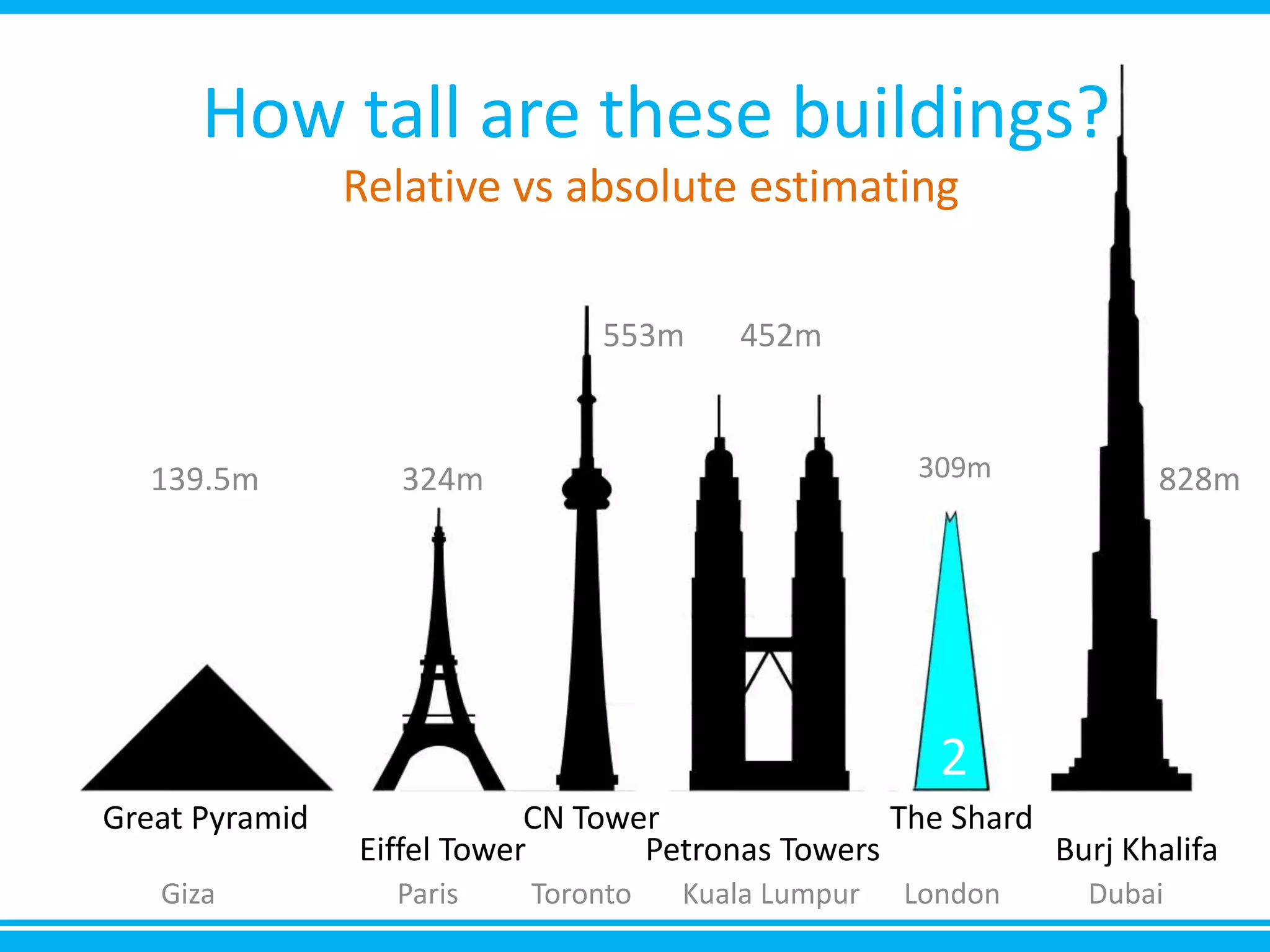
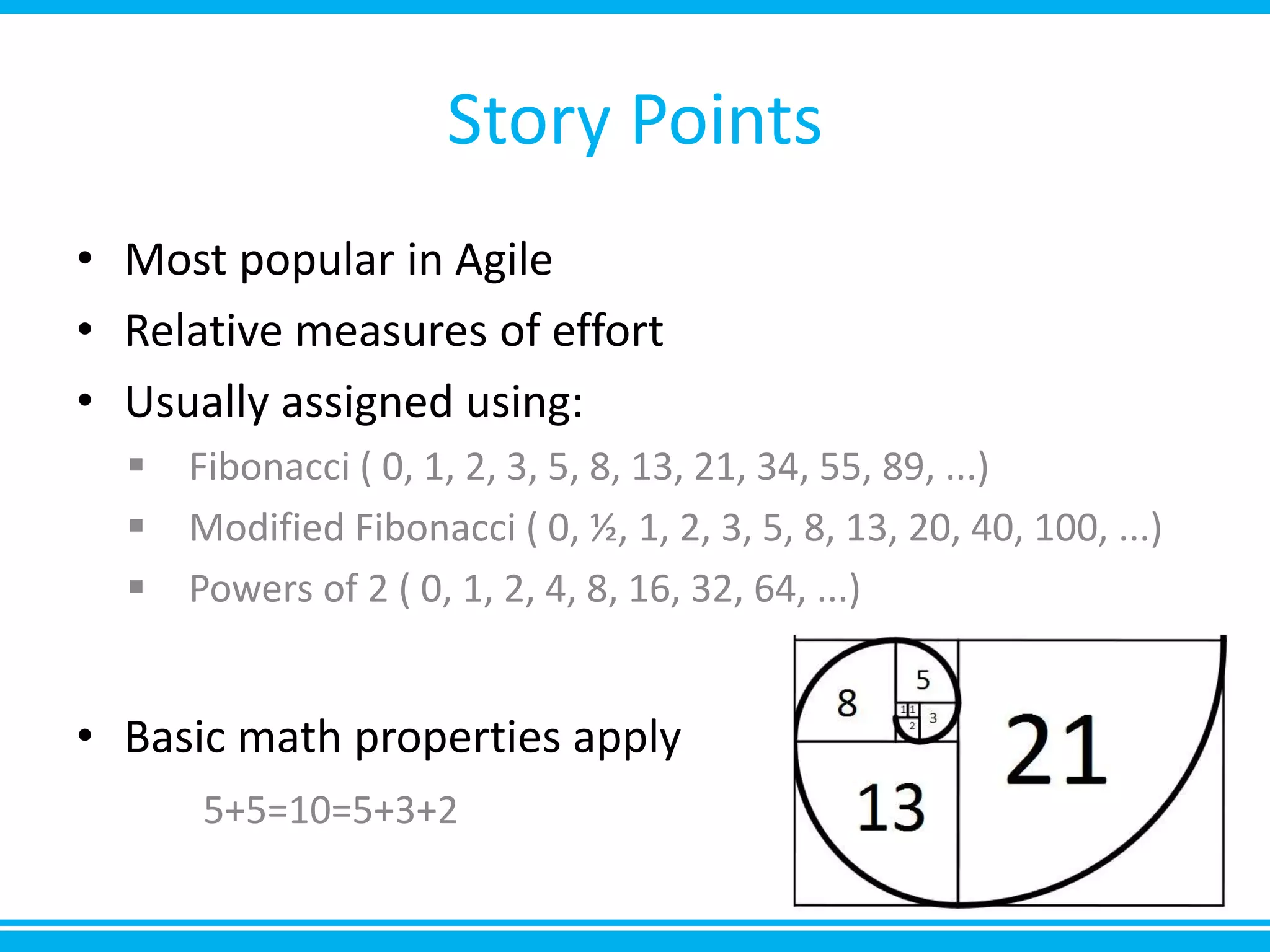
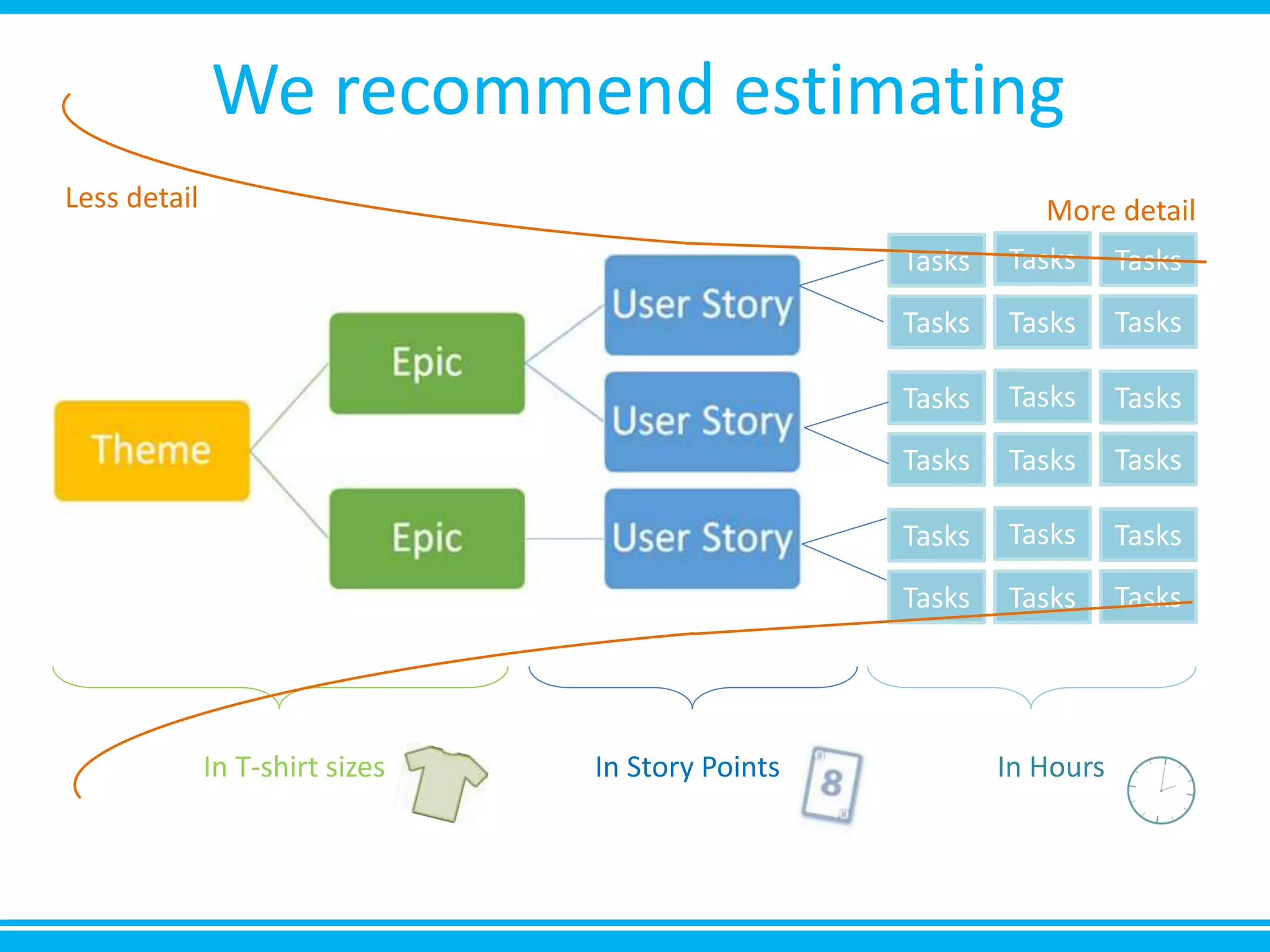
