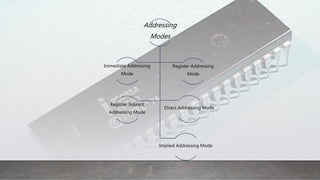
The document discusses the addressing modes of the 8085 microprocessor. It defines an addressing mode as the way operands are specified in an instruction. It then describes the five addressing modes of the 8085: immediate, register, direct, register indirect, and implied. Immediate mode embeds the data in the instruction. Register mode uses register-stored data. Direct mode specifies the data address in the instruction. Register indirect mode uses a register pair containing the data address. Implied mode uses the opcode to determine the implied operand.