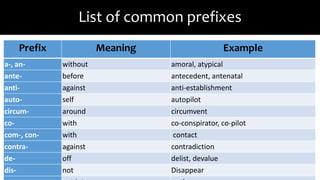
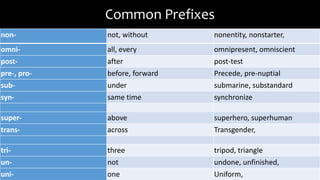
The document explains the concepts of roots and affixes in word formation, detailing types of roots (free and bound) and providing an extensive list of common prefixes and suffixes along with their meanings and examples. It differentiates between grammatical/infectional and derivational suffixes, outlining their functions in changing or providing grammatical information. Additionally, it includes exercises for active engagement in applying the concepts learned.