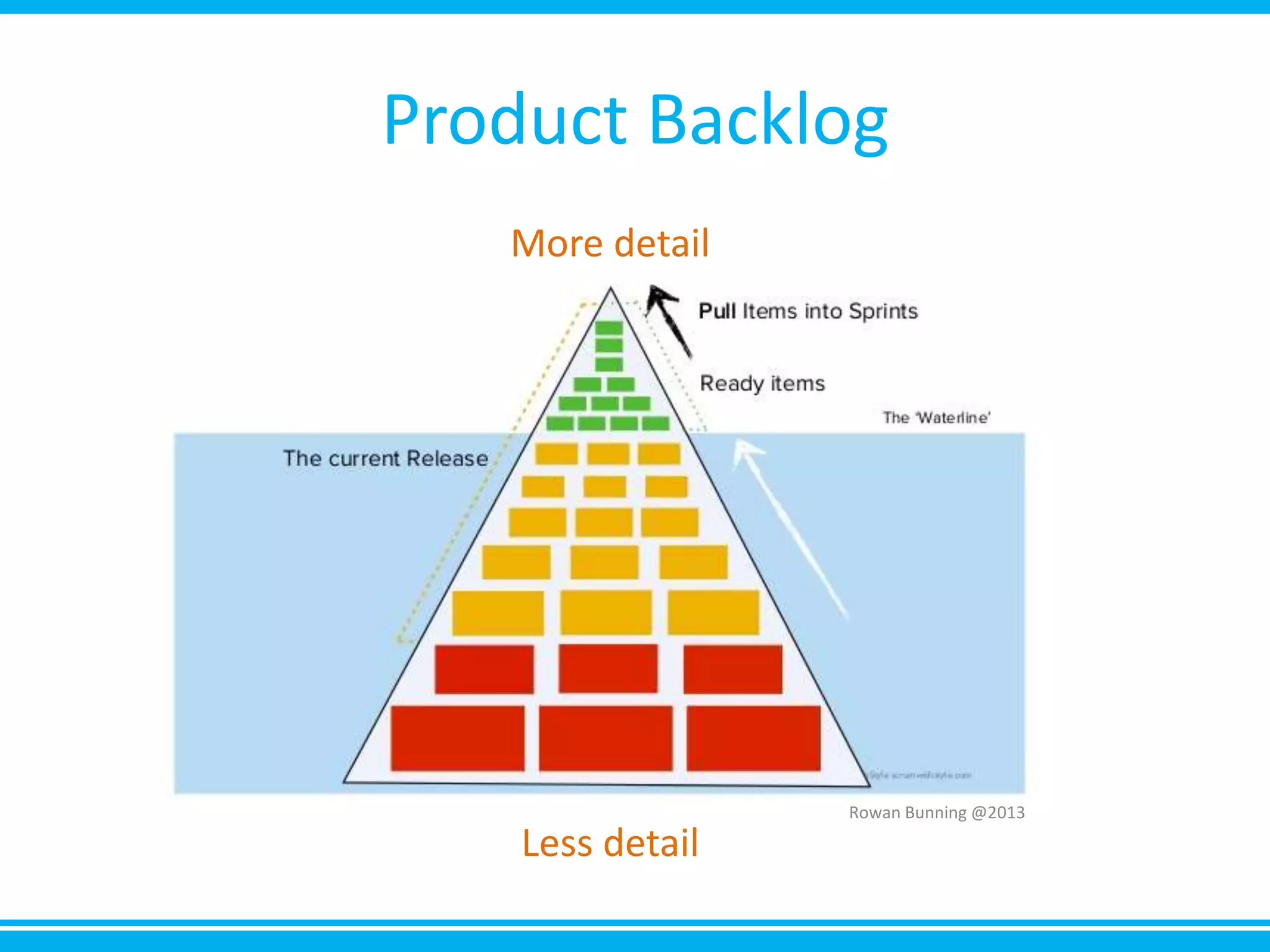
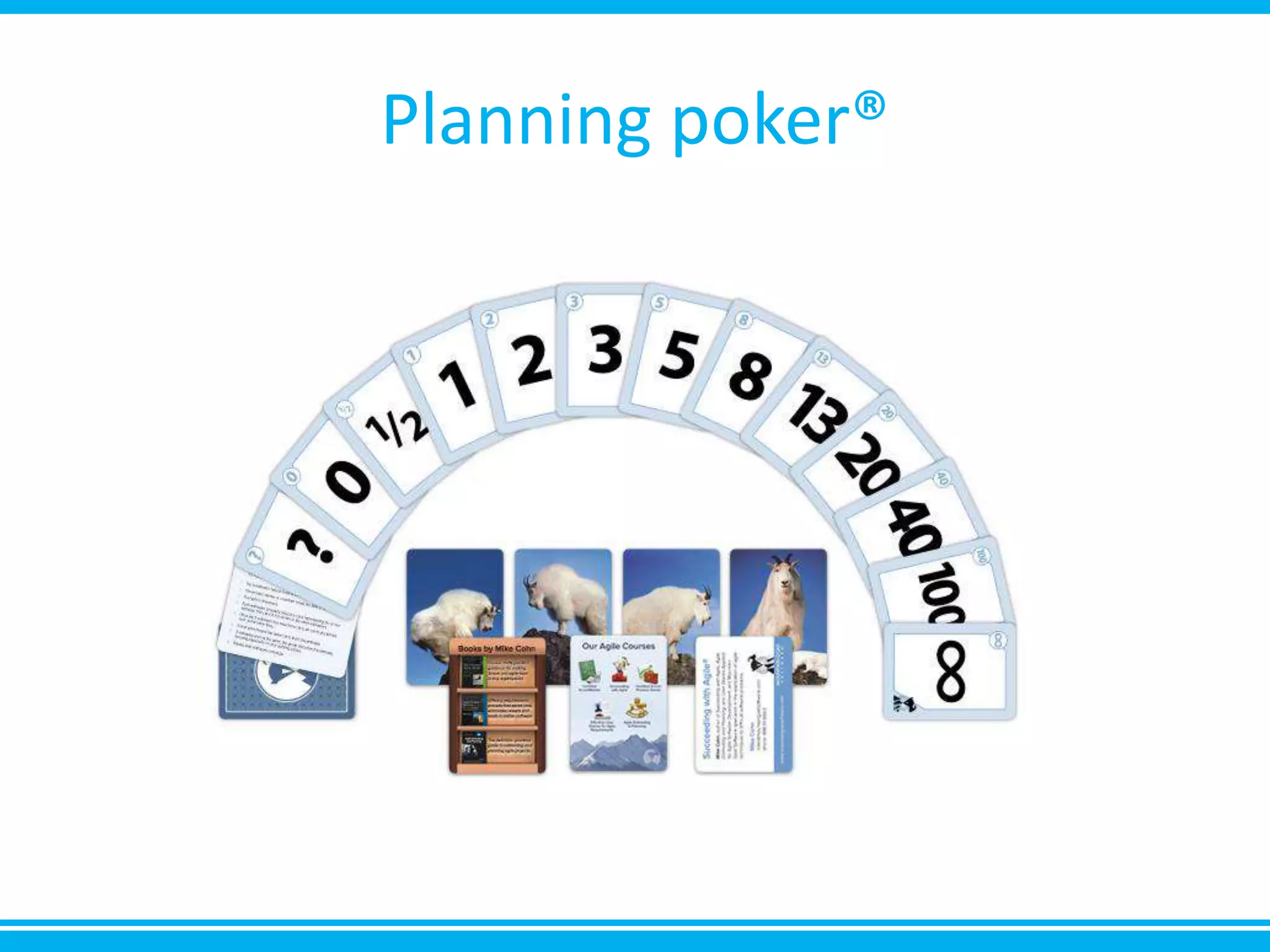
