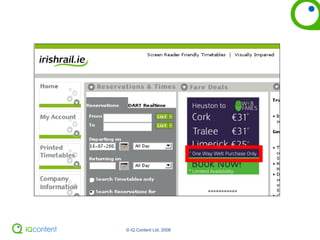
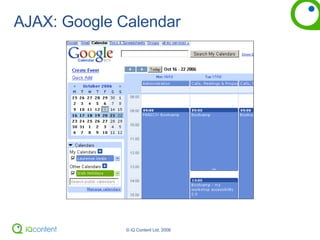
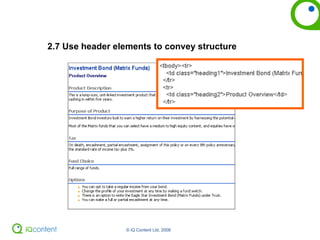
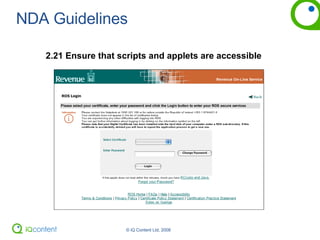
The document provides an overview of accessibility, including defining it, guidelines for making websites accessible, and how to audit a website for accessibility. It discusses the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) and how they are moving to WCAG 2.0. It also covers making PDFs accessible and alternatives to PDFs. The document encourages thinking about usable accessibility rather than just meeting checkpoints and provides tips for testing websites for accessibility.