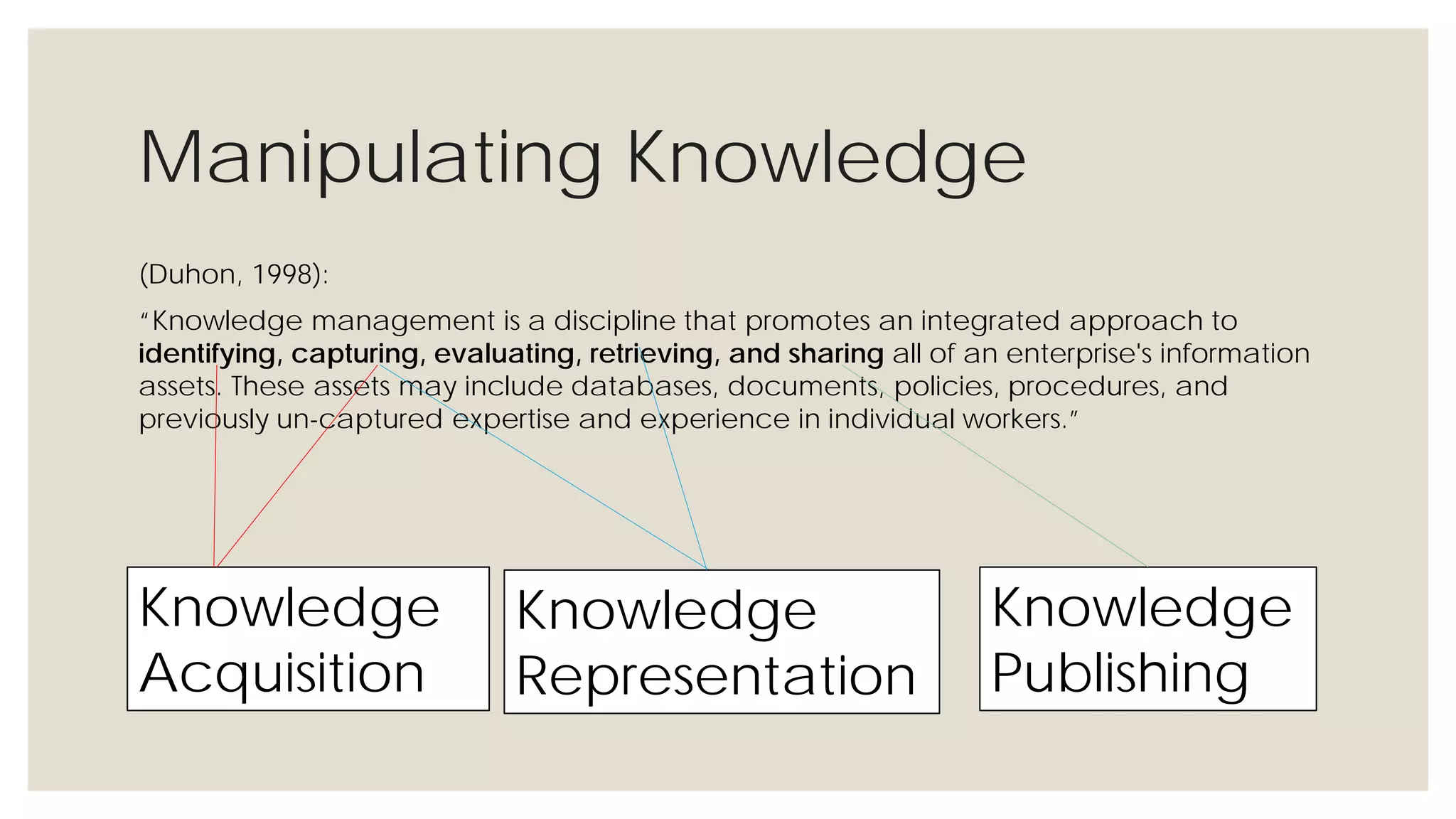
