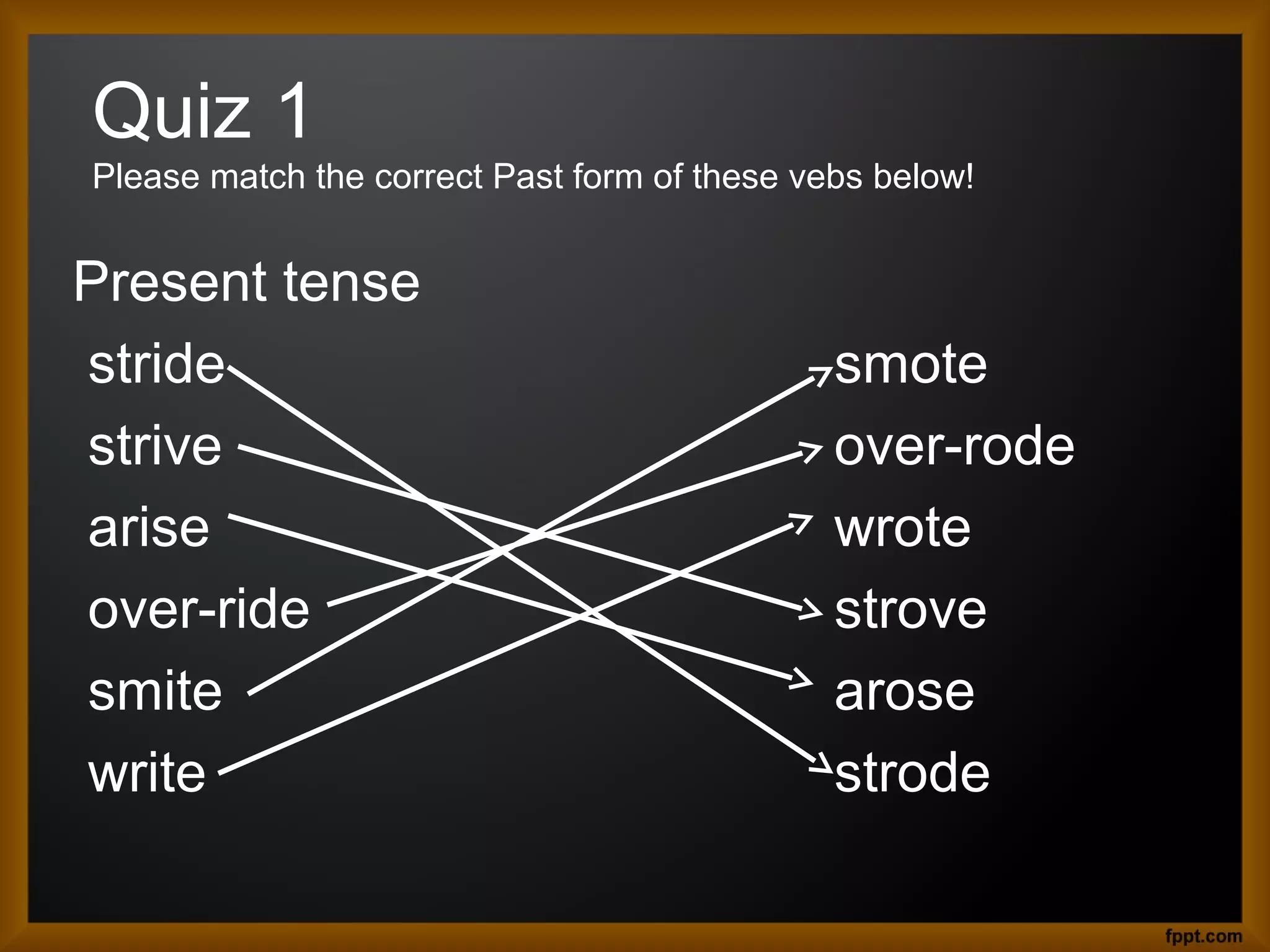
This document discusses inflection in lexical morphology. It provides examples of frozen historical relics like ablaut and umlaut that indicate changes in grammatical function. Ablaut involves changes in root vowels between present and past tense forms like drive/drove. Umlaut involves fronting of vowels before front vowels, like foot/feet. There are also some irregular plural formations with Latin and Greek loanwords. Beyond these relics, the document outlines lexical rules for adding inflections through affixation at different strata or levels, providing examples of rules for adding suffixes to nouns to mark plural forms. It distinguishes lexical rules from post-lexical rules.







![Morphological rules that attach
affixes to bases
Form :
insert A in environment [Y _______ Z]x
Output: word
Example:
Insert /ə/ in environment [dɛɪt_]
Output:/dɛɪtə/
Noun + Plural](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inflectioninlexicalmorphologyedit-140226053451-phpapp01/75/Inflection-in-Lexical-Morphology-8-2048.jpg)
![Stratum 2
Insert -s in environment [Y ______] Noun + Plural
Output: Y-s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inflectioninlexicalmorphologyedit-140226053451-phpapp01/75/Inflection-in-Lexical-Morphology-9-2048.jpg)