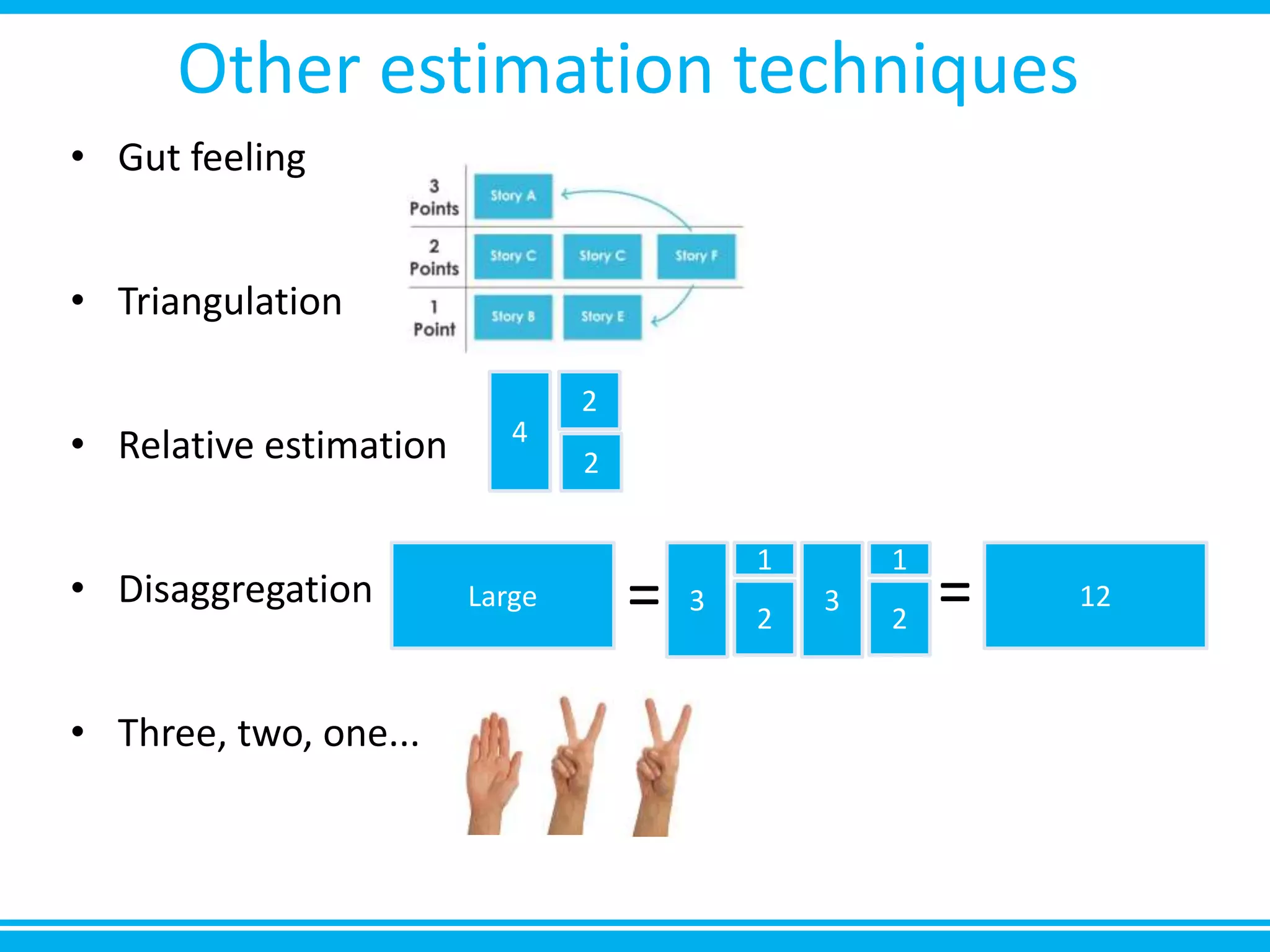
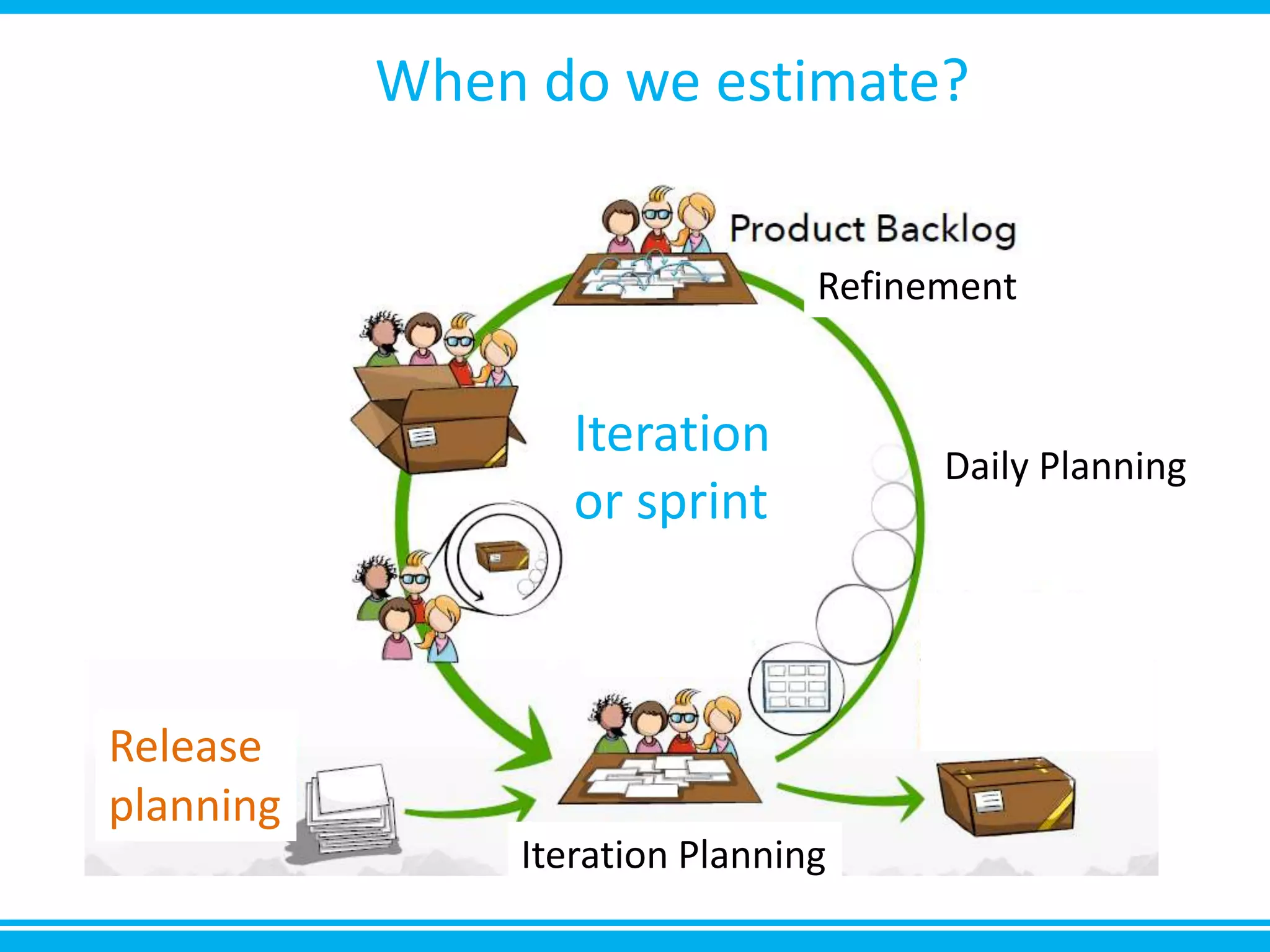
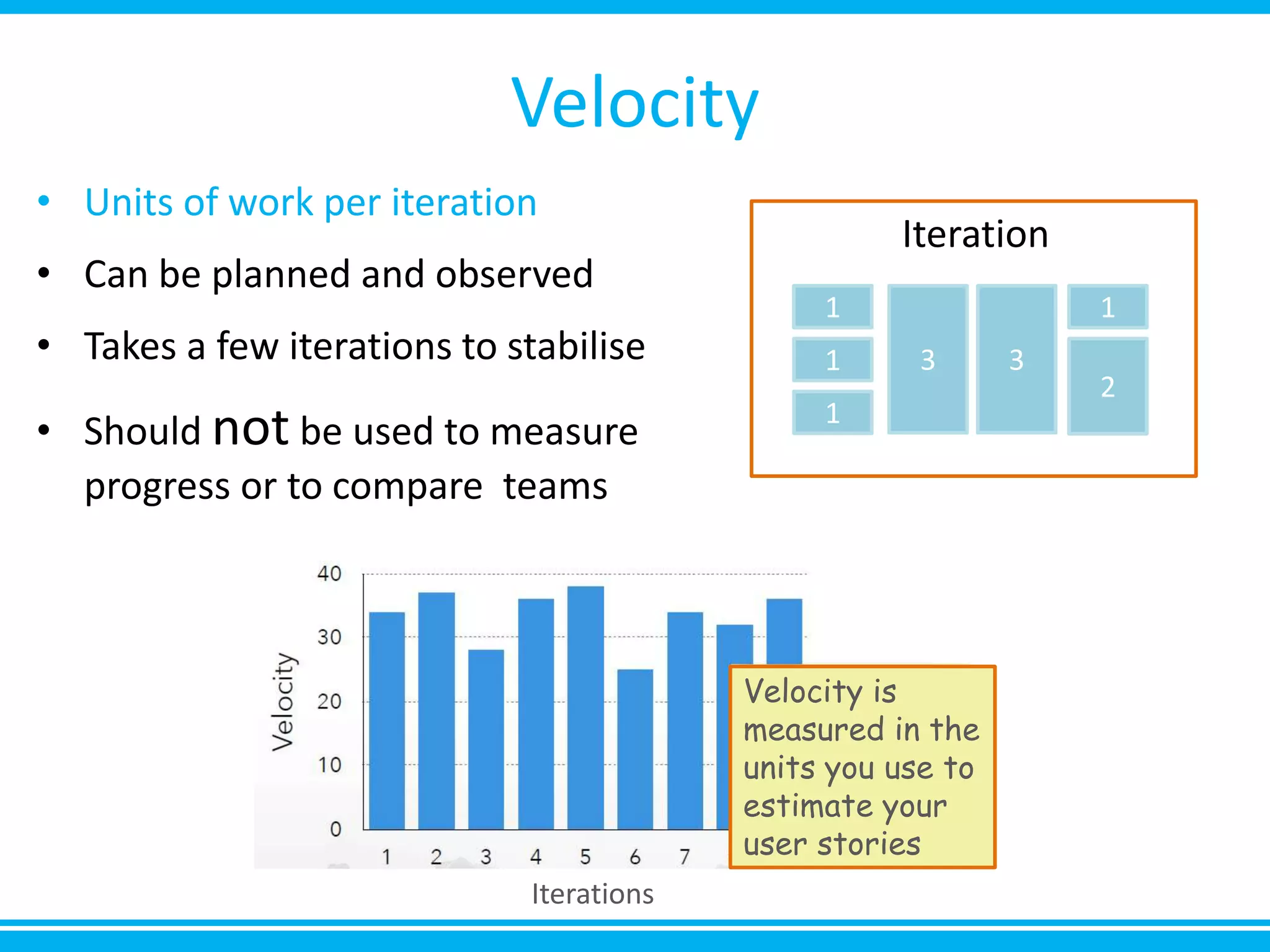
