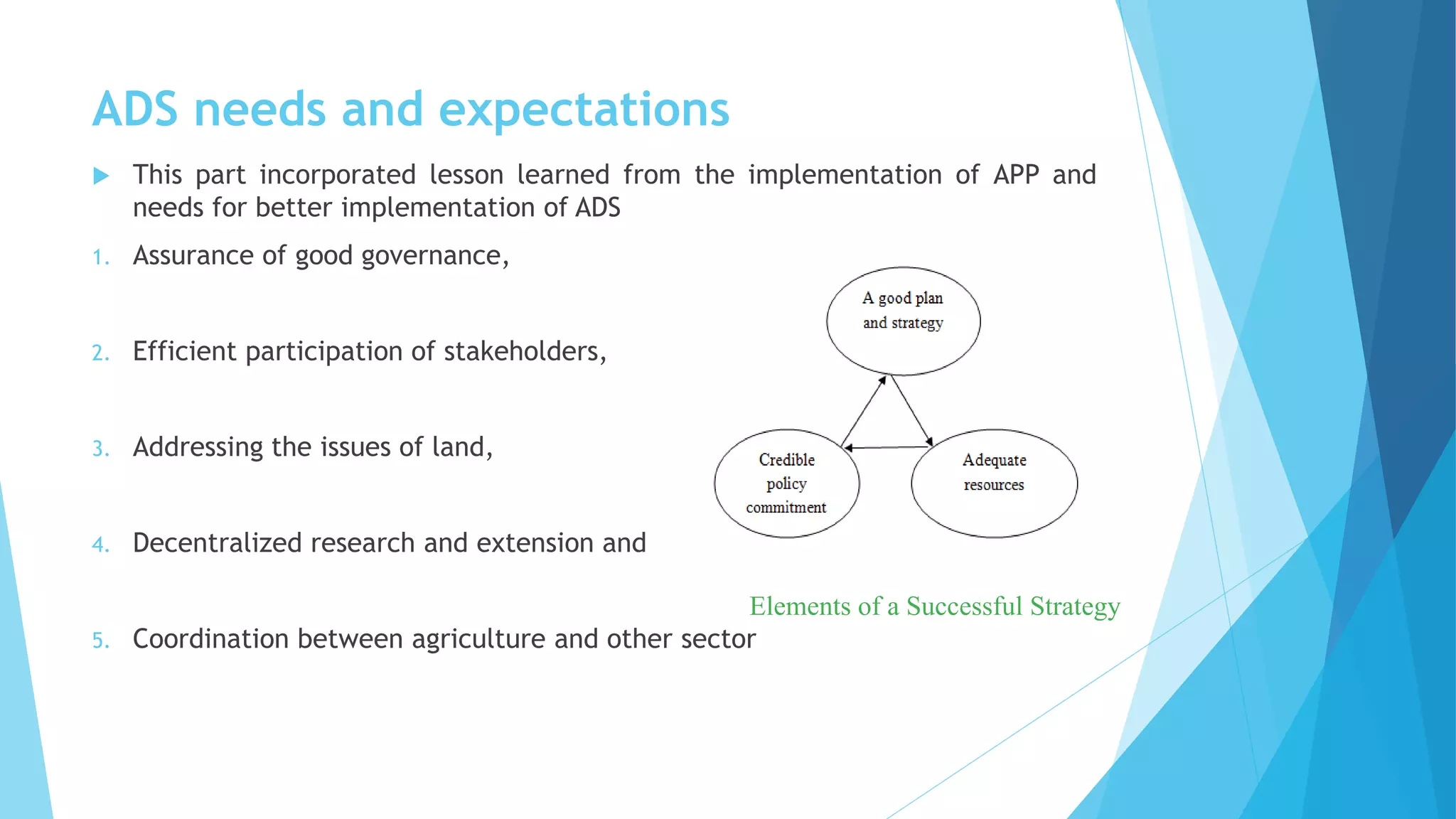
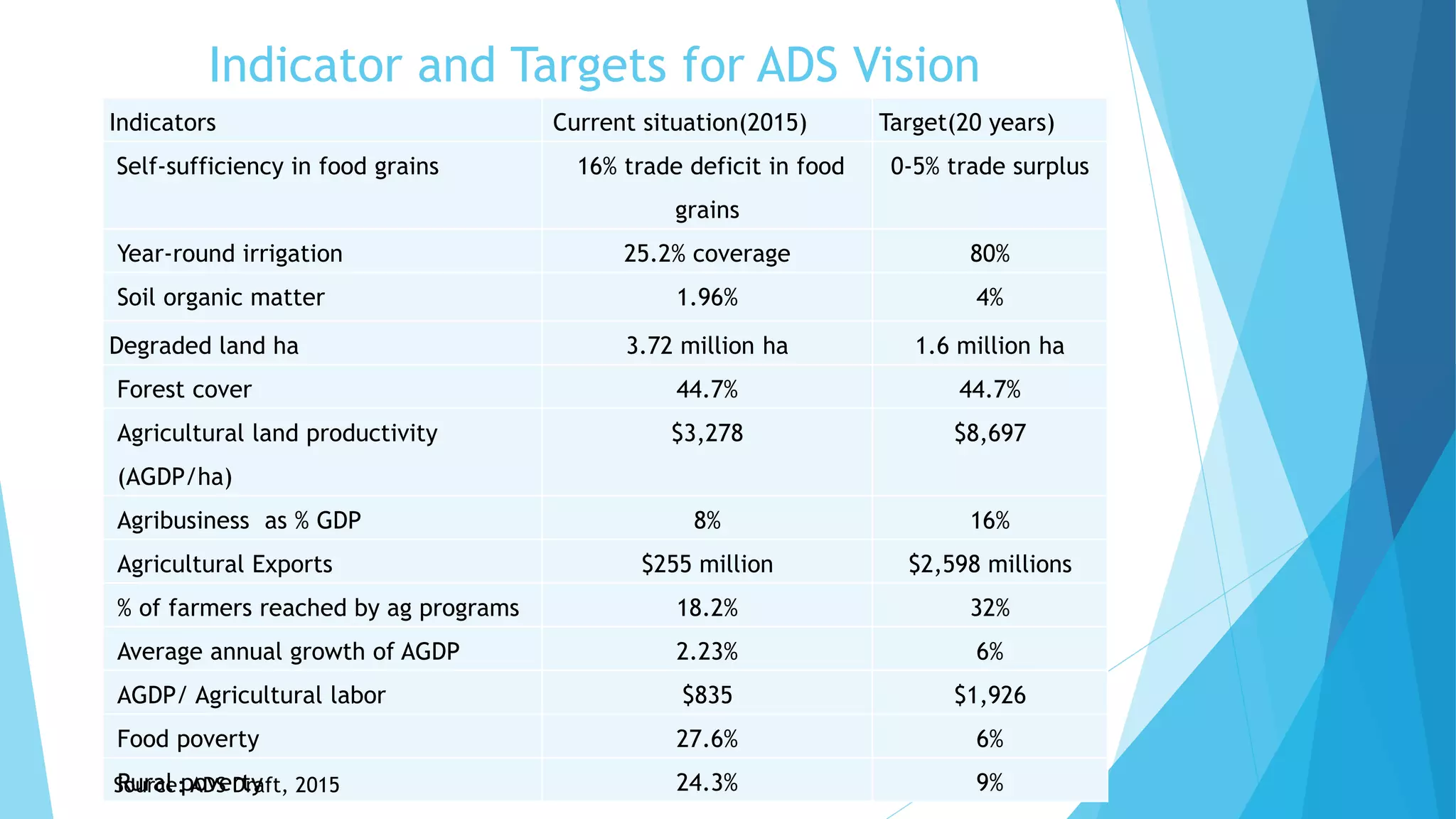
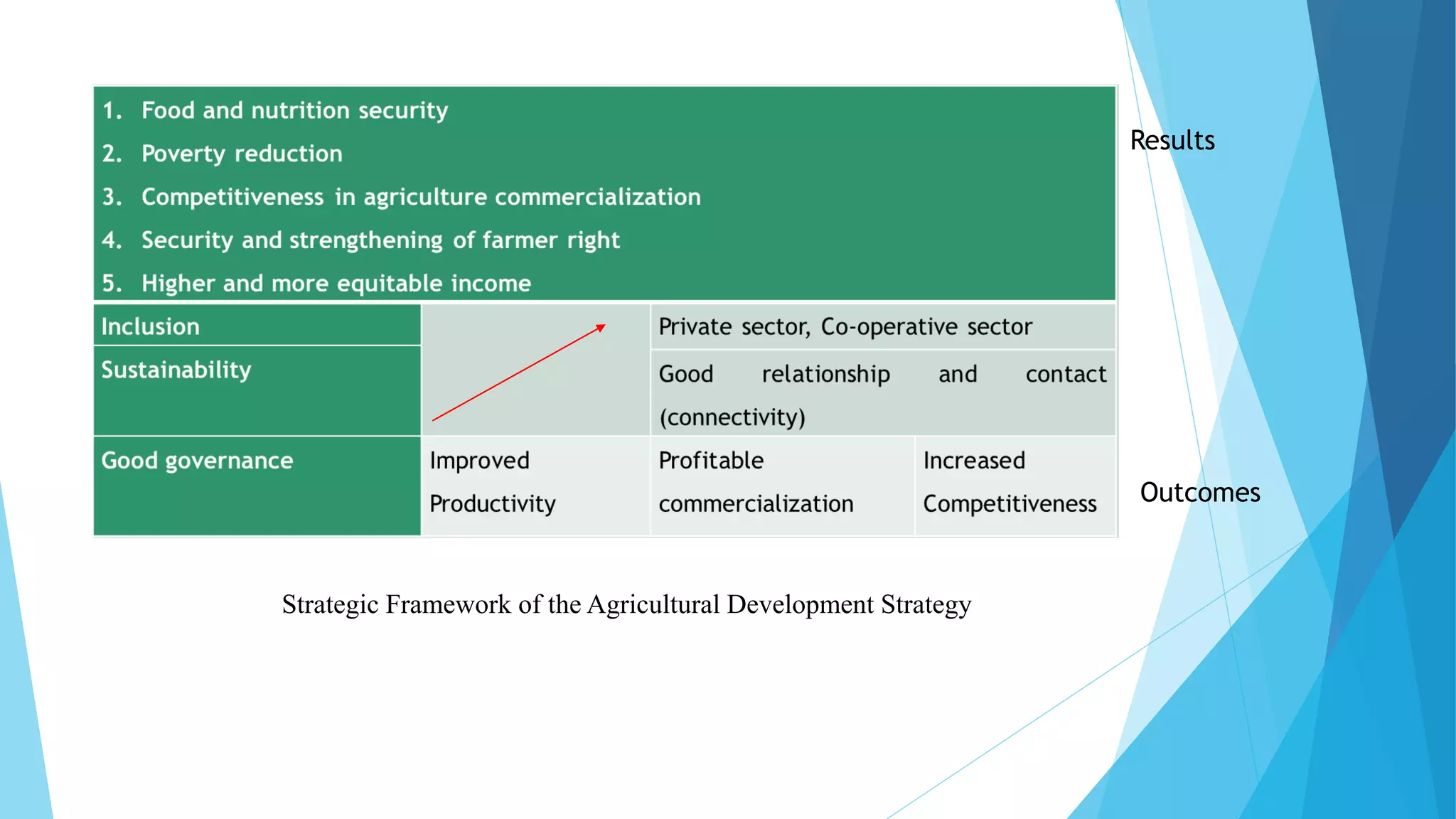
