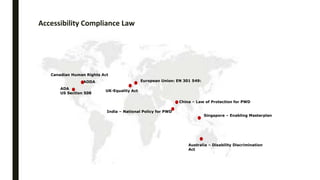
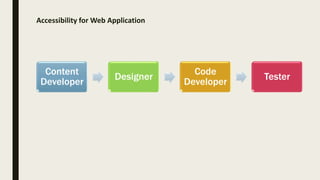
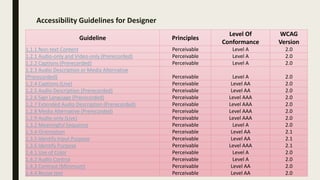
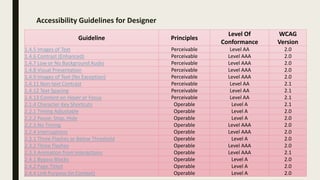
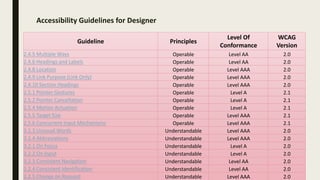
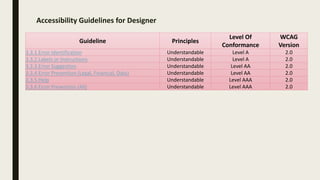
The document provides a comprehensive overview of digital accessibility, discussing its significance for content developers, designers, and testers in ensuring usability for individuals with disabilities. Key topics include the definition of accessibility, statistics about disabilities, various assistive technologies, compliance laws, and the urgent need for adherence to accessibility guidelines (WCAG). It also highlights case studies demonstrating the positive impact of accessibility enhancements on organizations and the importance of evolving guidelines to meet diverse needs.