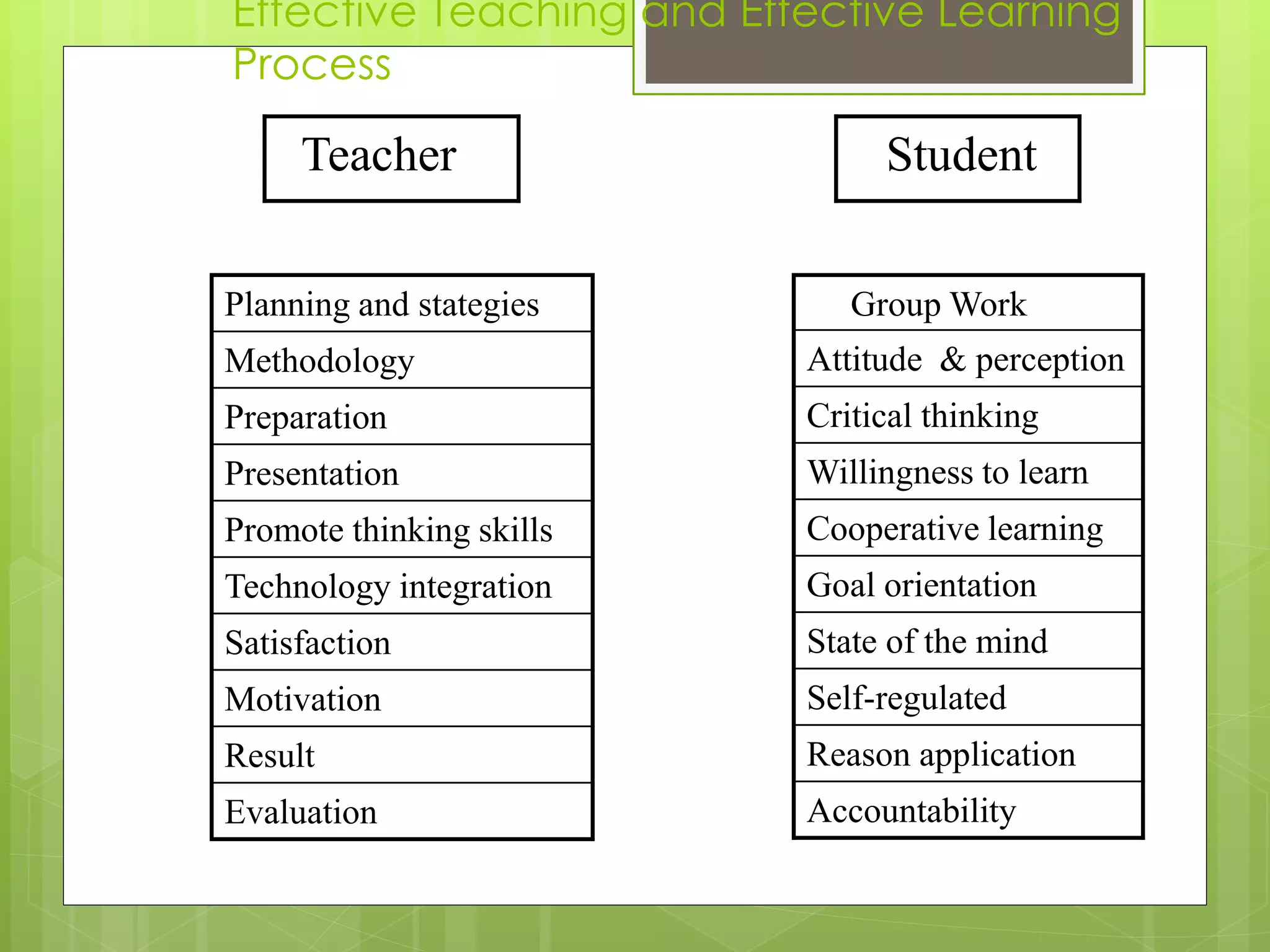
The document discusses English teaching methodology and strategies. It begins by defining methodology as the set of methods used for teaching English. It discusses the nature of language teaching and the teacher's role in creating desirable changes in student behavior. It then covers strategies for English language learning and teaching, Gardner's theory of multiple intelligences, various teaching methodologies like seminars and debates, the changing role of the teacher, techniques for positive teaching, and factors that affect learning outcomes.