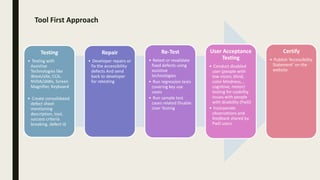
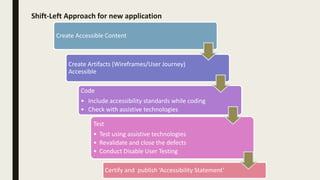
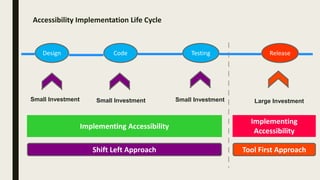
This document discusses accessibility testing approaches. It describes the "tool first" approach where testing occurs after development using assistive technologies to identify defects, and the "shift left" approach where accessibility is considered earlier in the design process through inclusive design and accessible coding practices. The document also provides definitions and examples of accessibility, examples of assistive technologies and compliance laws, case studies on the benefits of accessibility, and an overview of the WCAG guidelines and conformance levels.