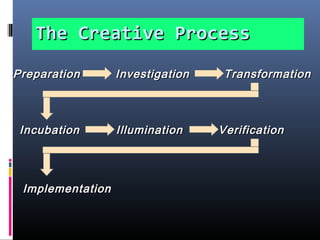
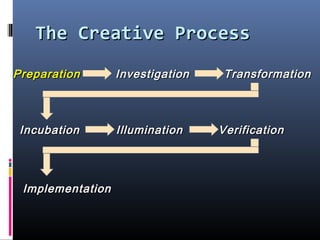
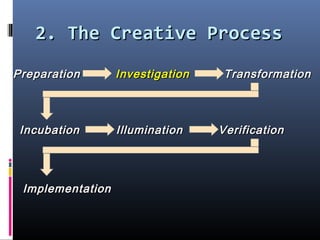
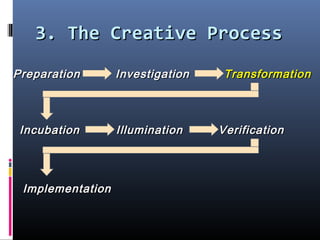
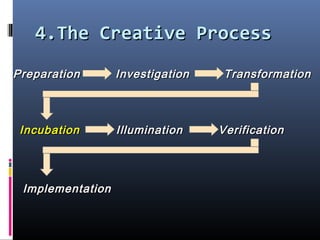
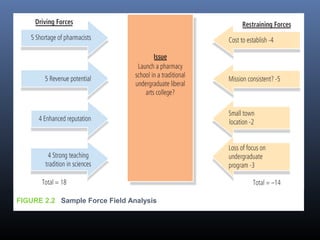
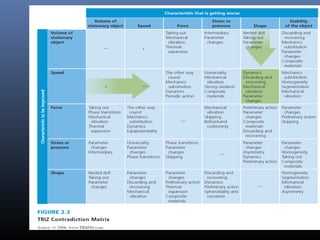
This document discusses creativity, innovation, and entrepreneurship. It defines creativity as developing new ideas, innovation as applying creative solutions, and entrepreneurship as connecting ideas to business opportunities. The creative process involves preparation, investigation, transformation, incubation, illumination, verification, and implementation. Techniques to enhance creativity include brainstorming, questioning assumptions, embracing failure, and obtaining diverse perspectives. Organizations can foster creativity by rewarding innovation and embracing diverse thinking.