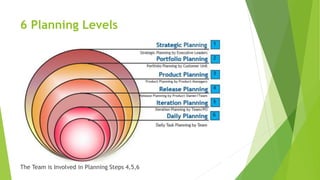
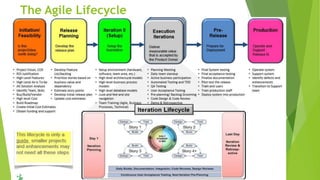
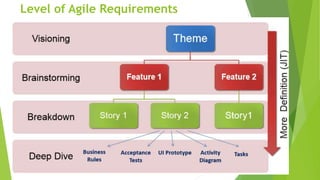
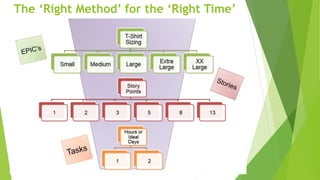
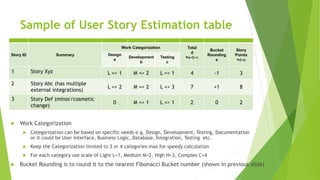
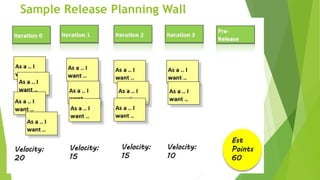
The document outlines the principles and methods of agile planning and estimation, emphasizing the importance of planning levels and the agile lifecycle. It discusses various estimating techniques, including relative and absolute estimating, and introduces the concept of story points to assess size and complexity. Additionally, it provides practical examples of user story estimation and the use of complexity buckets for categorizing work.