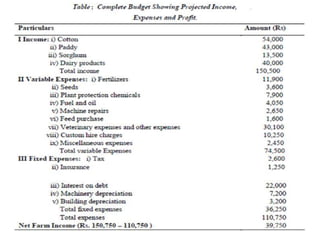
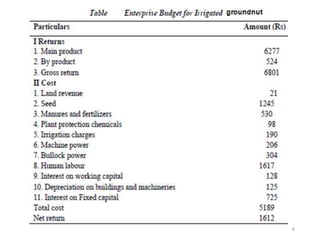
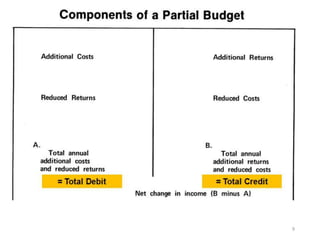
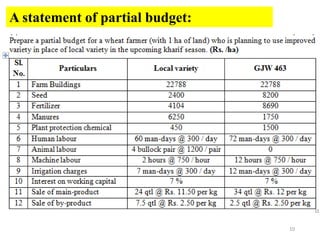
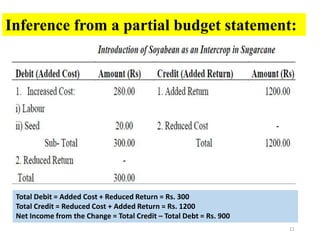
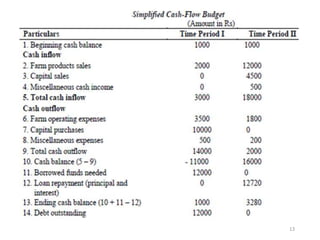
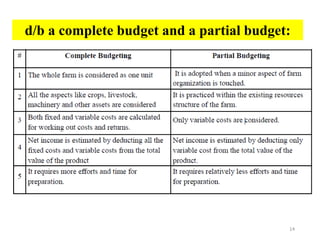
The document discusses farm budgeting as a method of analyzing agricultural resources in monetary terms. It explains various budgeting types, including enterprise budgeting, which estimates income, costs, and profitability for specific crops or livestock, and partial budgeting, which evaluates anticipated changes in costs and returns from minor modifications. Additionally, it covers cash flow budgeting, focusing on estimating future borrowing needs and loan repayment capacity.