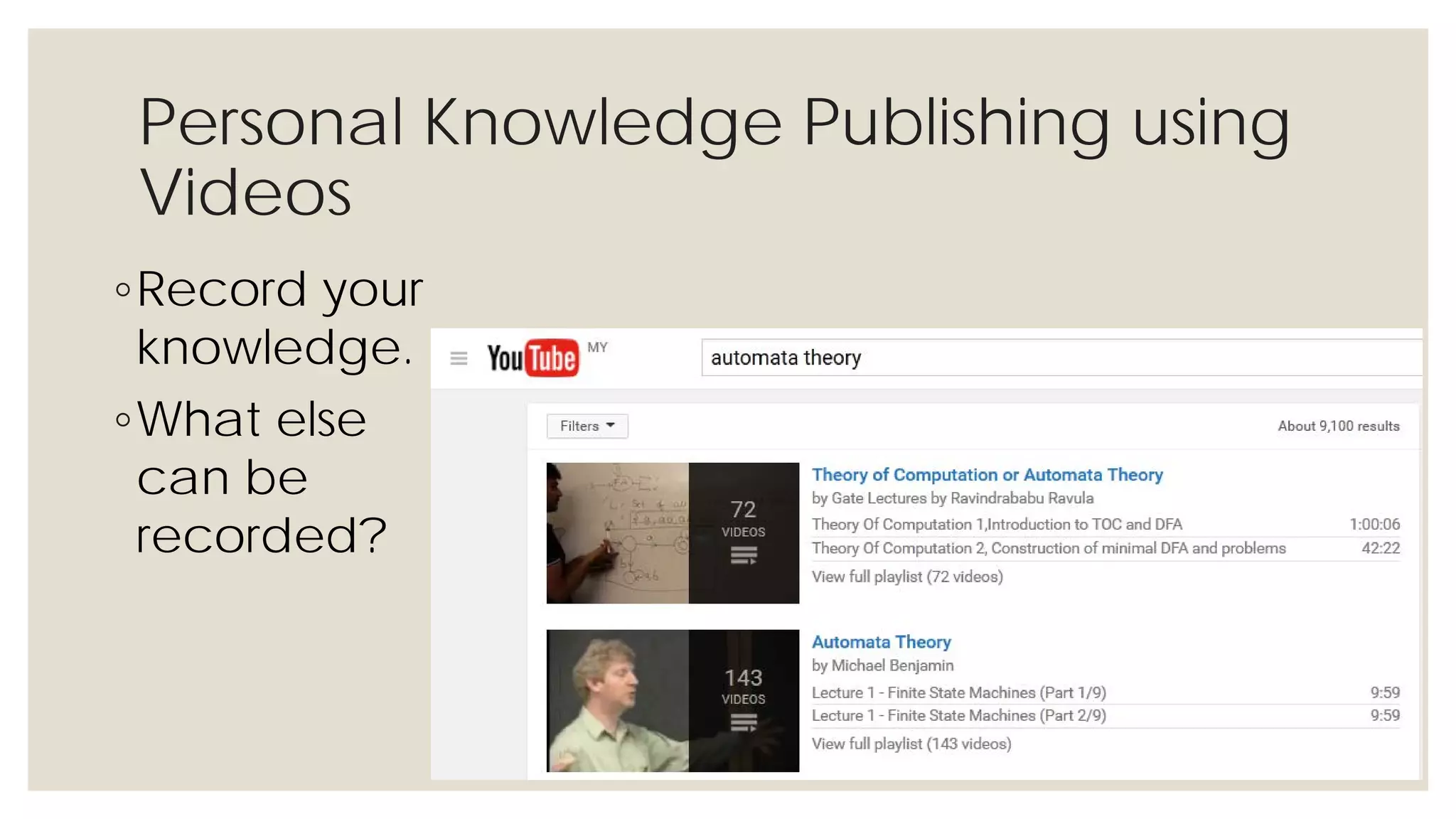
