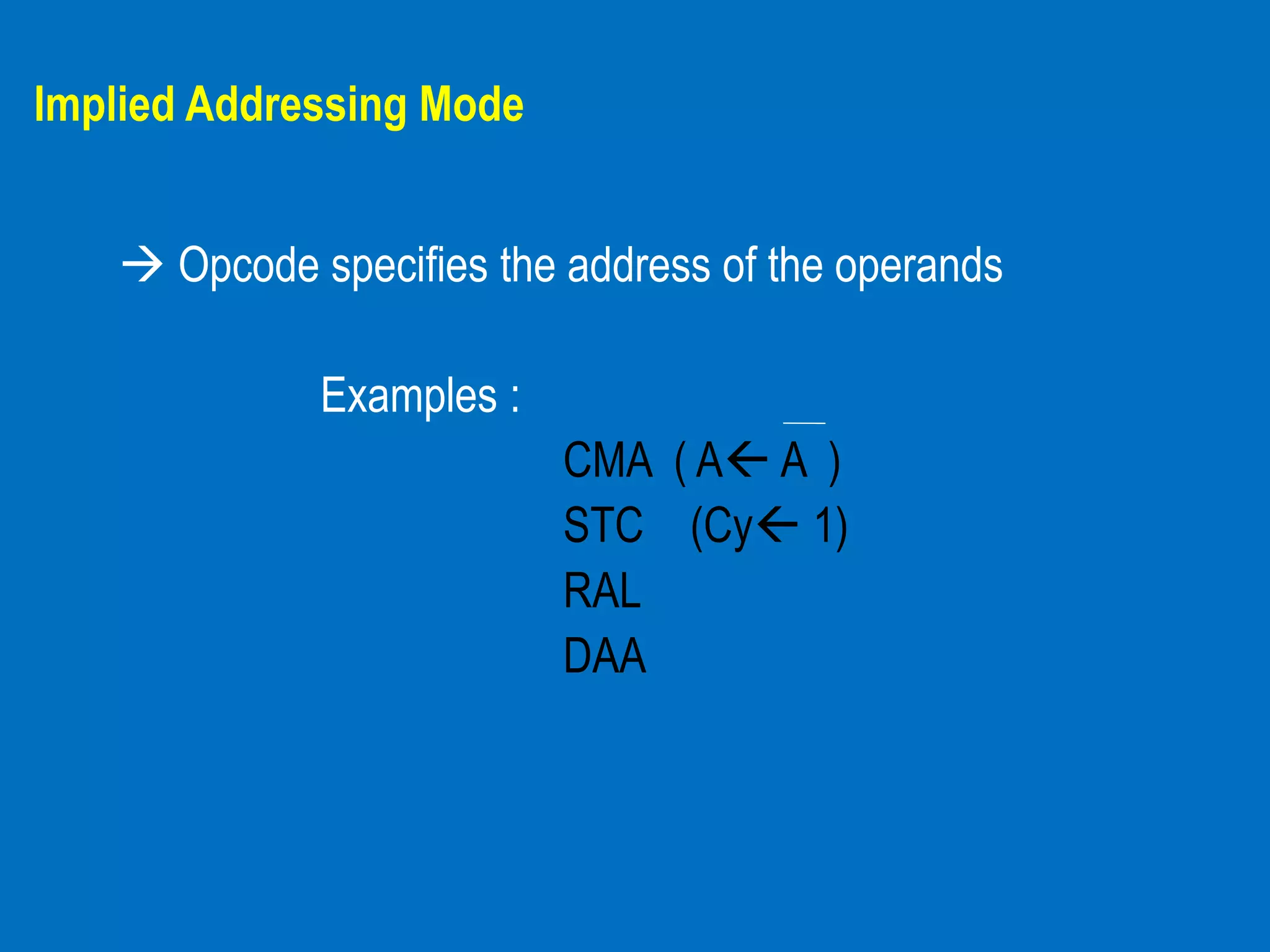
The document discusses different addressing modes used by the 8085 microprocessor to access data stored in memory, including immediate, register, direct, indirect, and implied addressing modes. It provides examples of instructions that use each addressing mode and briefly describes how each mode specifies the location of operands. The addressing modes determine how the processor references data through the instruction itself or by using register values as memory addresses.





![ The memory address where the operand located is
specified by the contents of a register pair
Examples :
LDAX B
MOV M,D
Immediate Indirect MVI M,55H
Register Indirect ADC M [A A +Cy+(M)]
DCR M [(HL)(HL)+1]
PUSH PSW
Indirect Addressing Mode](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/addressingmodes8085-181217123653/75/Addressing-modes-8085-6-2048.jpg)