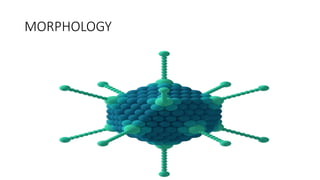
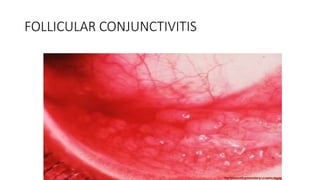
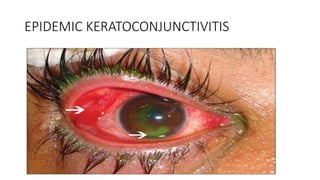
Adenoviruses are non-enveloped double stranded DNA viruses that are isolated from adenoid tissue. They cause respiratory, eye, urinary tract and intestinal infections in children and military recruits. There are over 50 serotypes classified into groups A through F. Symptoms vary depending on the infected site and serotype but include respiratory diseases, sore throat, follicular conjunctivitis and epidemic keratoconjunctivitis. Diagnosis involves tissue culture, complement fixation tests, PCR and electron microscopy. While there is no vaccine for general use, some vaccines exist to control outbreaks in closed communities.