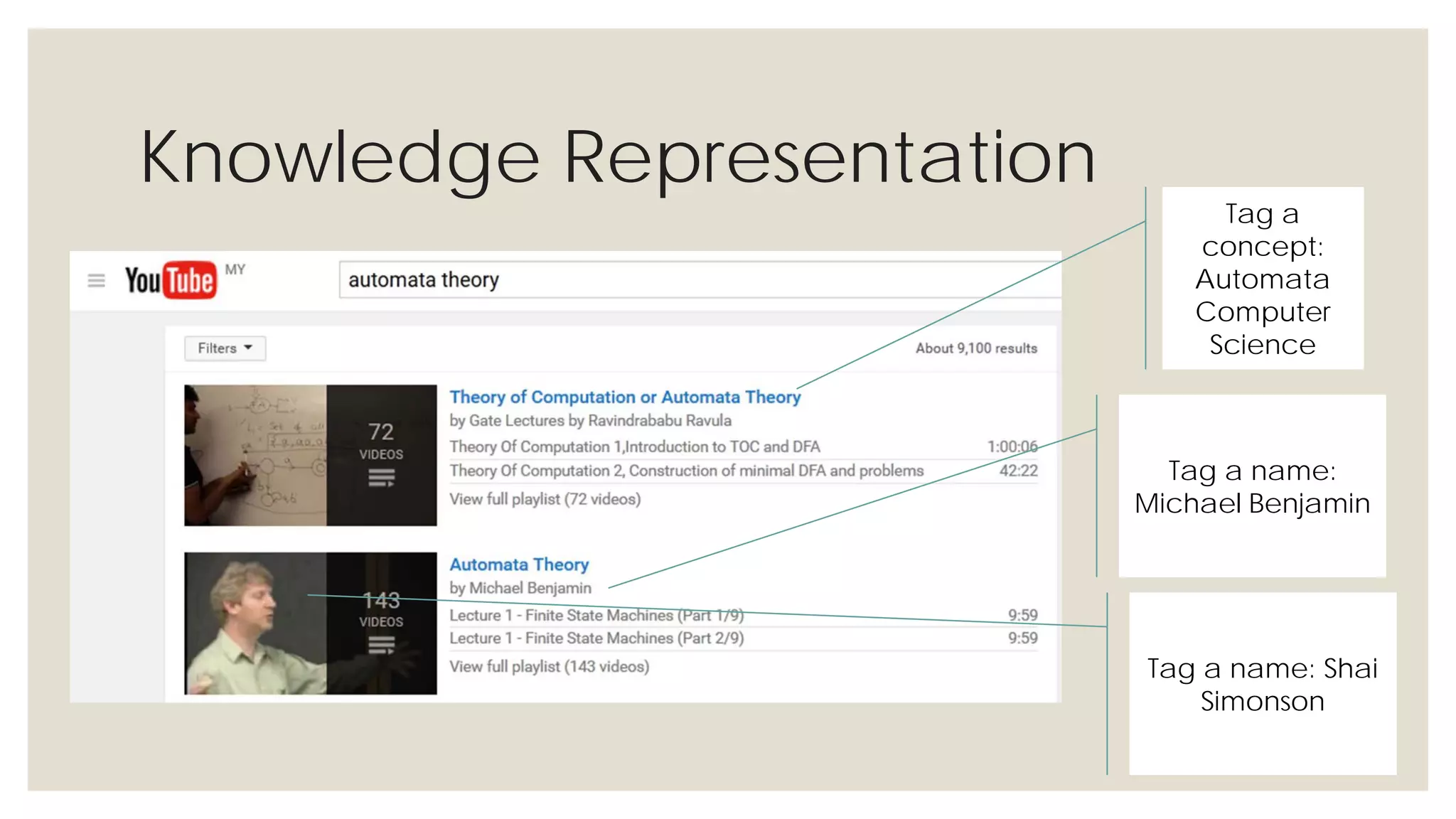
