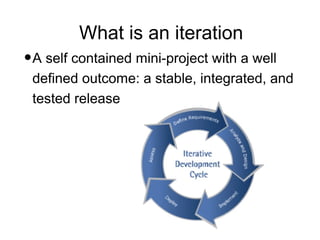
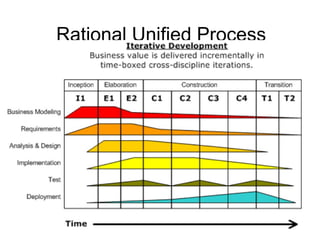
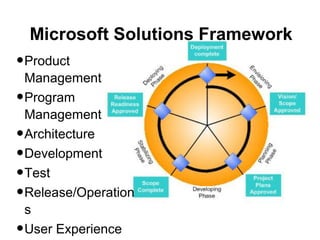
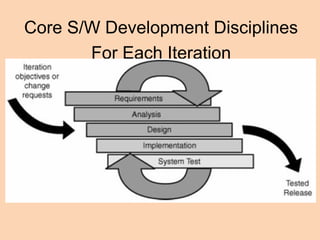
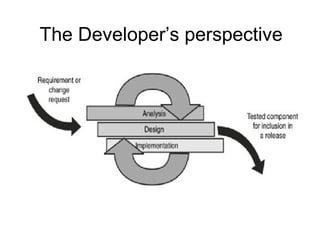
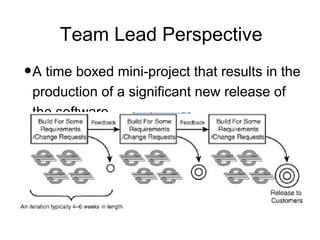
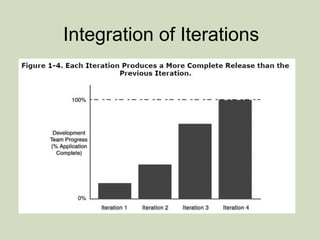
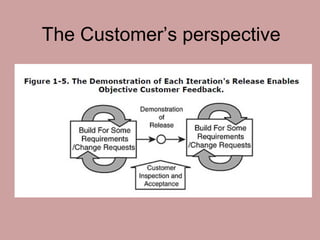
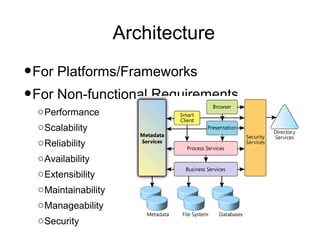
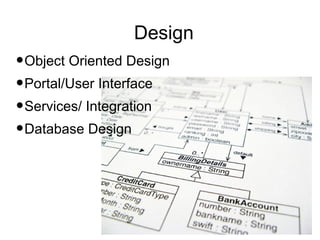
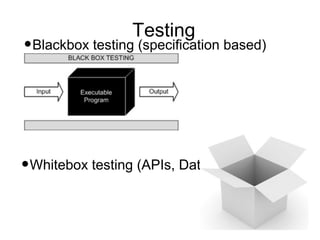
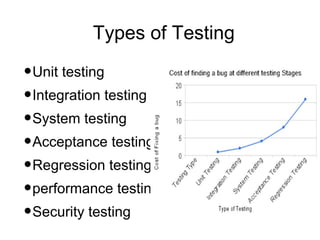
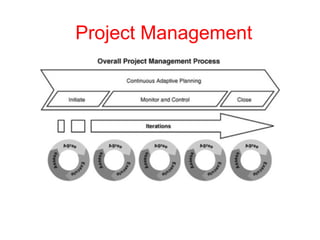
Iterative software development involves breaking projects into short iterations where cross-functional teams work to develop and test incremental releases. Each iteration results in a stable, integrated release. Core activities within each iteration include requirements gathering, analysis, design, development, testing, and deployment. This allows continuous integration and feedback between developers, customers, and management.