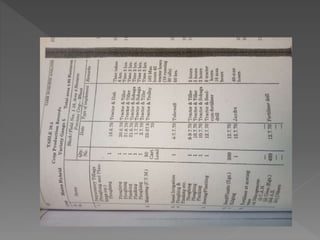
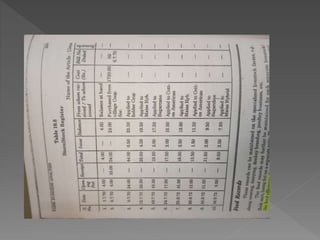
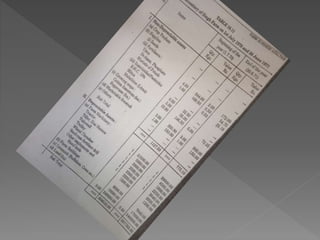
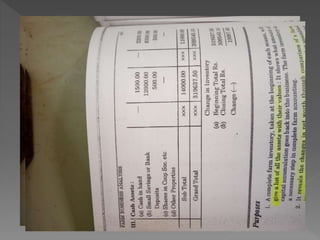
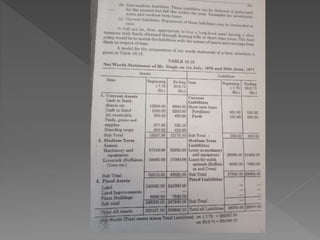
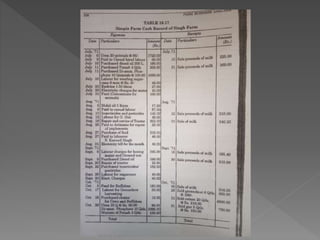
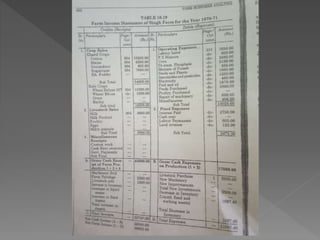
The document discusses farm accounting and record keeping. It explains that farm accounting involves systematically recording farm business transactions to analyze farm performance and identify areas for improvement. Effective record keeping involves maintaining physical records of production, financial records of income and expenses, and supplementary records. Physical records track production details, while financial records include inventories, cash accounts, and income statements. Keeping accurate and organized records allows farmers to evaluate their business and make informed management decisions.