1. Acute viral hepatitis is defined as inflammation of the liver caused by viral infection, resulting in elevated liver enzymes for less than 6 months. The most common causes are hepatitis A, B, C, D, E viruses.
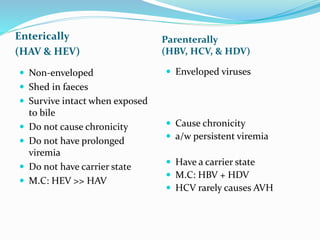
2. The document discusses the pathogenesis, clinical features, investigations, management, and prevention of different viral hepatitis types. Hepatitis A and E are usually self-limiting while hepatitis B, C and D can sometimes lead to chronic liver disease.
3. Supportive care is the main treatment approach for most cases of acute viral hepatitis. Specific antiviral therapy may be used for severe hepatitis B cases to prevent progression to liver failure. Vaccines exist to prevent hepatitis A and B infection