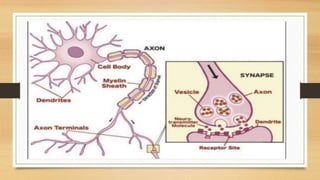
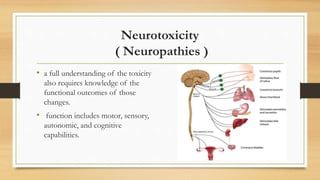
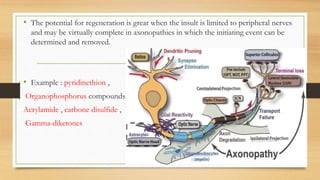
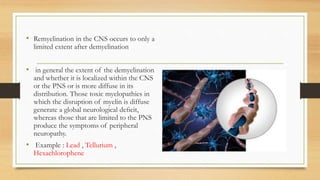
Neurotoxicity can cause adverse changes in the structure or function of the central nervous system due to exposure to chemicals, physical agents, or biological factors. The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (CNS; brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system (PNS; nerves connecting CNS to body). Neurotoxicity can impact neurons, axons, myelinating cells, or neurotransmitter systems. Mechanisms include neuropathies (neuron death), axonopathies (axon degeneration), myelinopathies (myelin disruption), or toxicity associated with neurotransmitters like acetylcholine. Examples of neurotoxic agents are methyl mercury, doxorubicin, trimethyltin, pyridinethion