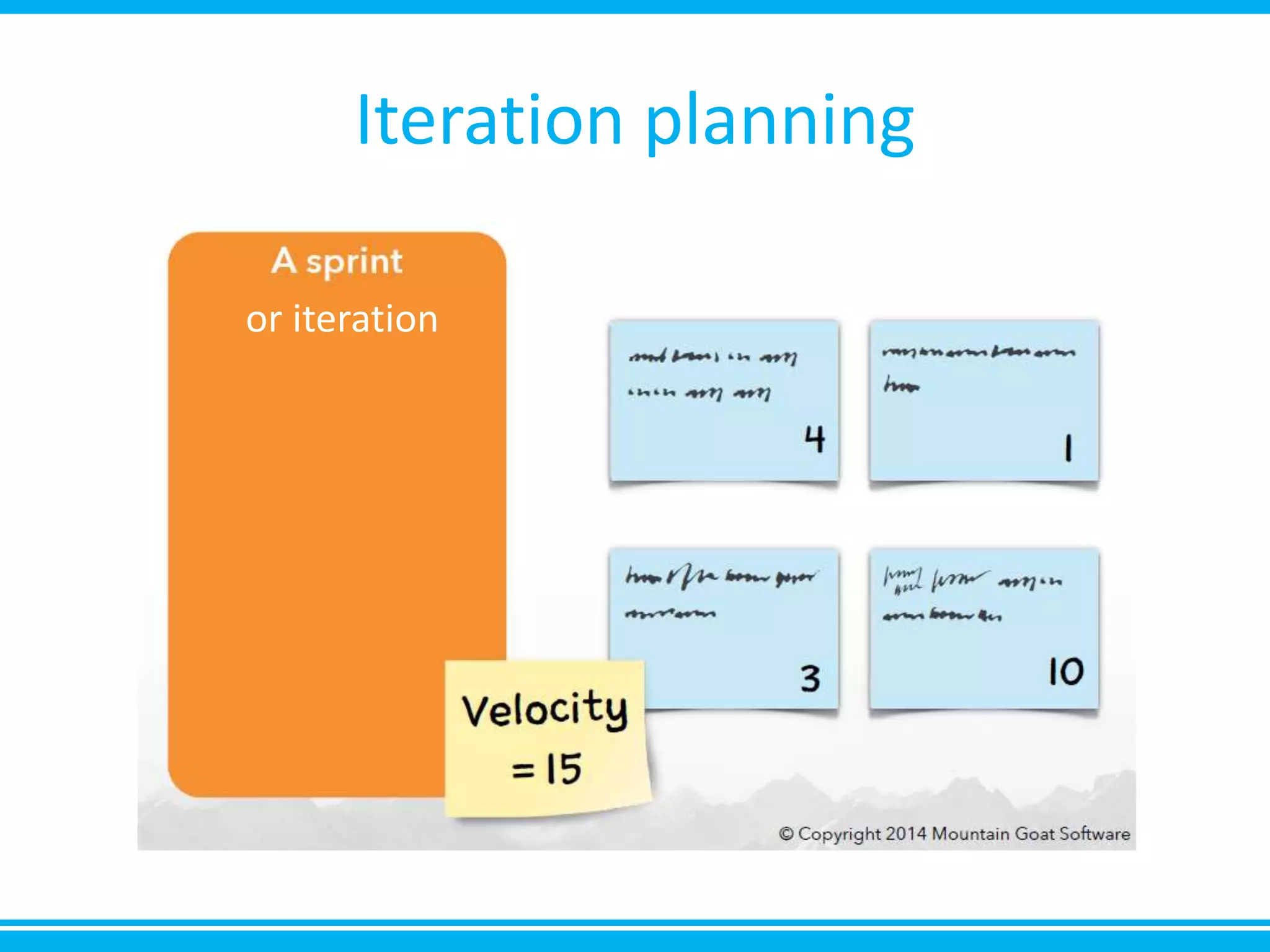
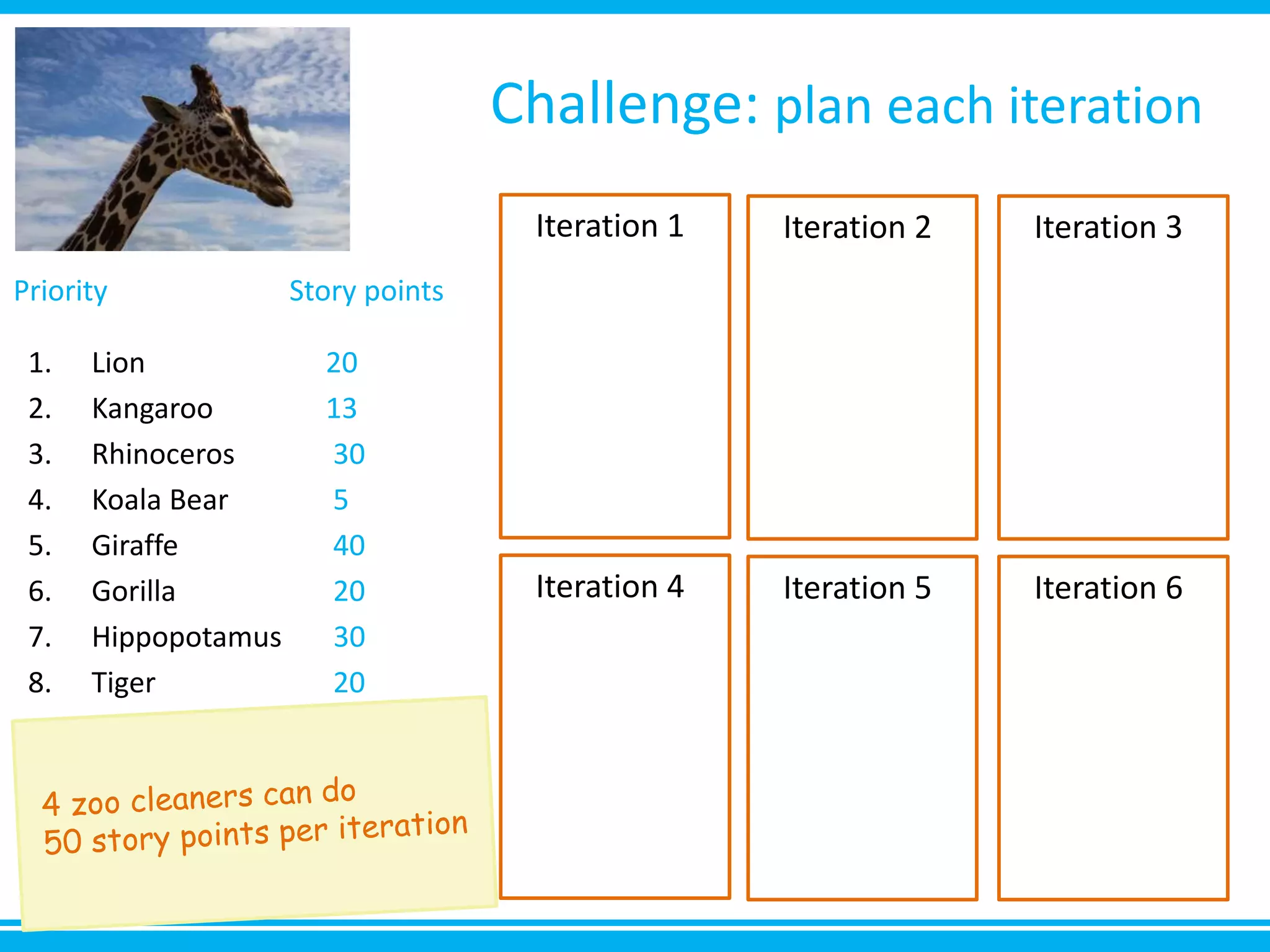
