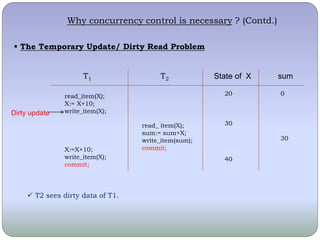
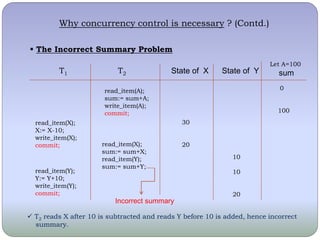
The document discusses transaction states, ACID properties, and concurrency control in databases. It describes the different states a transaction can be in, including active, partially committed, committed, failed, and terminated. It then explains the four ACID properties of atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability. Finally, it discusses the need for concurrency control and some problems that can occur without it, such as lost updates, dirty reads, incorrect summaries, and unrepeatable reads.