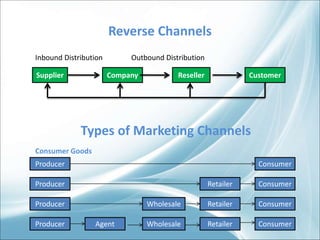
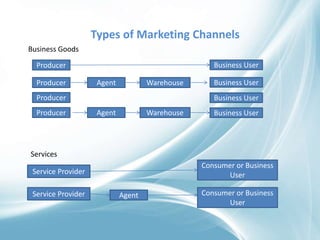
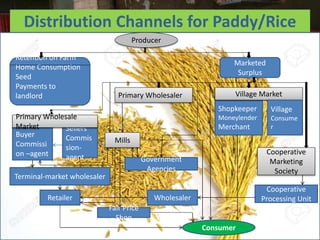
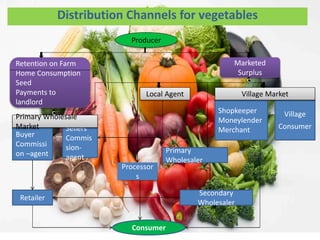
The document discusses the complex distribution channels involved in the marketing of agricultural commodities in India, highlighting their variability based on product type and seasonality. It underscores the unique challenges faced by agricultural products, such as perishability, transportation difficulties, and varying quality, alongside the role of middlemen in the supply chain. In conclusion, it points out that the distribution system in India is multilayered with various intermediaries facilitating the movement of goods from producers to consumers.