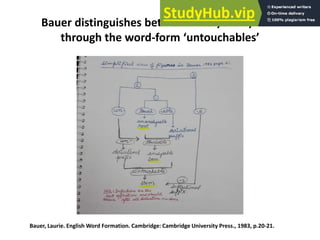
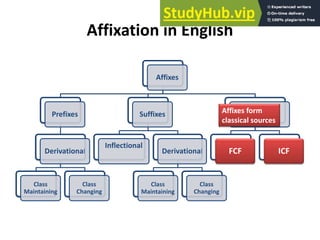
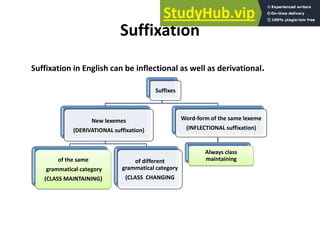
This document discusses affixation in the English language. It begins by defining an affix as an additional constituent appended at the beginning or end of another constituent that modifies or alters its meaning. It then distinguishes between roots, stems, and bases. The major types of affixation are identified as prefixation, suffixation, and infixation. Prefixation and suffixation are discussed in further detail, including their classification based on syntactic categories and semantic functions. Examples are provided to illustrate class-maintaining and class-changing affixation.