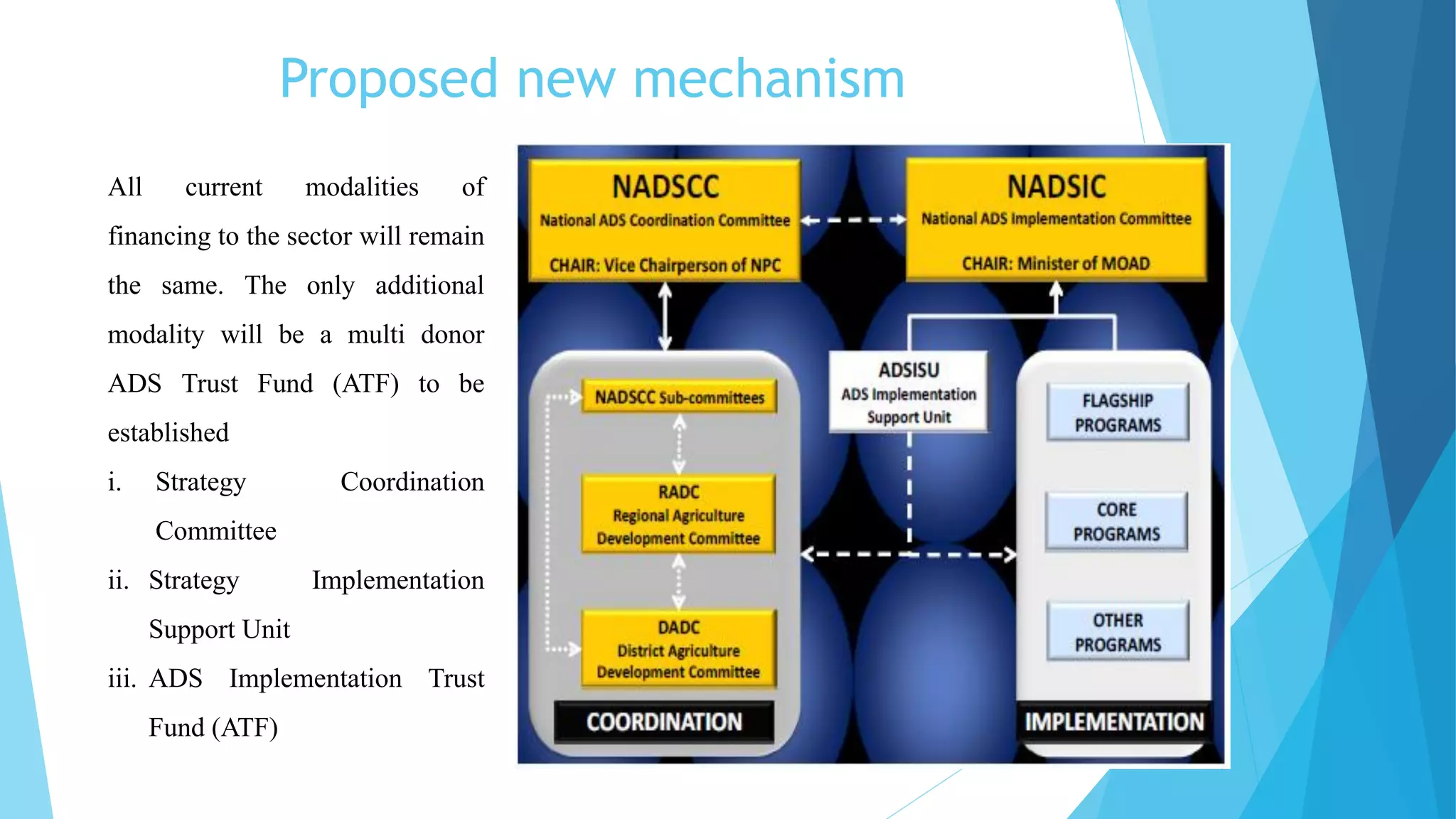
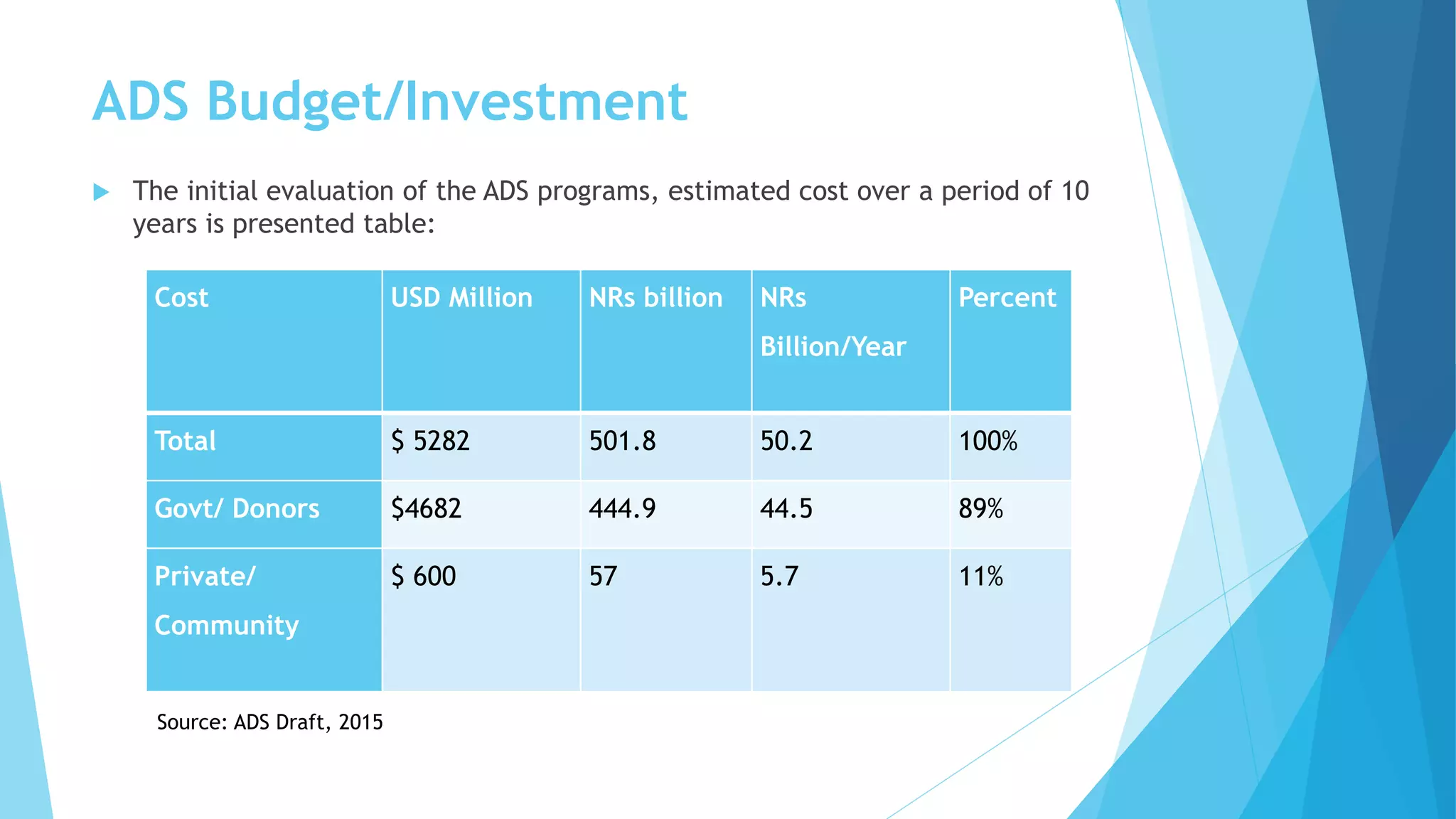
