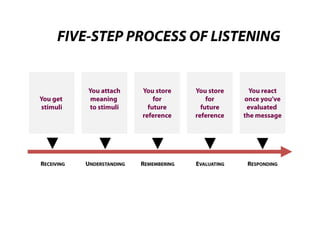
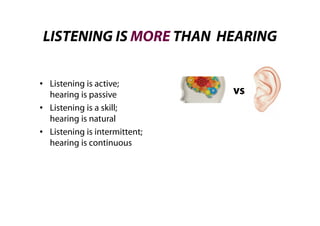
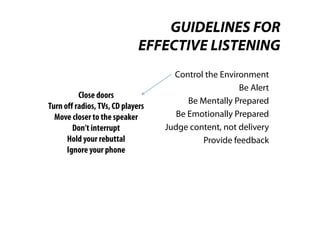
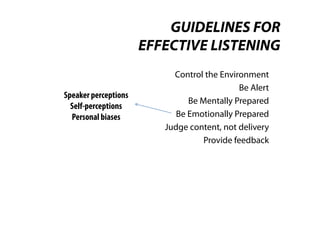
This document discusses effective listening. It begins by providing listening facts, such as most people spend 45% of their communication time listening but understand only a quarter of what is said. It then describes the five-step listening process of receiving stimuli, understanding, remembering, evaluating, and responding. Several bad listening habits are identified, such as tuning out if uninterested or distracted. The document distinguishes between hearing, which is passive, versus listening, which is an active skill. It concludes by providing guidelines for effective listening, such as controlling your environment, being alert and prepared, judging the content rather than delivery, and providing feedback.