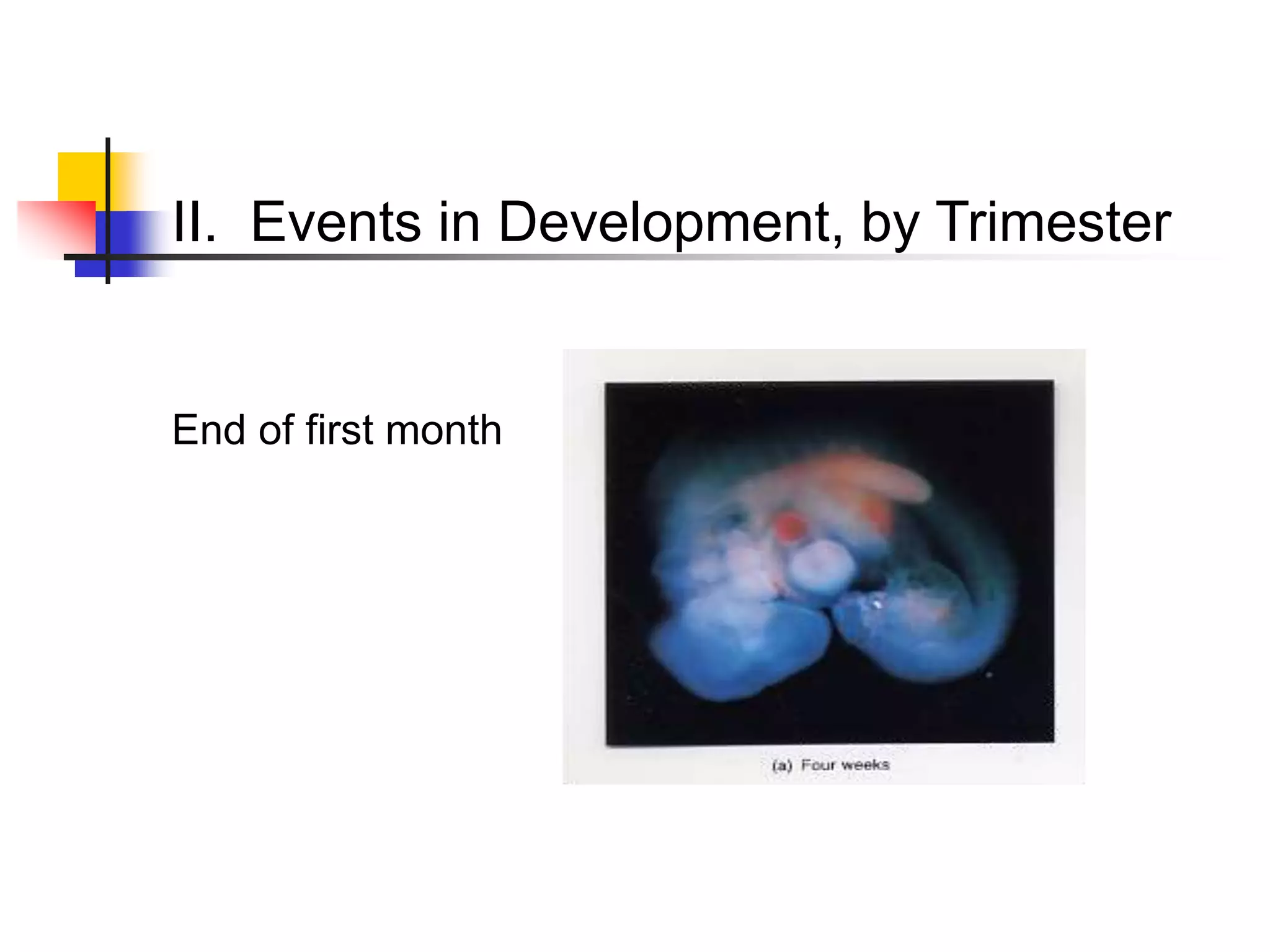
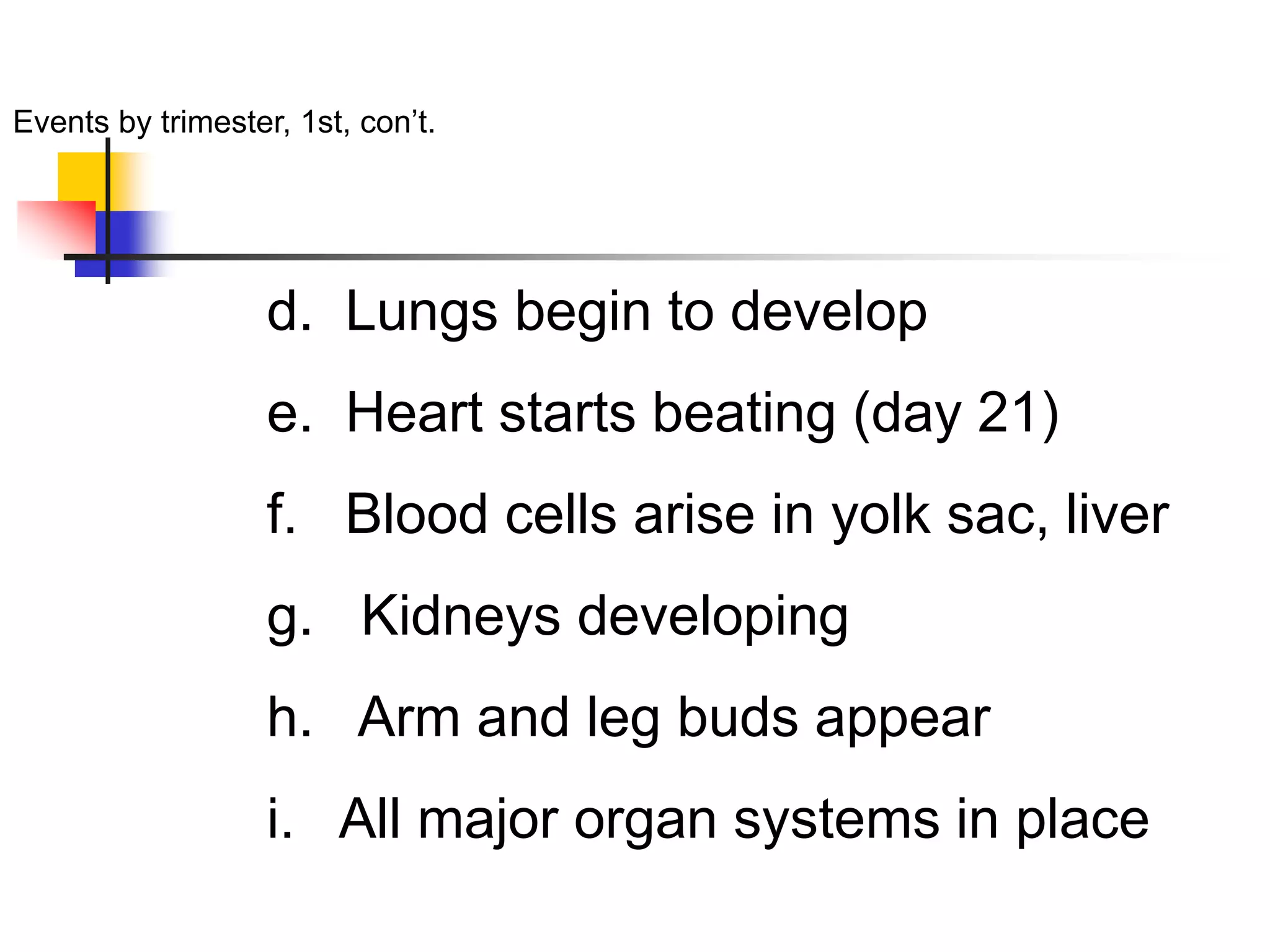
Embryology deals with human development from fertilization through the first 8 weeks, known as the embryonic period. Key processes include fertilization, cleavage, differentiation of the germ layers (ectoderm, endoderm, mesoderm), implantation, formation of the embryonic disc and germ layers, and development of the major organ systems. During the first trimester, the embryo develops most of its major structures. In the second trimester, growth and development of organs continues. The third trimester places increased demands on the mother as the fetus grows and develops further in preparation for birth.



