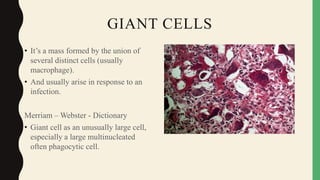
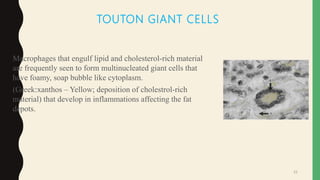
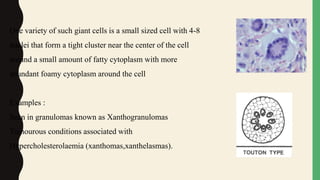
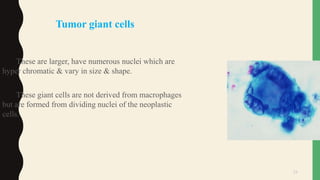
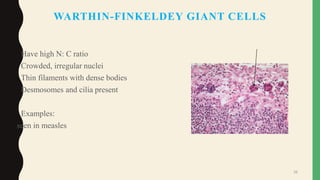
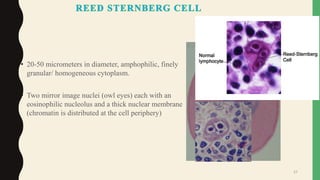
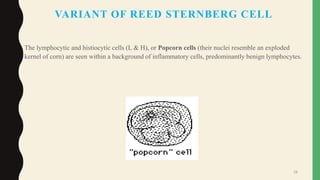
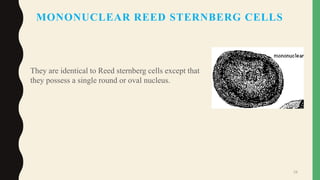
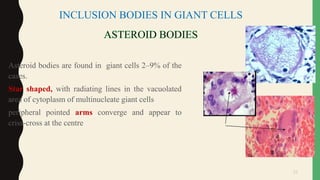
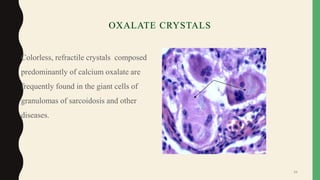
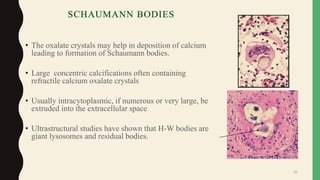
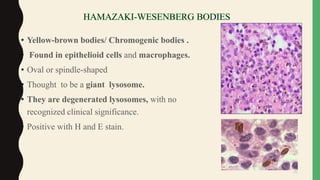
- Giant cells are large multinucleated cells formed by the fusion of macrophages in response to infection or foreign material.
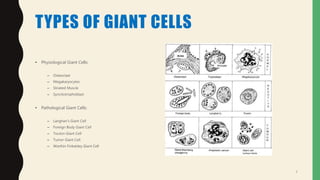
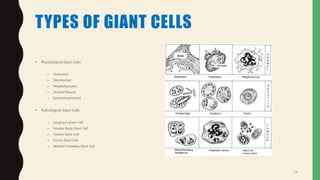
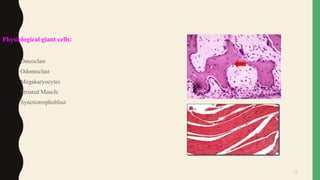
- There are physiological giant cells like osteoclasts and pathological giant cells seen in conditions like tuberculosis.
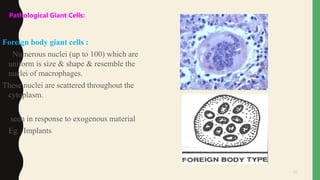
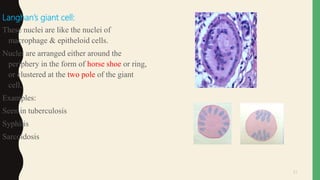
- Pathological giant cells include foreign body giant cells, Langhans giant cells, and tumor giant cells.
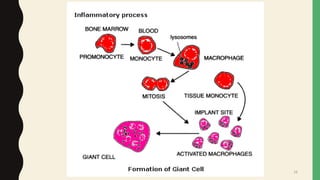
- Giant cells form through the fusion of macrophages mediated by cytokines, adhesion molecules, and oxidative stress. Nuclei and inclusion bodies can provide clues to the etiology of giant cell formation.