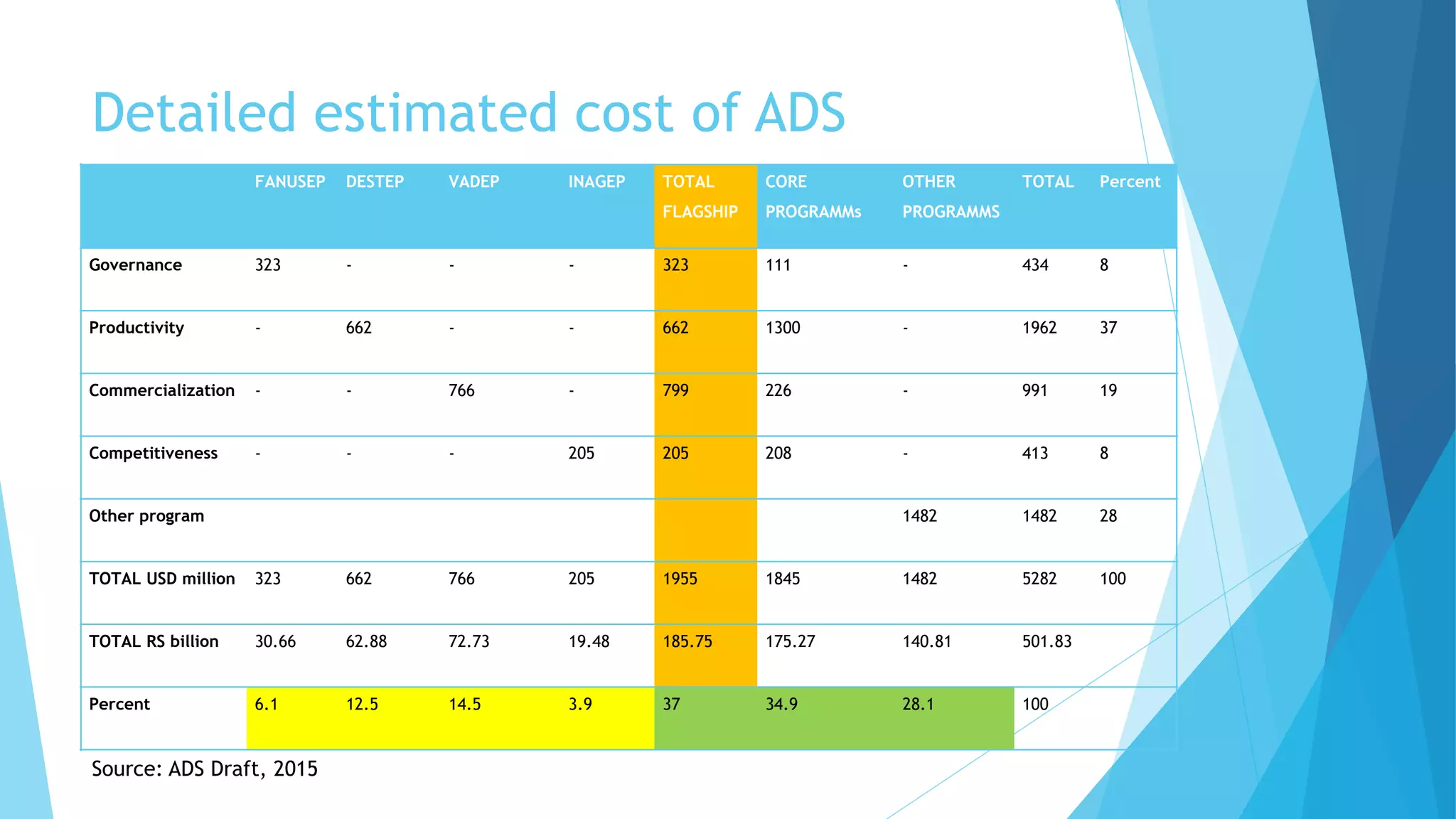
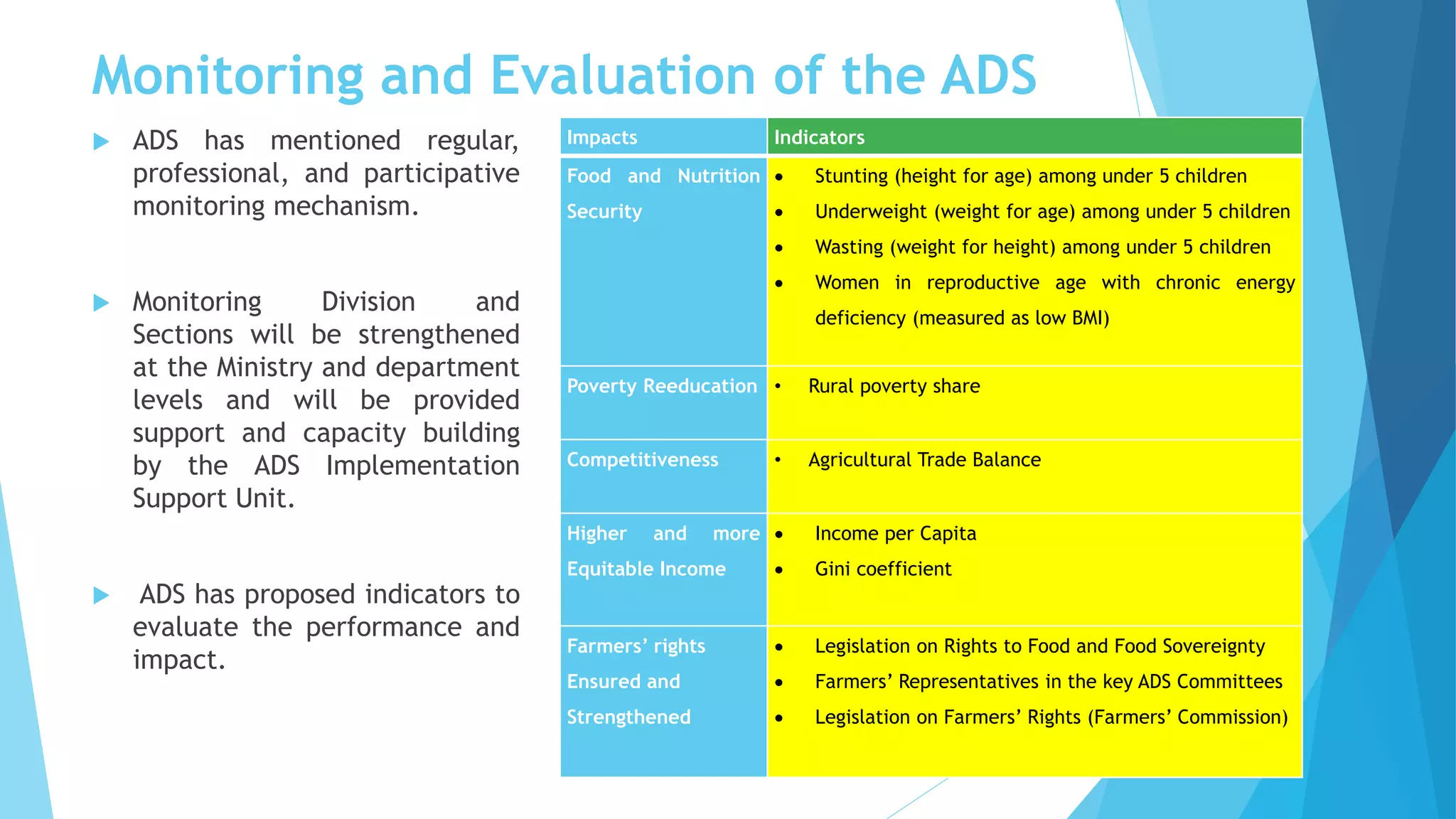
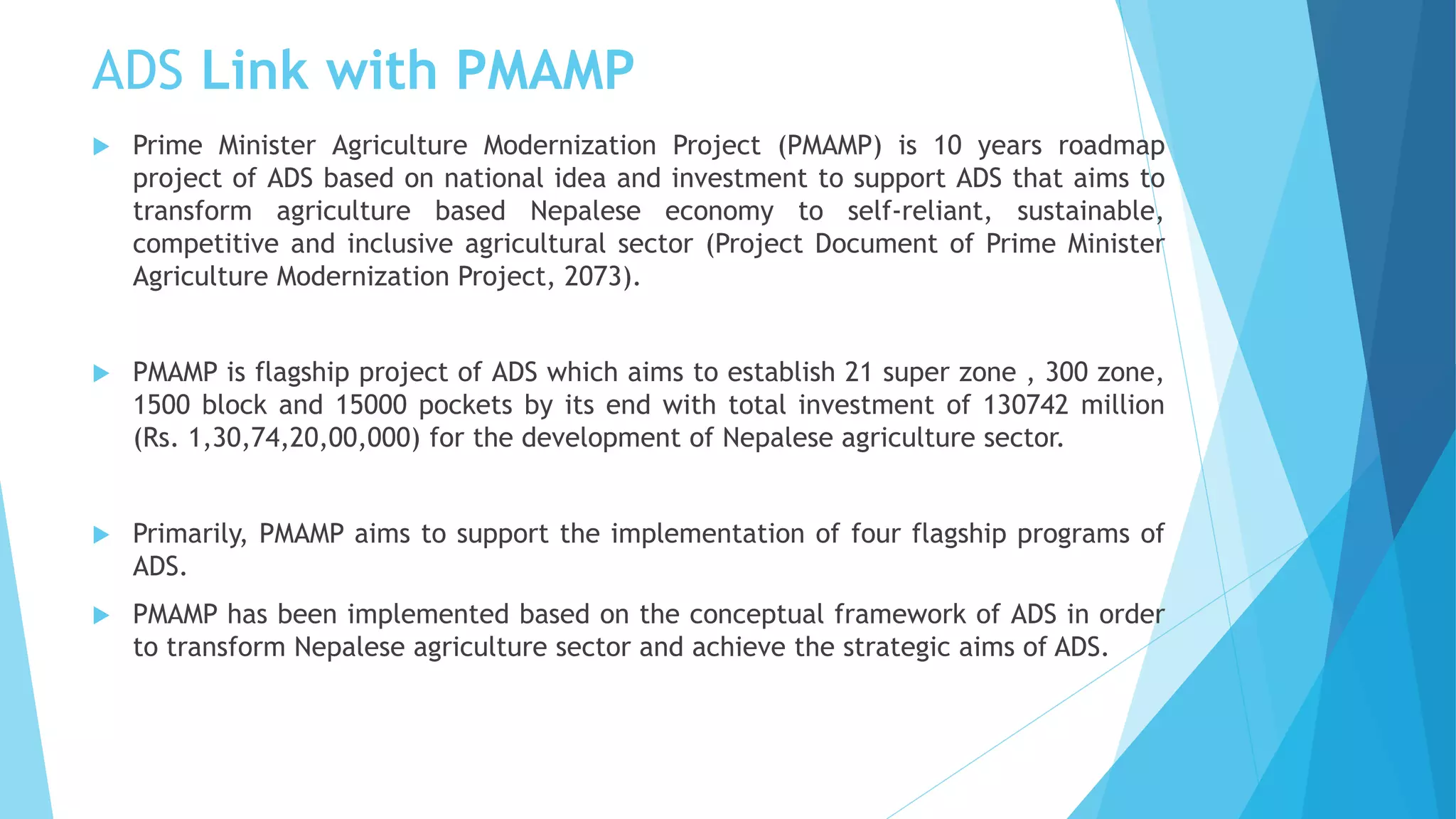