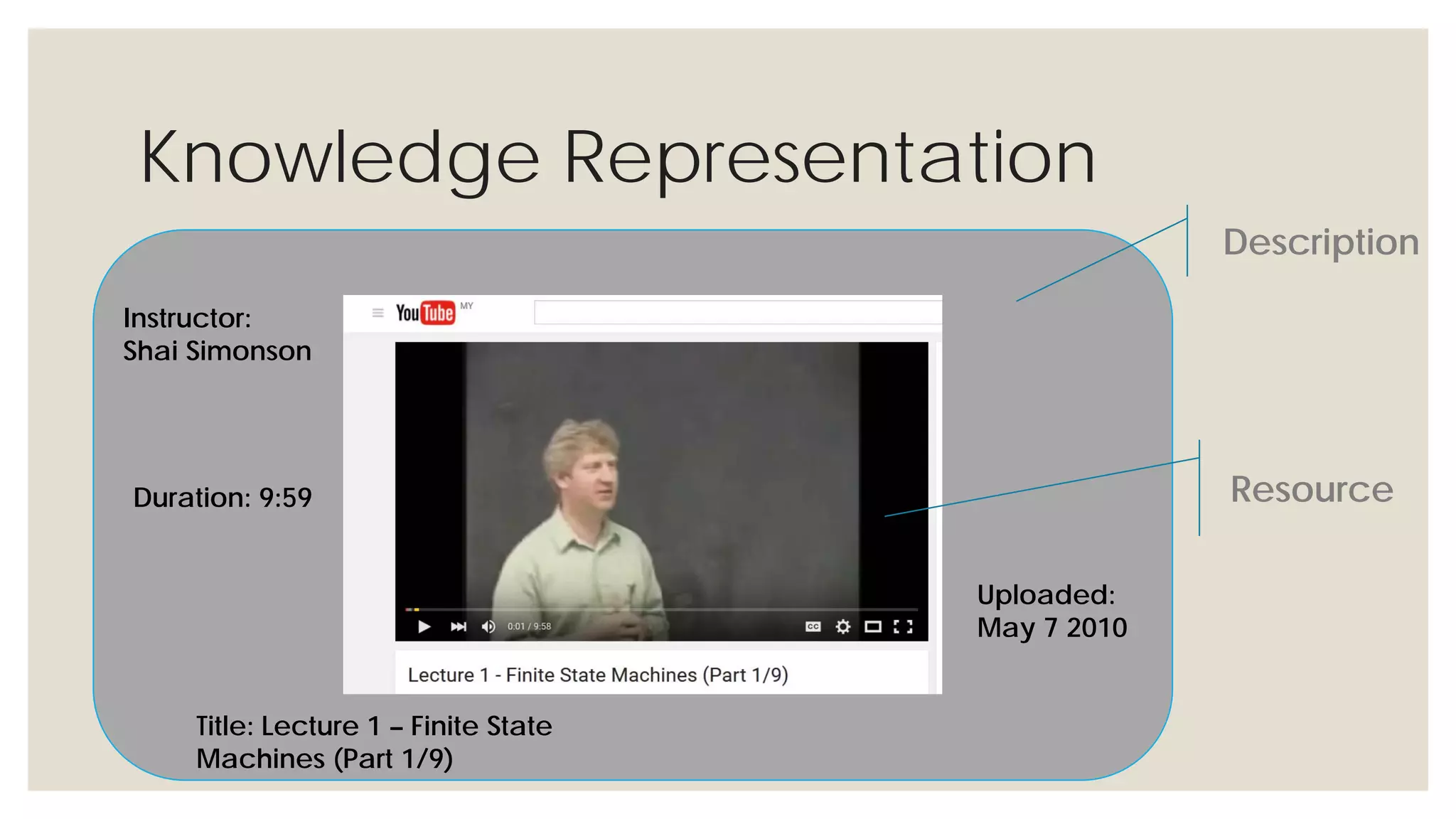
