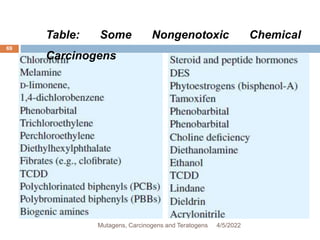
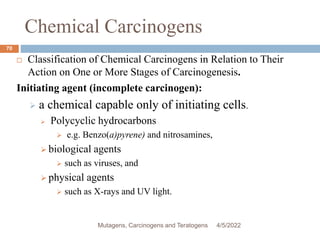
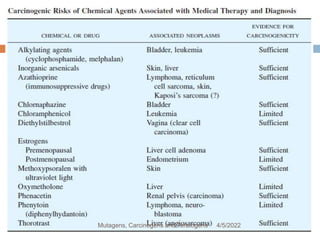
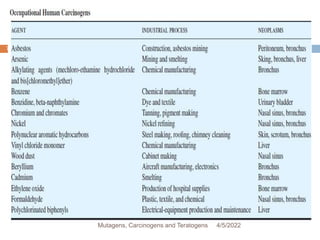
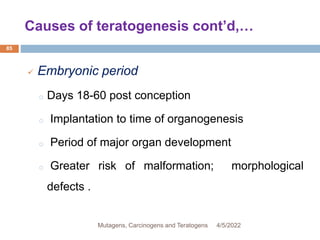
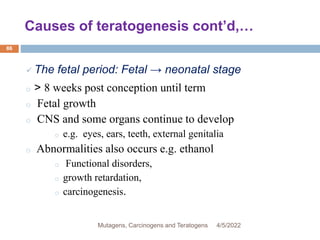
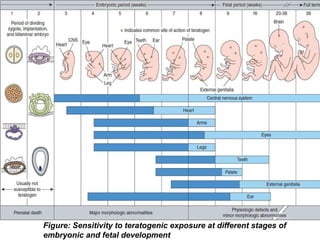
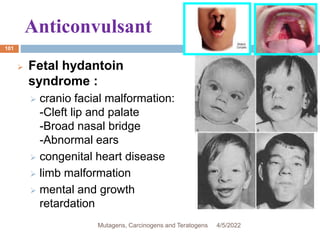
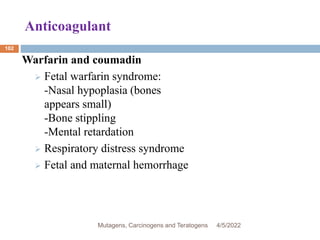
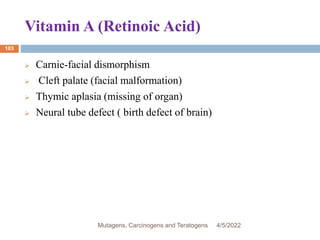
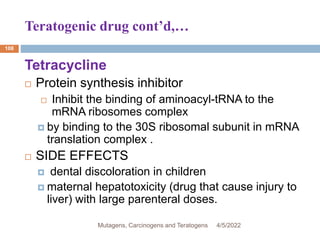
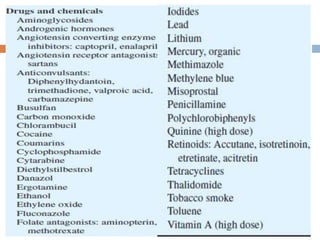
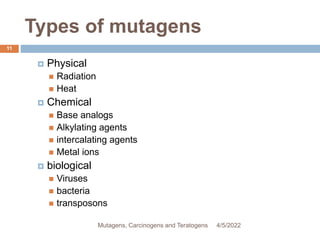
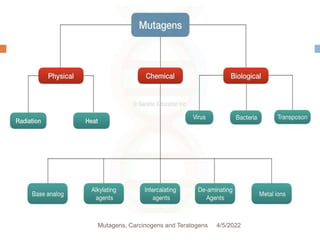
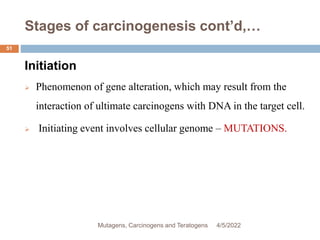
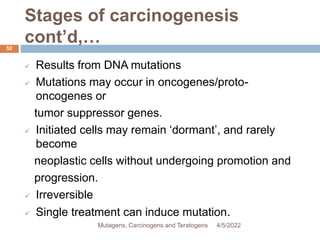
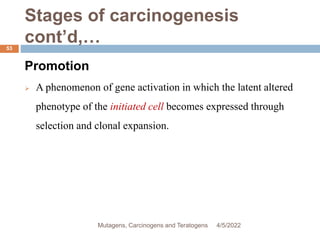
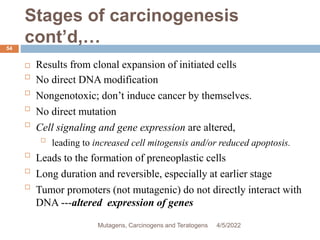
This document discusses mutagens, carcinogens, and teratogens. It begins by defining mutagenesis as the process by which genetic information is changed, resulting in a mutation. This can occur spontaneously or due to exposure to mutagens. Mutagens are then defined as physical, chemical, or biological agents that cause mutations by altering genetic material. Examples of different types of mutagens are provided, including radiation, heat, base analogs, alkylating agents, and viruses. The effects of mutagens, such as changes at the chromosomal and molecular levels, are described. Some mutagens are classified as carcinogens, which induce cancer, or teratogens, which cause birth defects. While mutagens can cause harm, some






































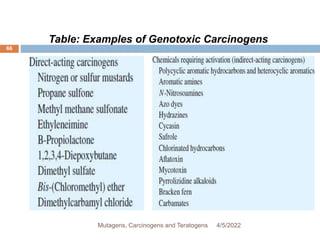
![DNA-damaging agents (genotoxic)
cont’d,…
64
Indirect-acting carcinogens
require metabolic activation by cellular enzymes
to form the ultimate carcinogenic species.
o Examples include
o dimethylnitrosamine,
o benzo[a]pyrene,
o 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene,
o aflatoxin B1and
o 2-acetylaminofluorene
4/5/2022
Mutagens, Carcinogens and Teratogens](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-220220081149/85/3-mutagen-carcino-and-teratogen-64-320.jpg)