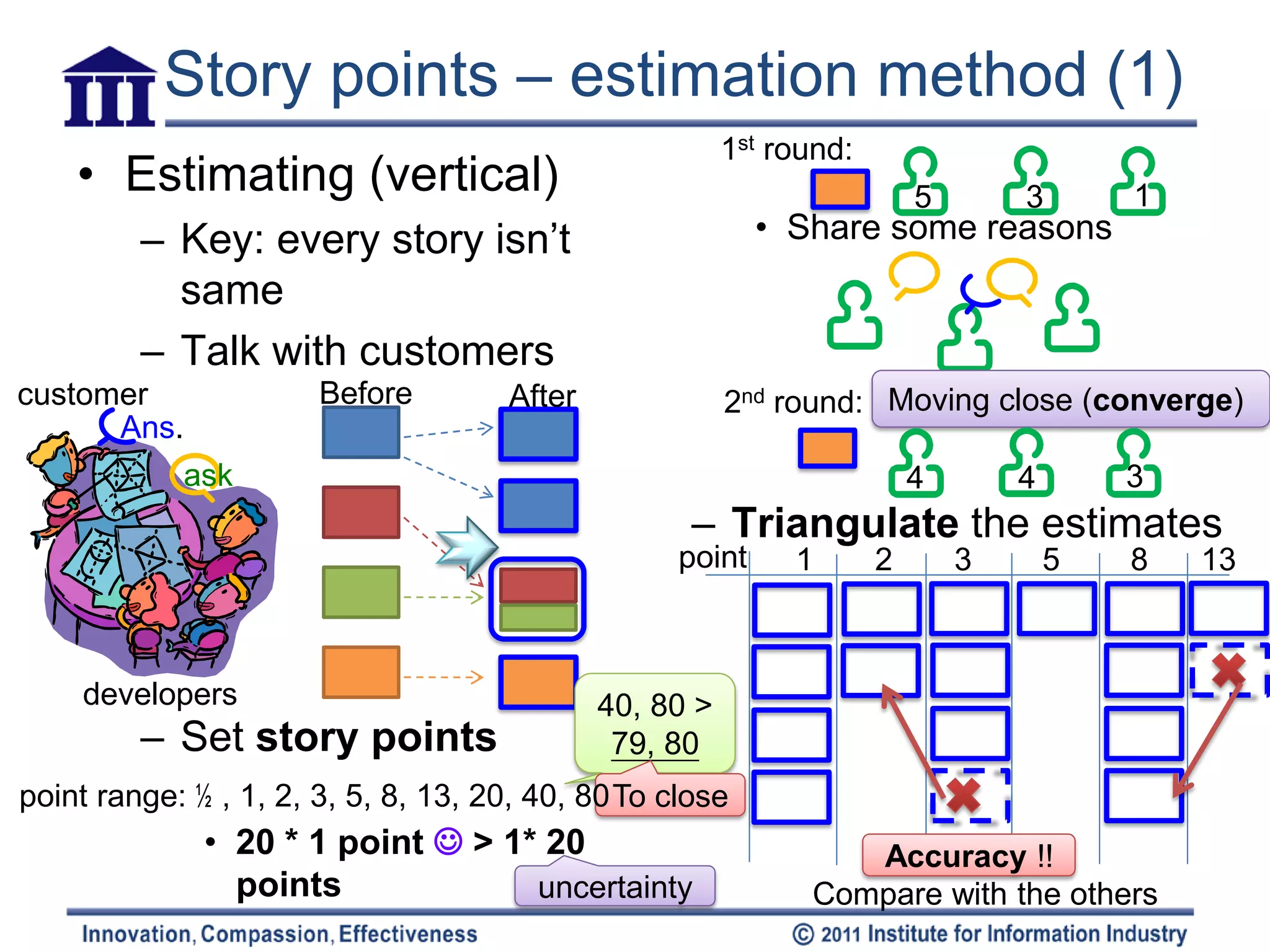
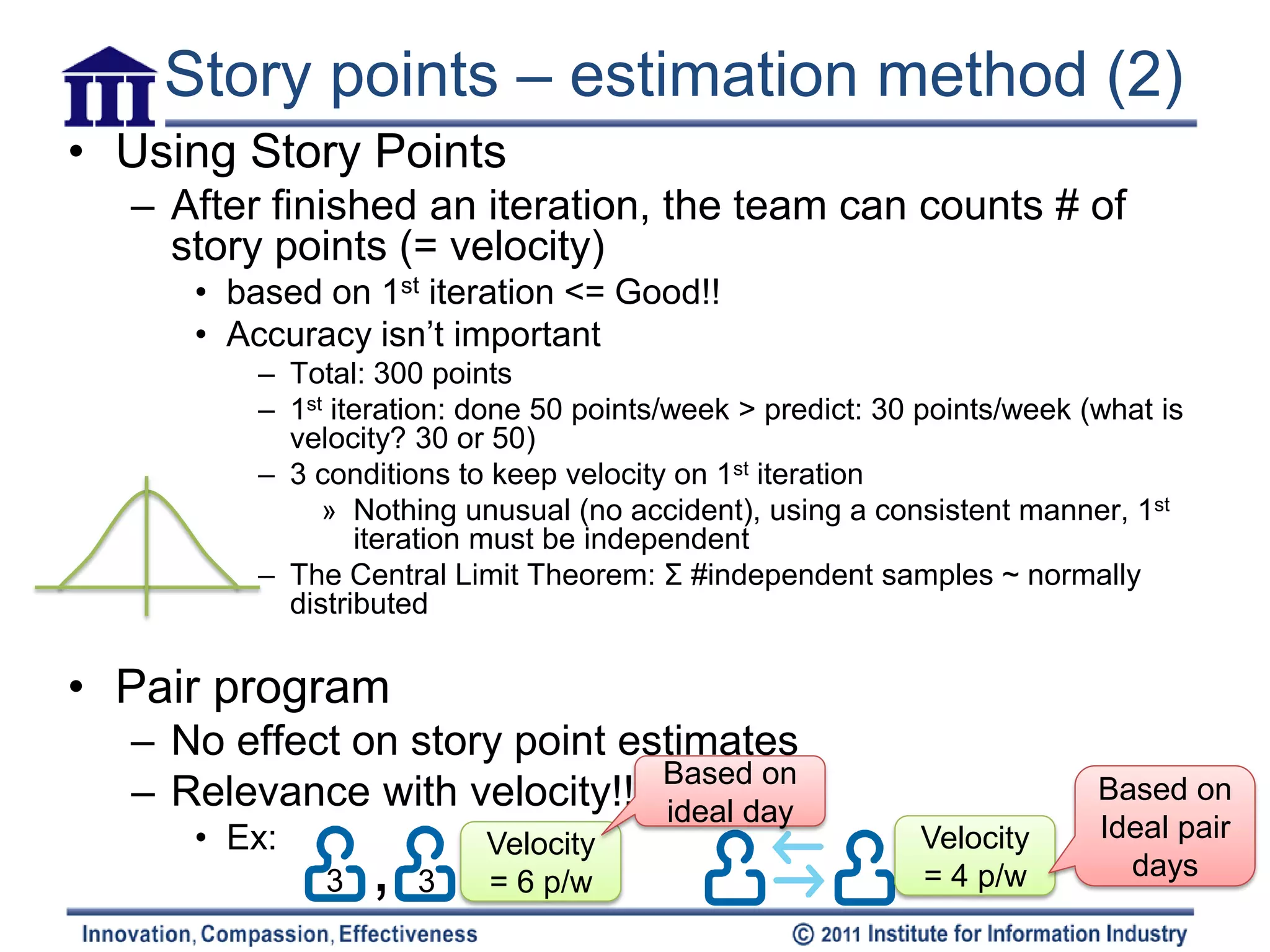
User stories are estimated in story points to plan project timelines. Story points are a relative unit used to estimate complexity rather than time. The team estimates stories together by first independently assigning points, then discussing to converge on a shared estimate. Velocity is calculated based on the number of points completed in an iteration to predict future capacity. Pair programming may impact velocity but not the story point estimates themselves. Estimates should consider the story complexity and effort from the team perspective rather than individuals.