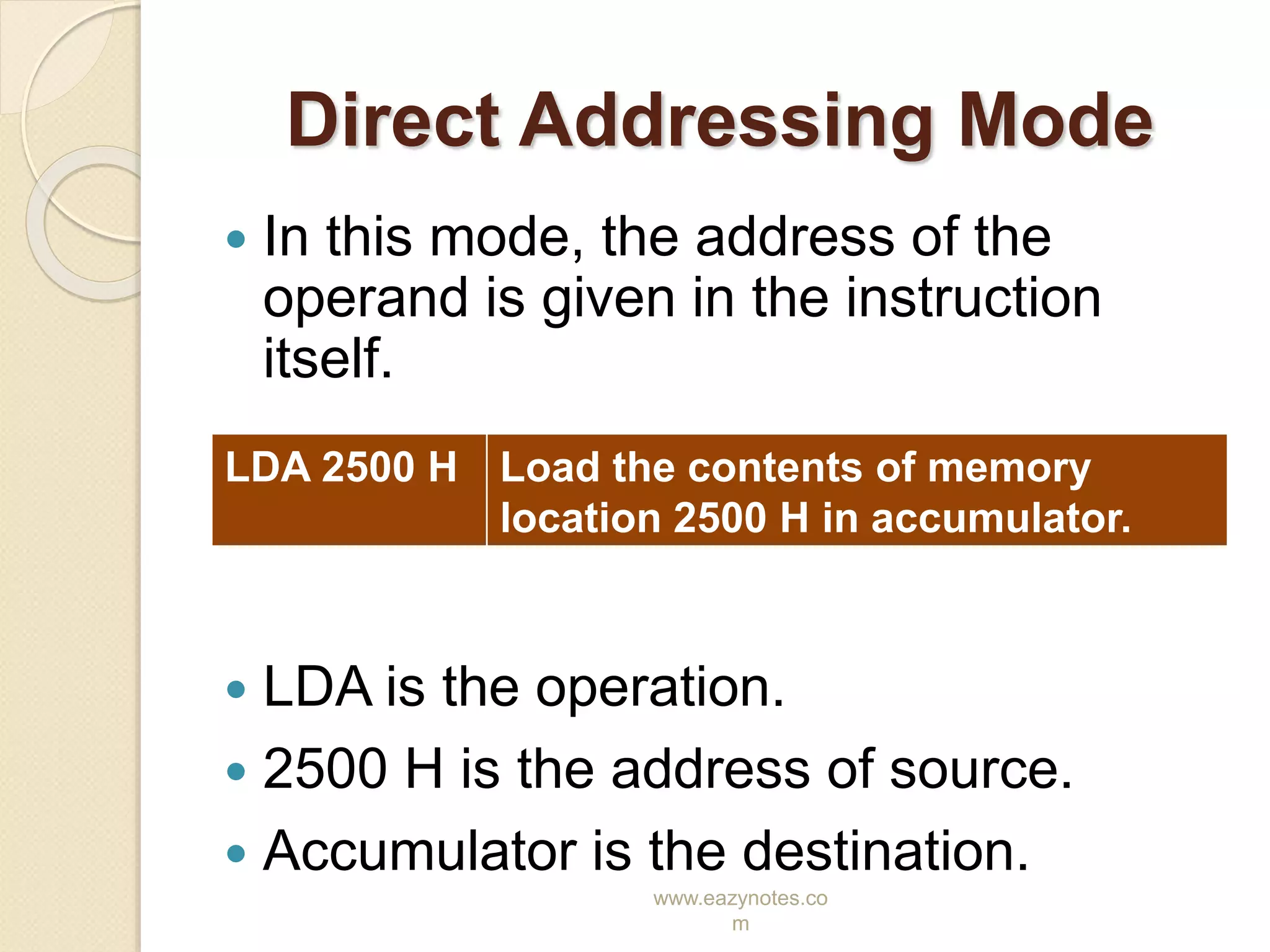
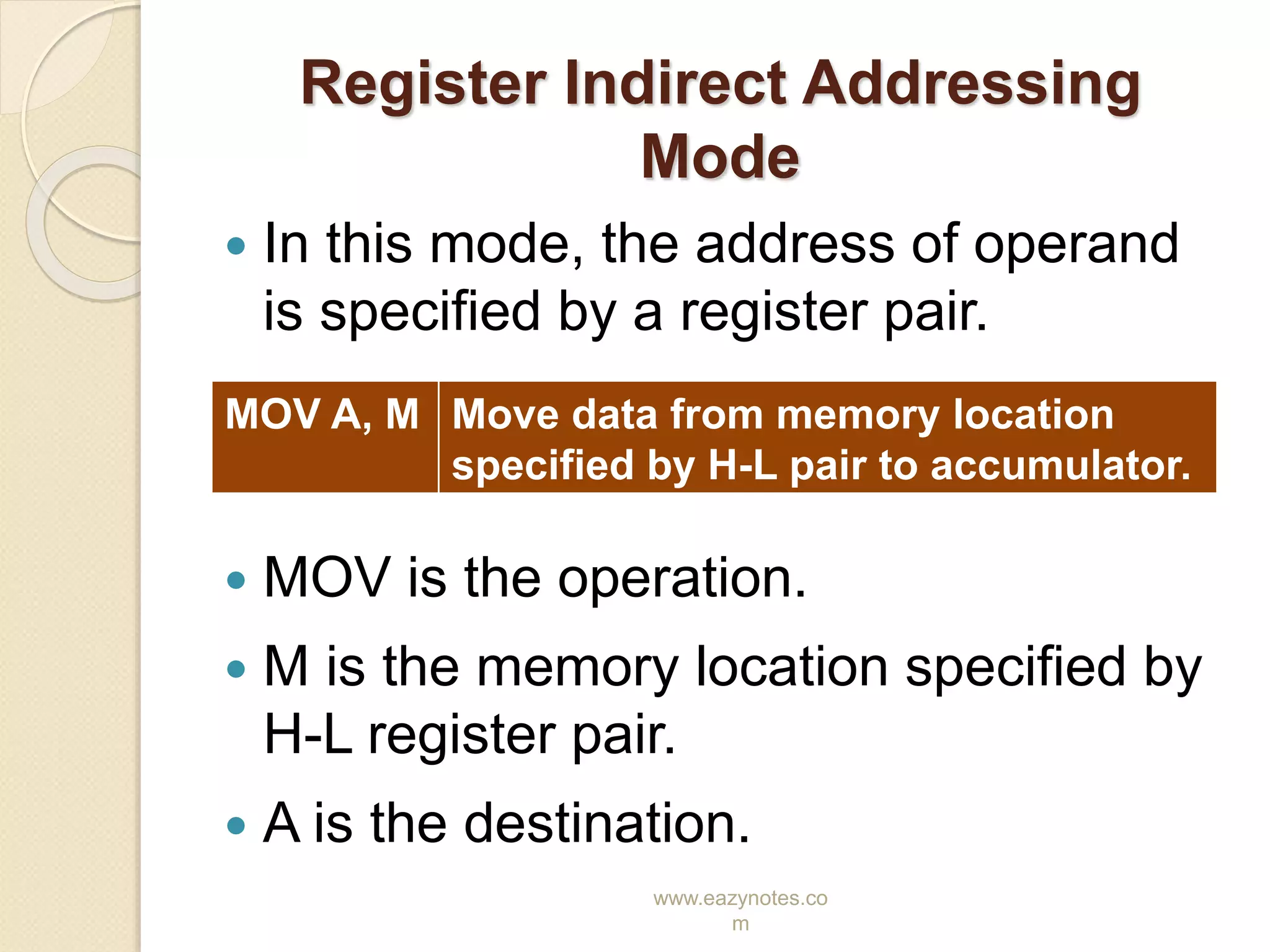
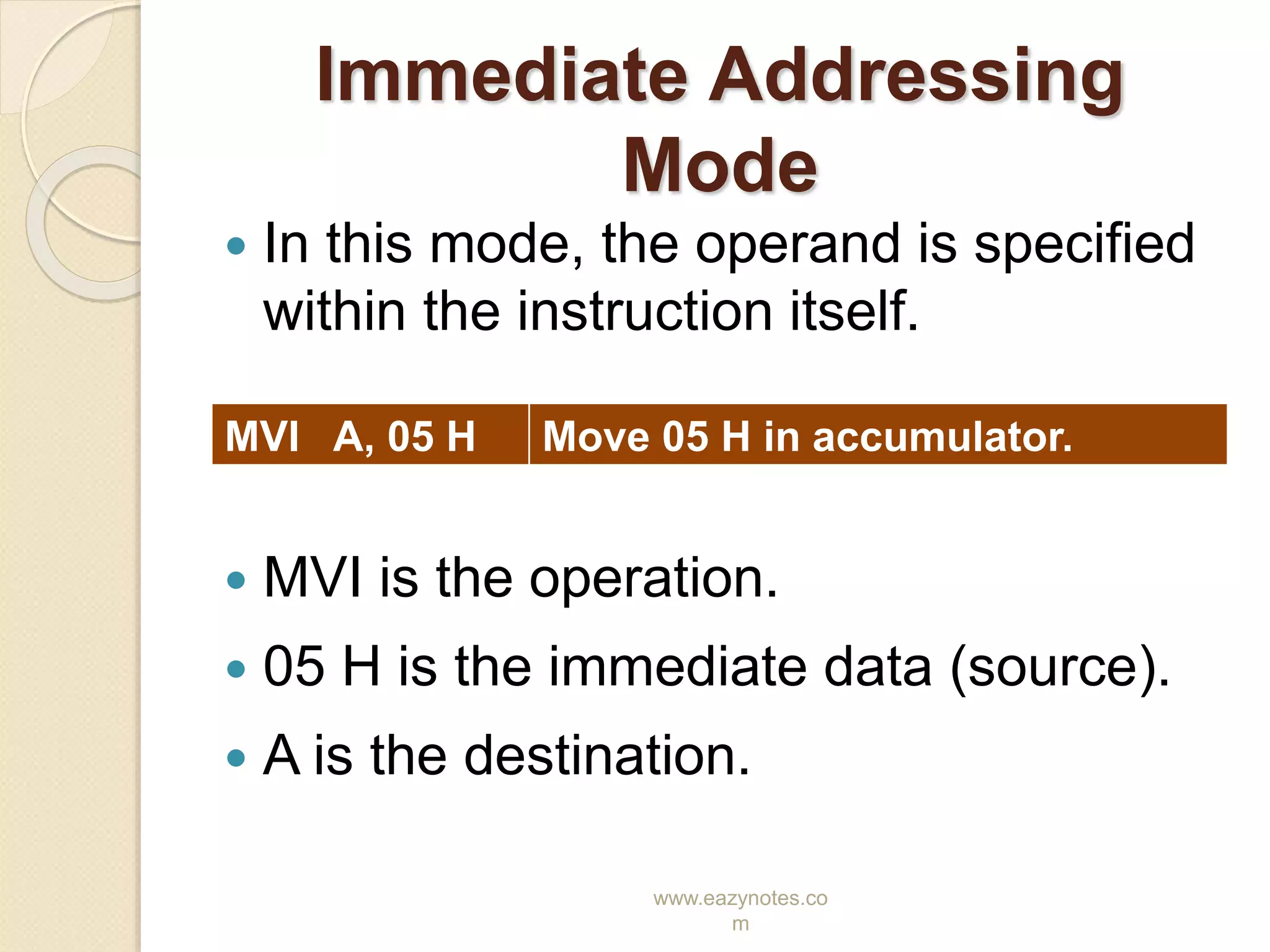
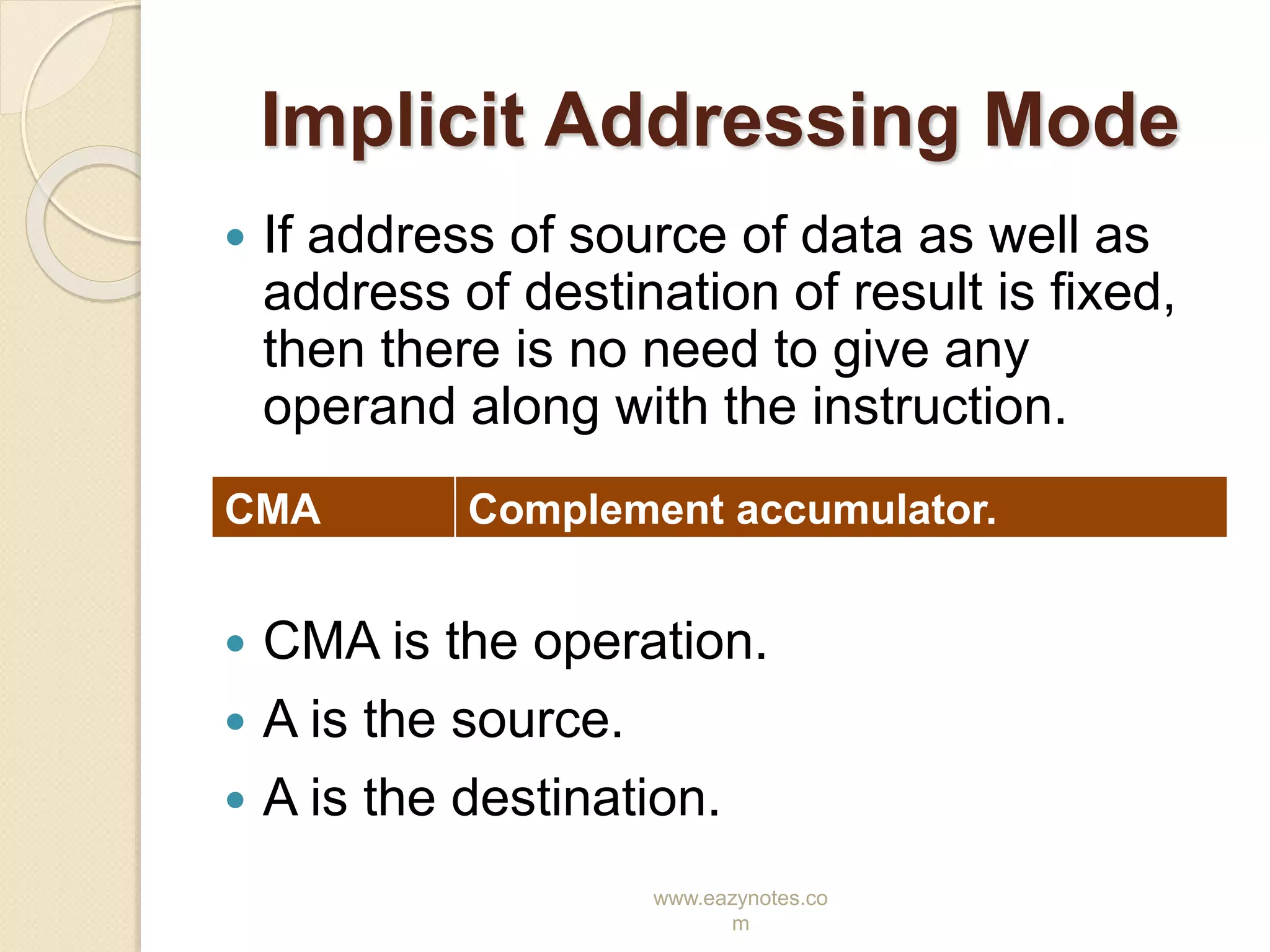
This document discusses the different addressing modes of the 8085 microprocessor. It explains that an addressing mode refers to how the operand of an instruction is specified. It then describes the five addressing modes of the 8085: direct, register, register indirect, immediate, and implicit. For each mode, it provides an example instruction to illustrate how the operation, source, and destination are specified.