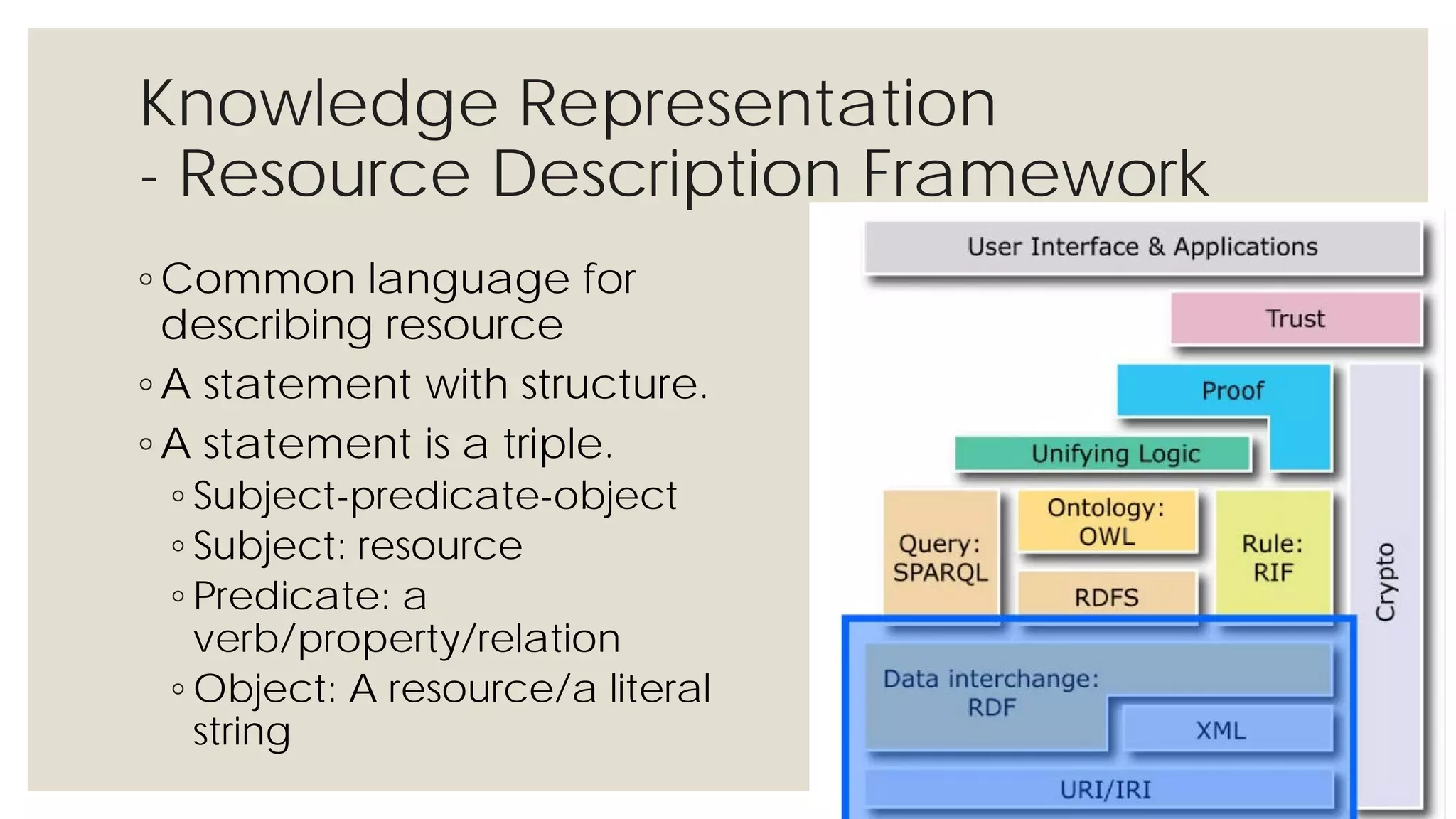
