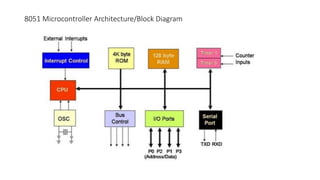
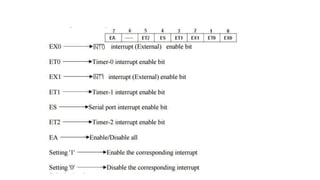
The document provides an overview of the 8051 microcontroller architecture, highlighting its introduction by Intel in the 1980s and its evolution from NMOS to CMOS technology. It details key features such as its memory capacity, register banks, and applications in various fields including home automation, industrial control, and medical devices. The document also outlines the microcontroller's components, including the CPU, memory, interrupts, and bus systems.