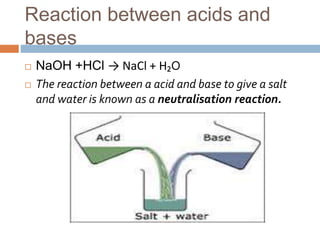
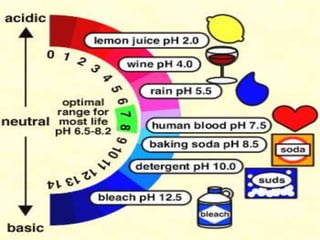
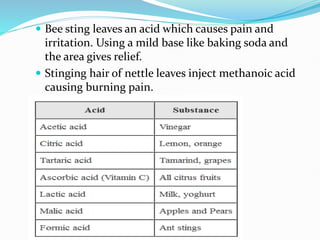
The document provides an overview of acids, bases, and salts, detailing their properties, reactions, and importance in everyday life. It describes the pH scale, the formation of salts from different acid-base combinations, and various applications of substances like sodium hydroxide and baking soda. Additionally, it covers the water of crystallization and transformations between hydrated and anhydrous states of certain salts.