![Embryology
A. Processes involved
1. Ovulation: release of ovum
2. Fertilization: union of sperm and
ovum
3. Mitosis of fertilized ovum
[zygote (2N)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyfinal-220829094849-81ad0509/75/Embryology-ppt-4-2048.jpg)








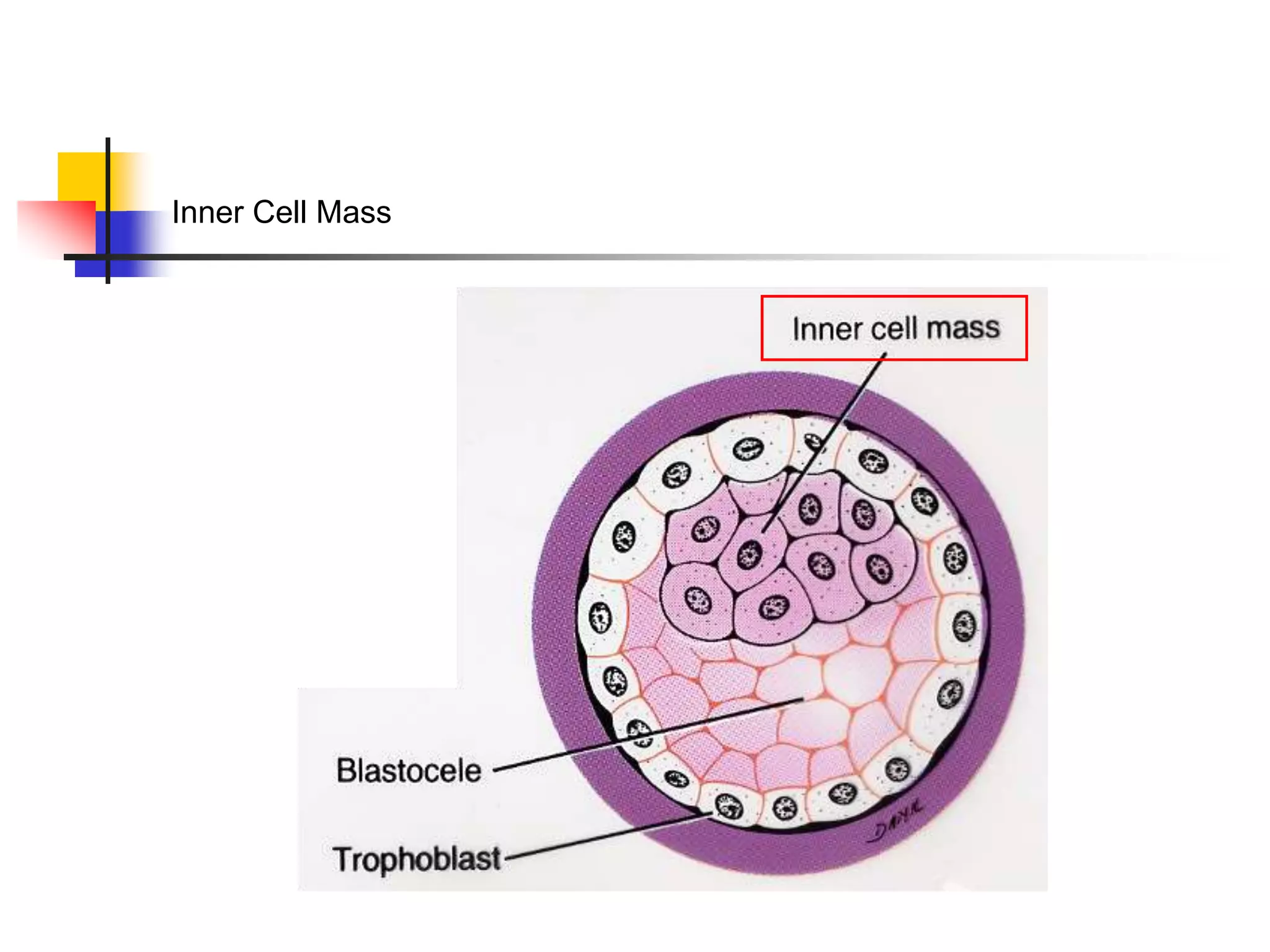









![3. Initial placental formation
a. Extraembryonic mesoderm
[from trophoblast cell division]
b. Trophoblast + mesoderm =
chorion
c. Projections grow from chorion
