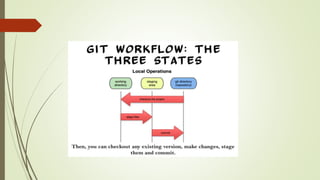
Git is a version control system that allows users to track changes to files over time. It allows users to revert files or entire projects to previous states, see who made changes and when, and compare changes over time. Basic Git commands include clone to copy a remote repository locally, commit to submit files to the local repository, fetch/pull to update from a remote repository, and push to submit code to a remote repository. Users configure Git with their username and email and initialize repositories locally with git init. Files are added to repositories with git add before committing changes.