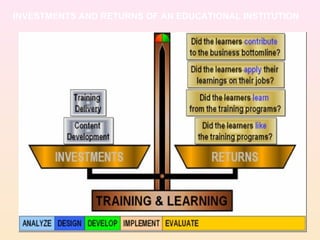
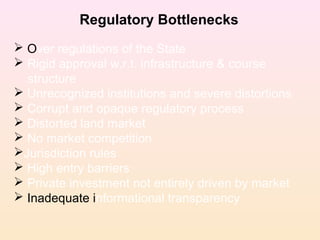
Action research involves teachers, students, and parents working together to solve problems in the classroom. It is a reflective process of progressive problem solving to improve situations. Some common problems teachers encounter include how to make learning more enjoyable, accommodate different needs, and encourage parental support. Action research involves both taking action, such as trying new teaching methods, and conducting research, such as analyzing student test scores, to evaluate the effects of changes. Allowing foreign investment and institutions in higher education can help address lack of funding, stop the outflow of students, and increase opportunities through competition and improved quality. However, there are also regulatory issues and concerns about decreased subsidies for marginalized groups that need to be addressed.