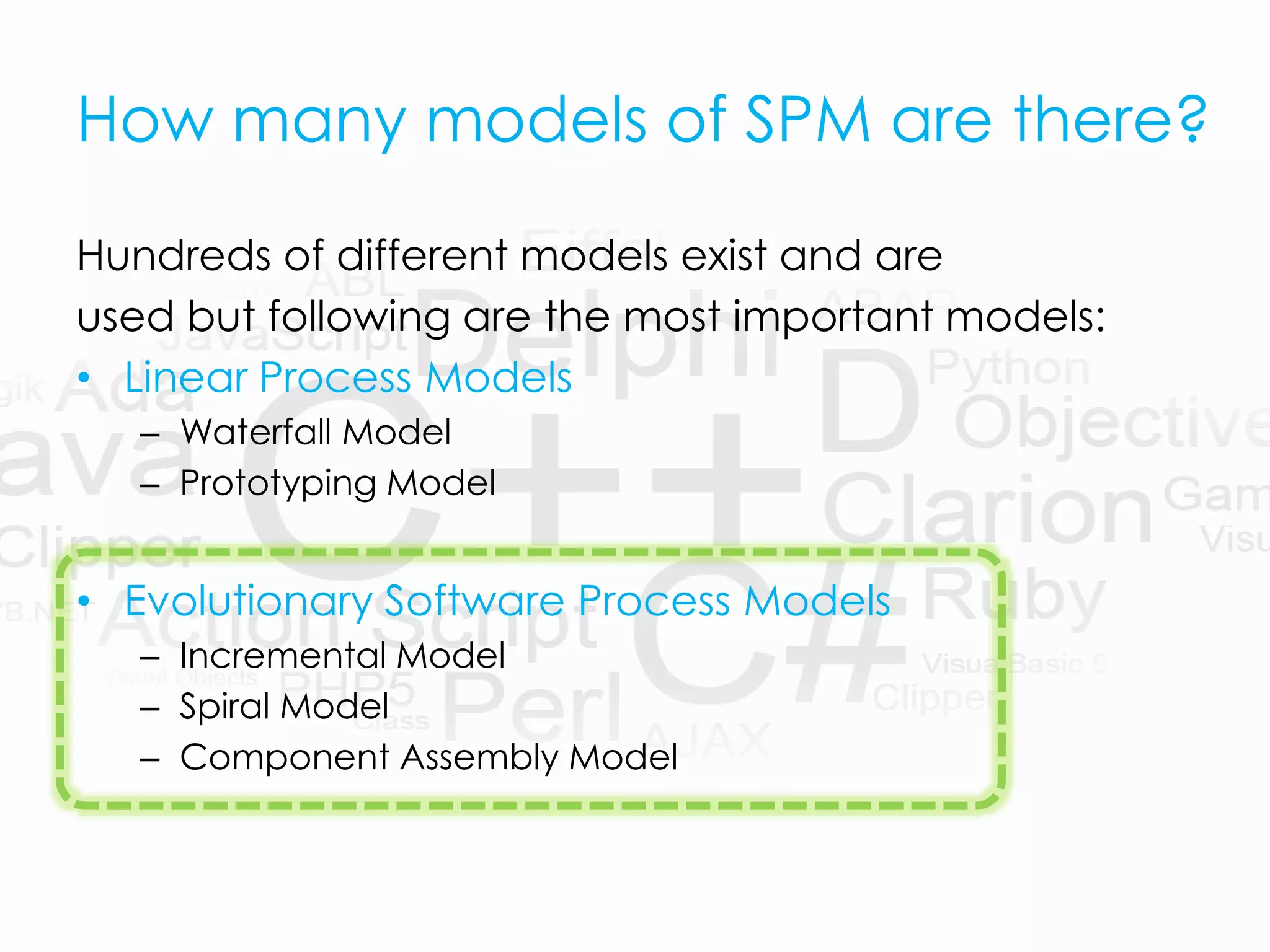
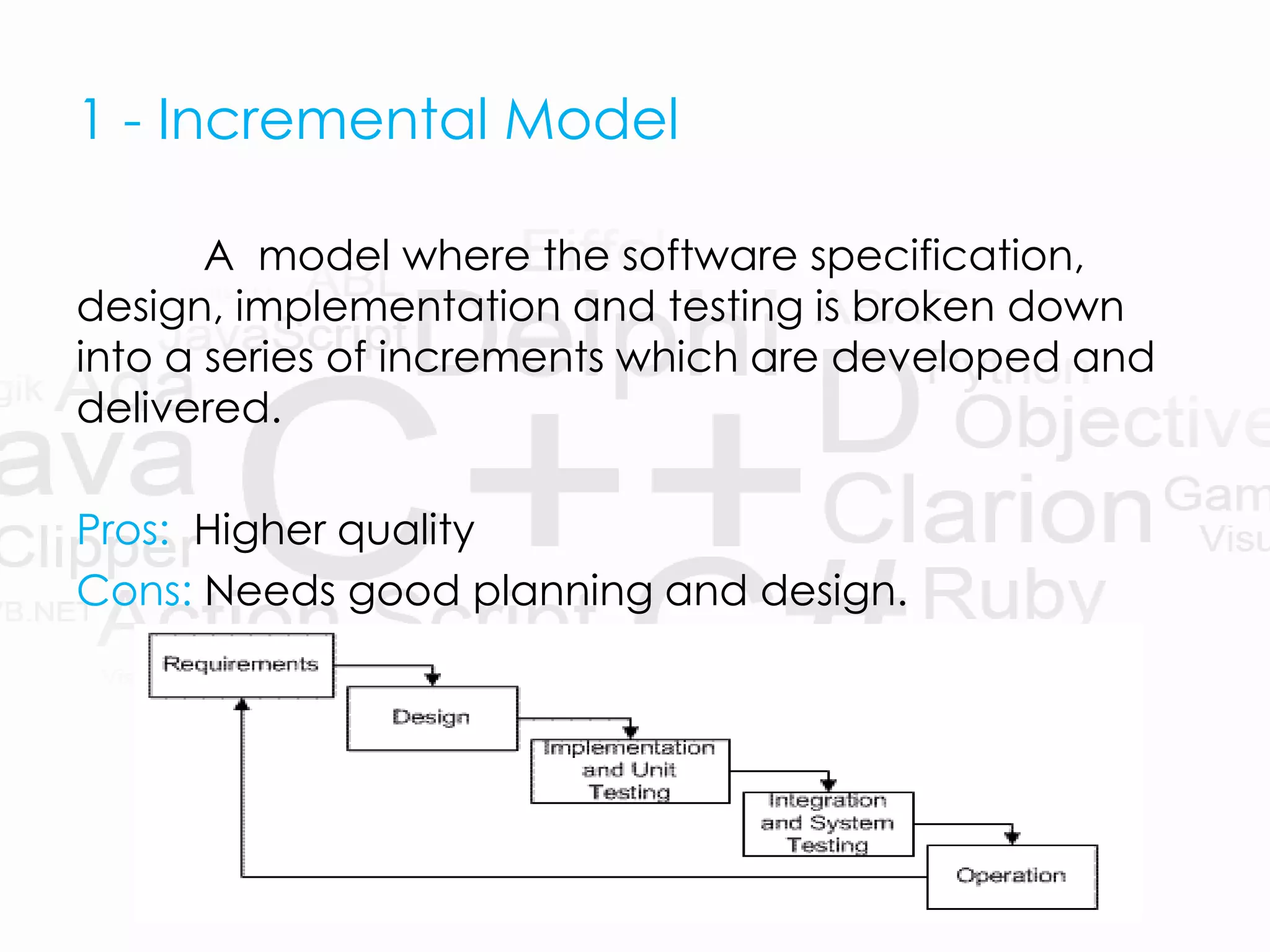
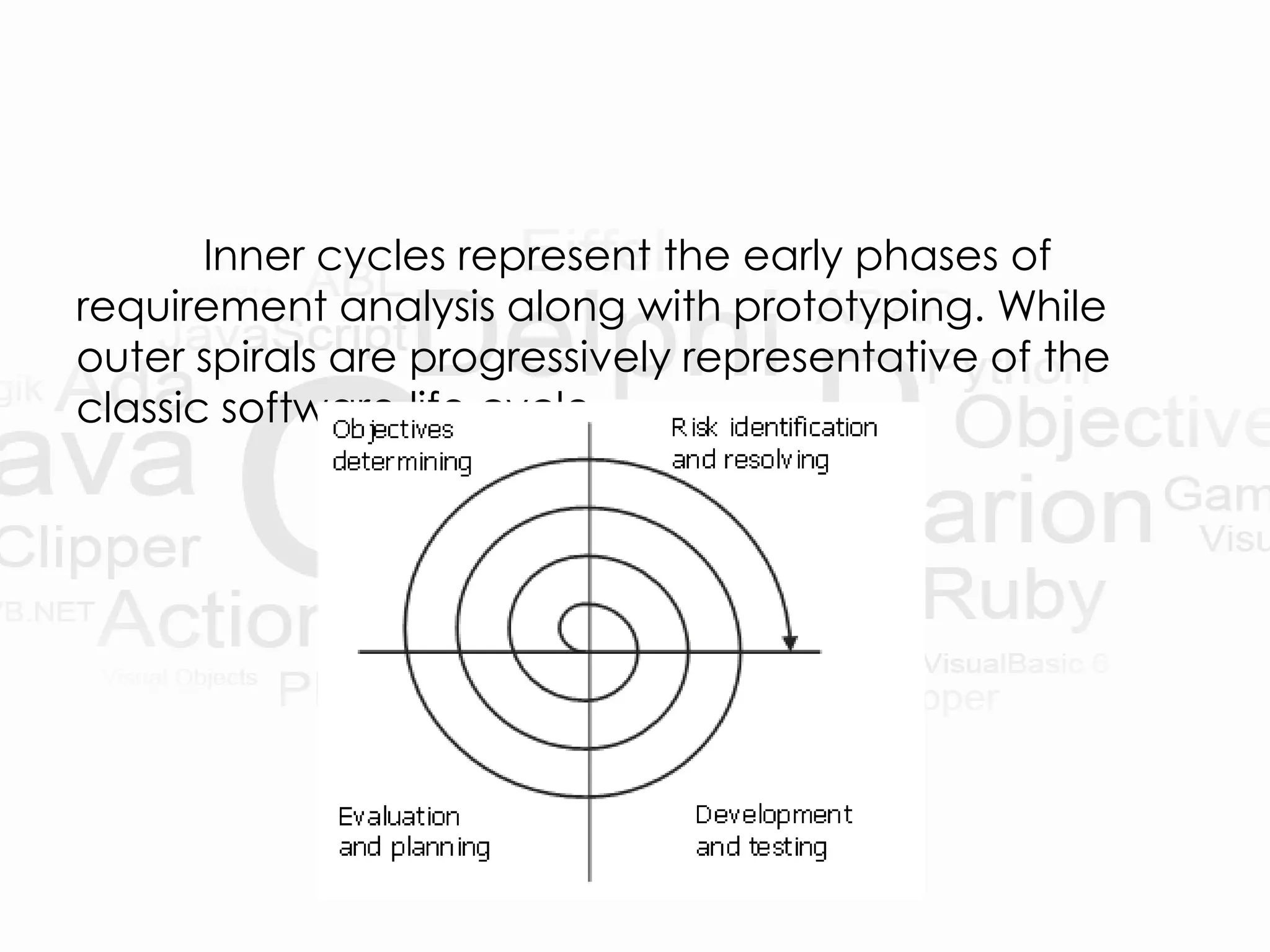
The presentation introduces software process models and specifically focuses on evolutionary software process models (ESPM), which are defined as iterative models that allow software engineers to develop increasingly complete versions of software. It highlights three main types of ESPM: incremental model, spiral model, and component assembly model, each with its own pros and cons. Additionally, the document compares these models with traditional linear process models like the waterfall and prototyping models.