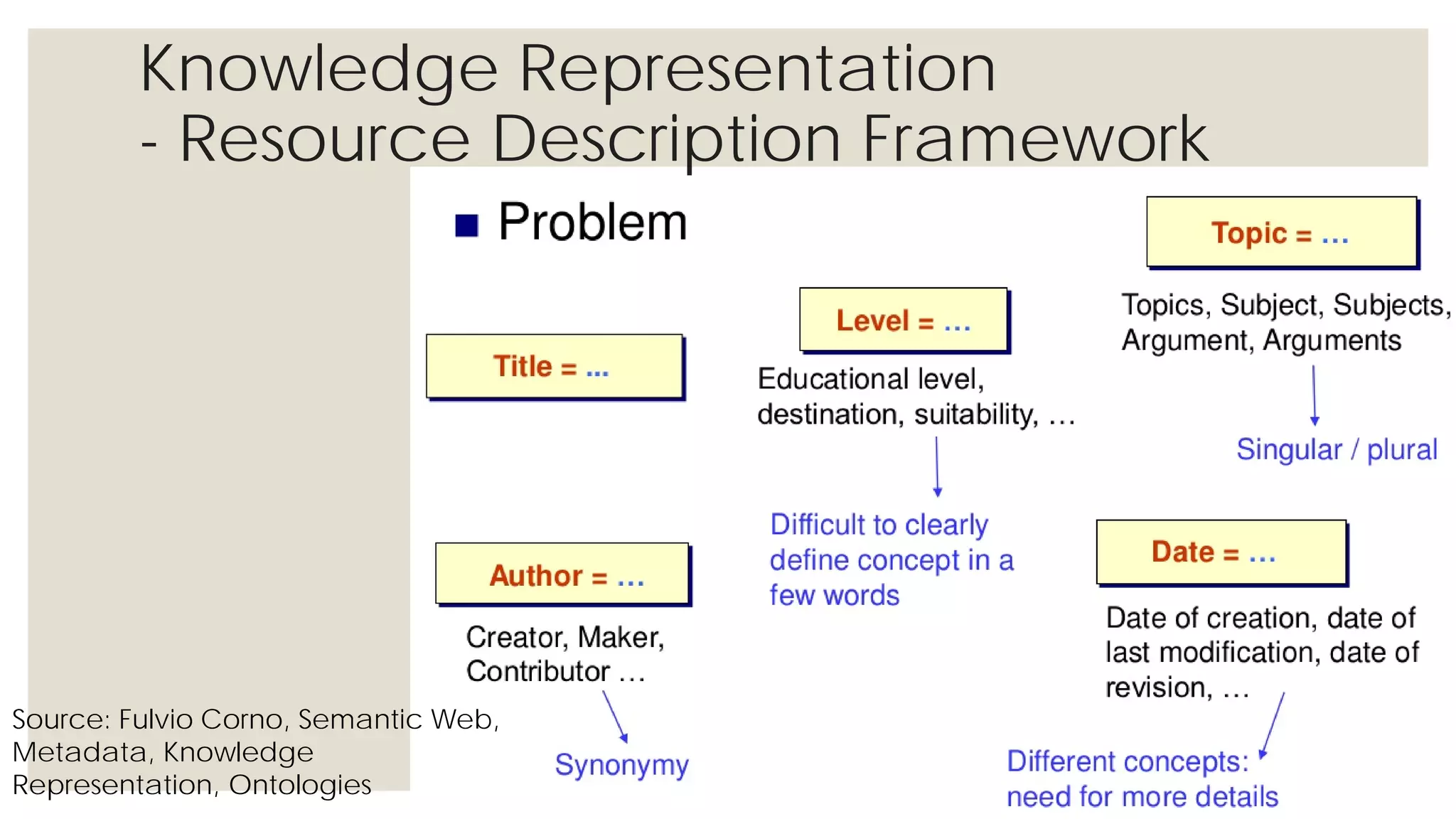