1. Chorionic villi
2. Form fetal part of placenta](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyfinal-220829094849-81ad0509/75/Embryology-ppt-24-2048.jpg)



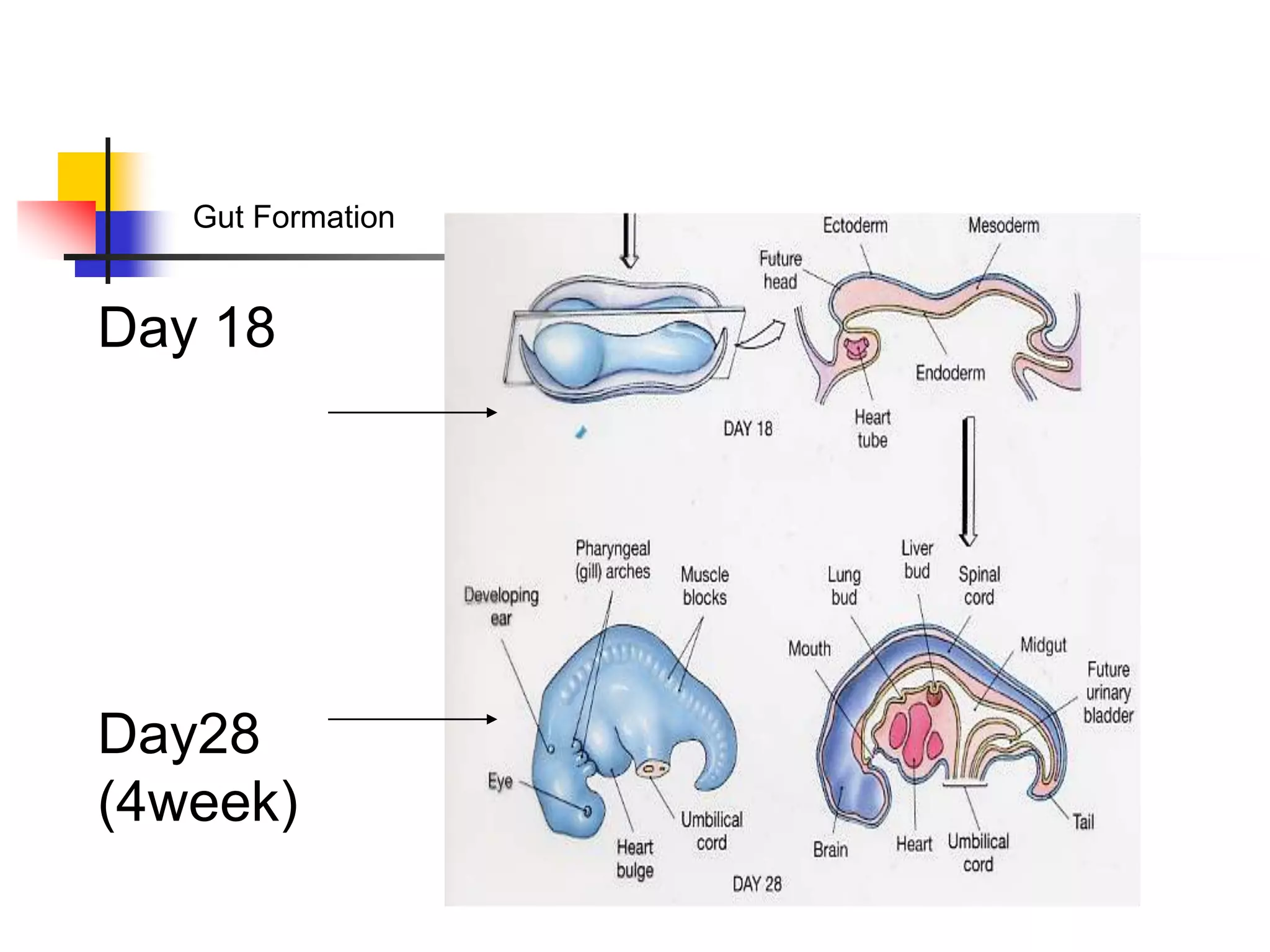



![c. Somites
1. Thickened mesoderm lying on
either side of notochord
[Notochord: axis of vertebral development]
2. Primary segmentation
3. Forms muscles, skeleton](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyfinal-220829094849-81ad0509/75/Embryology-ppt-32-2048.jpg)