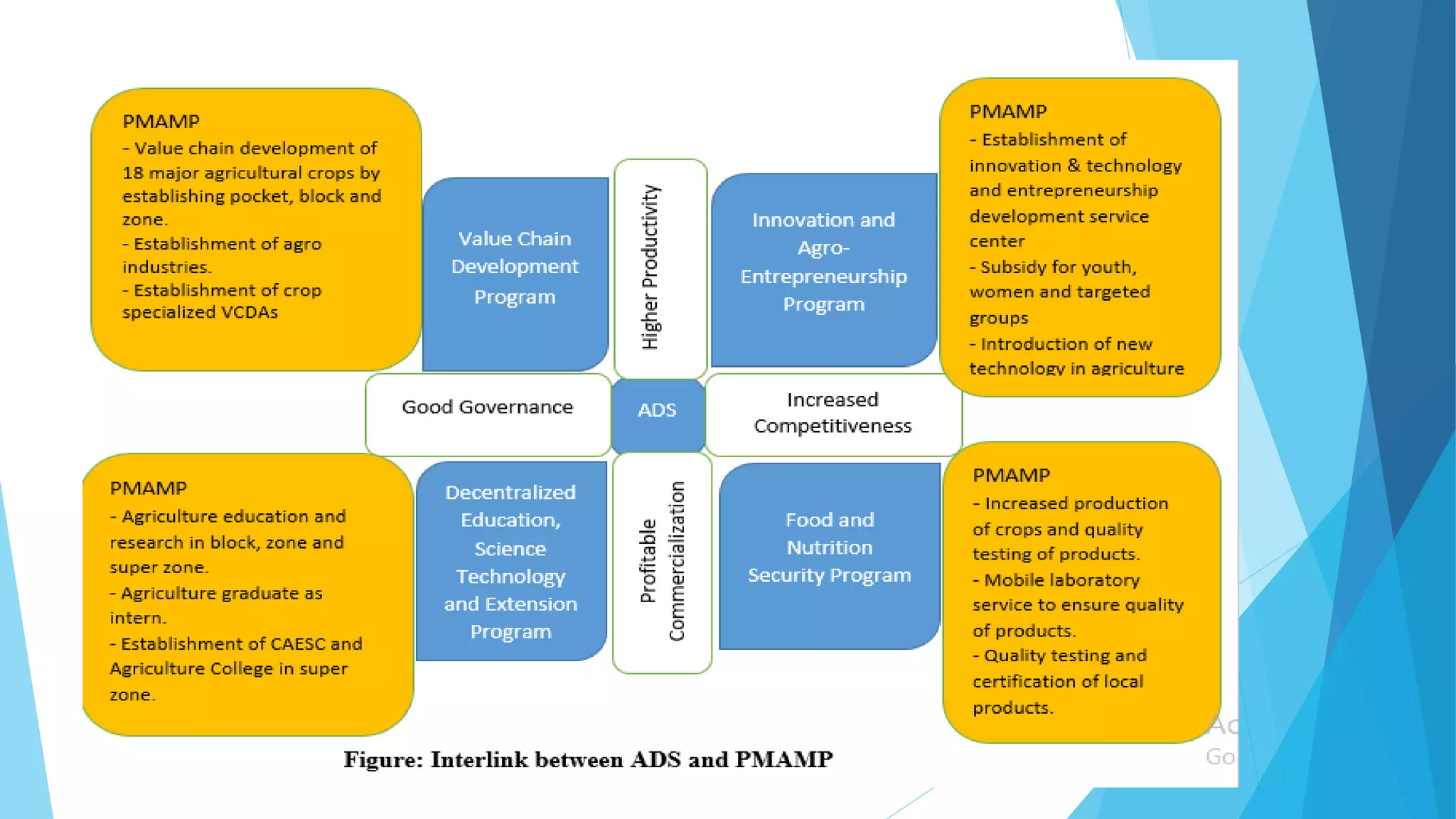
The document summarizes an agricultural development strategy (ADS) for Nepal. It outlines the ADS's objectives to transform Nepal's agriculture sector and reduce poverty through four strategic programs. It also discusses the Prime Minister Agriculture Modernization Project (PMAMP) and how it is linked to and builds upon the ADS. The total estimated cost of implementing the ADS over 10 years is 501.8 billion Nepali rupees (approximately $5.28 billion). Monitoring and evaluation of progress will be done using defined indicators.