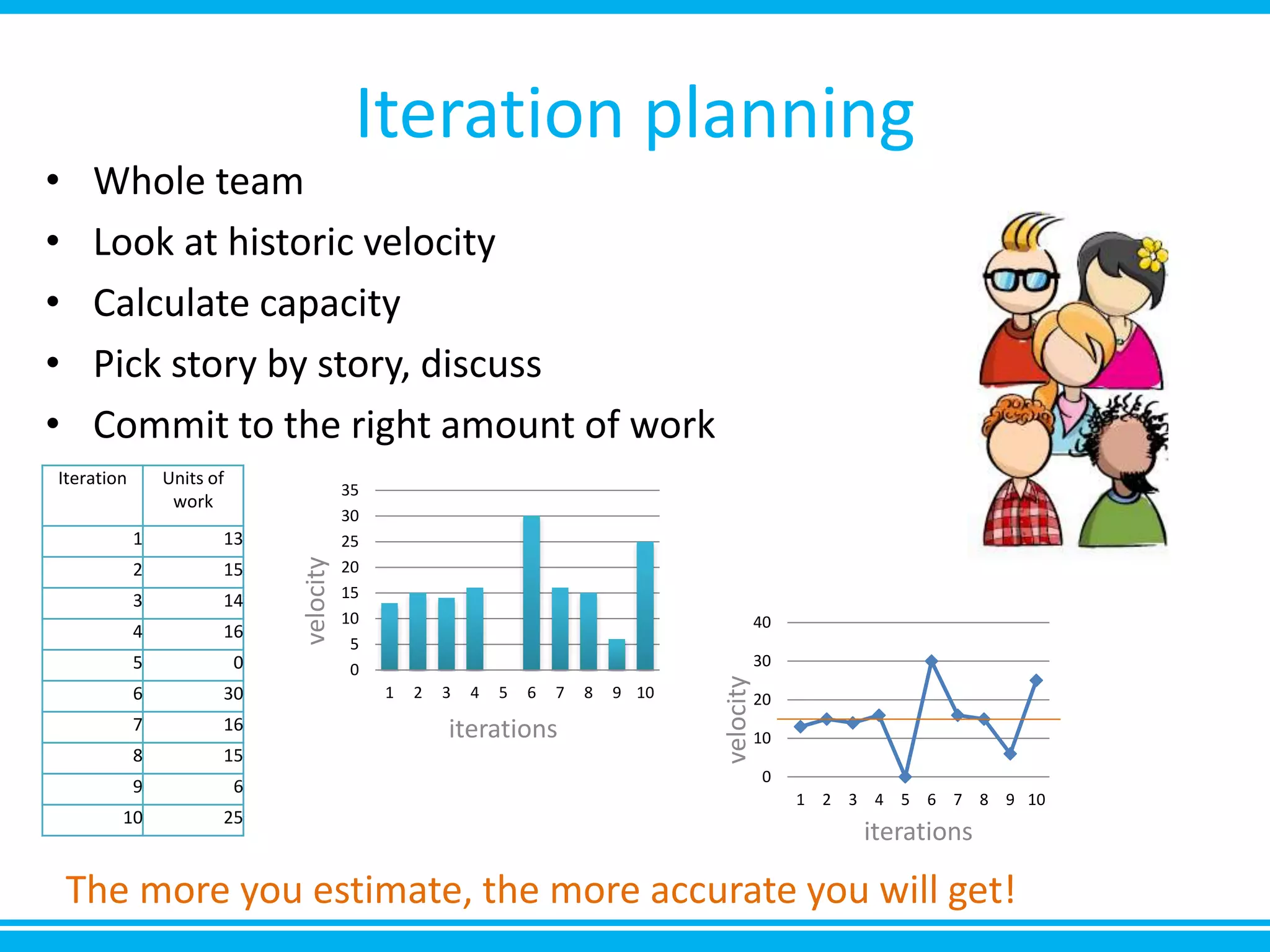
The document discusses estimation and planning in Agile methodologies, highlighting the importance of story points and various estimation techniques like planning poker. It emphasizes the need for relative measures of effort to improve accuracy and discusses how to estimate for tasks and plan iterations effectively. Additional resources for agile planning are also provided.