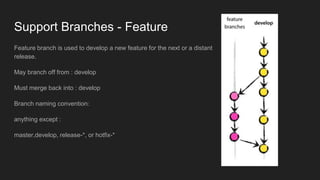
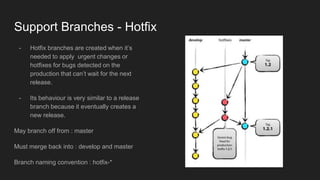
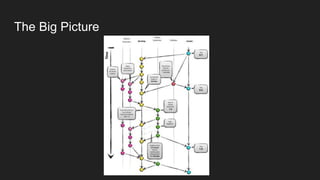
This document outlines a Git branching model to allow for smooth development with isolated features. The model uses main branches of master and develop, and support branches of feature, release, and hotfix. Feature branches isolate new work and merge back to develop. Release branches prepare releases and merge to both develop and master. Hotfix branches address urgent bugs in master and also merge to both develop and master. This model aims to allow multiple developers to work independently while reducing conflicts and enabling flexible releases and rollbacks.