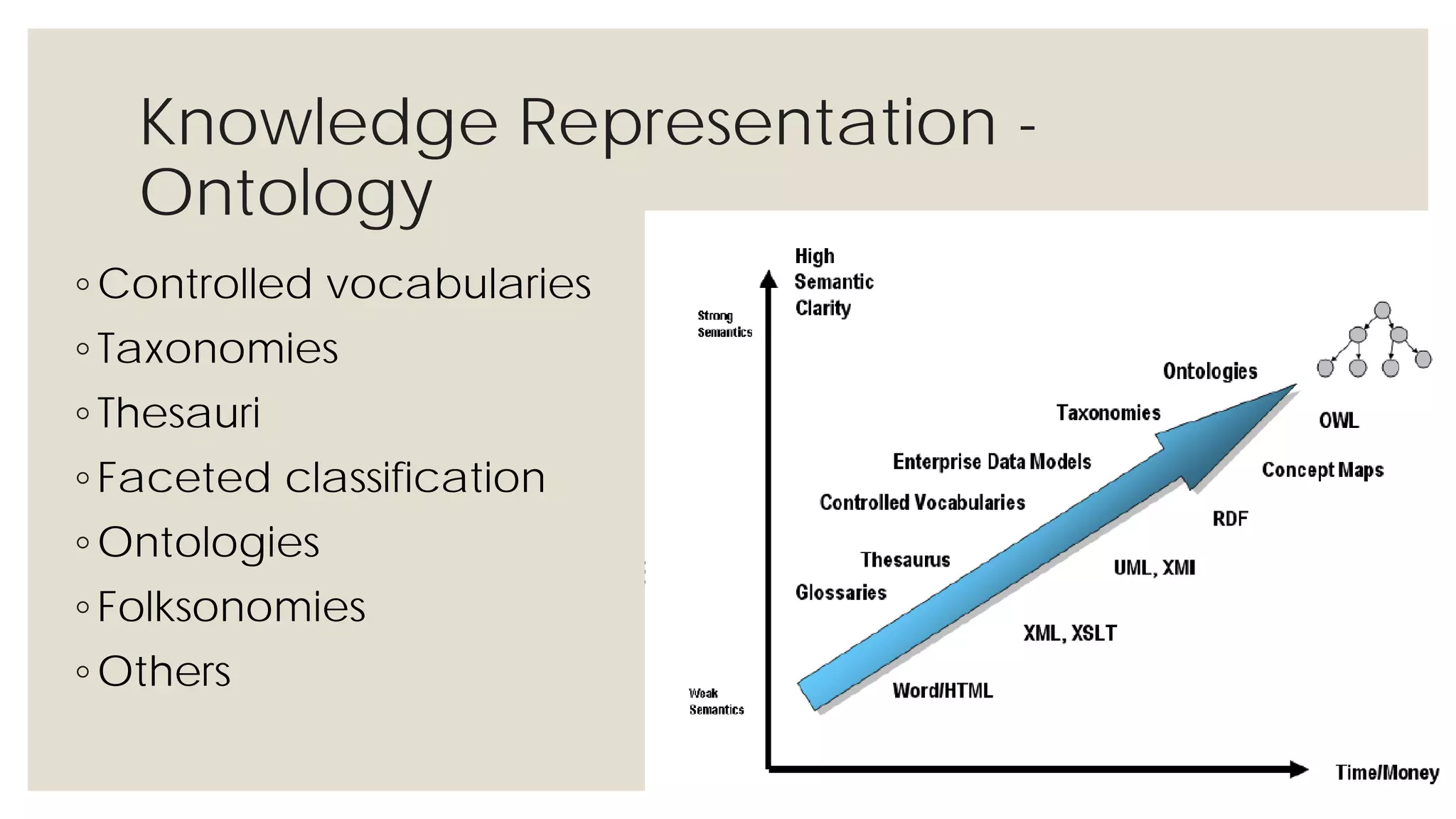
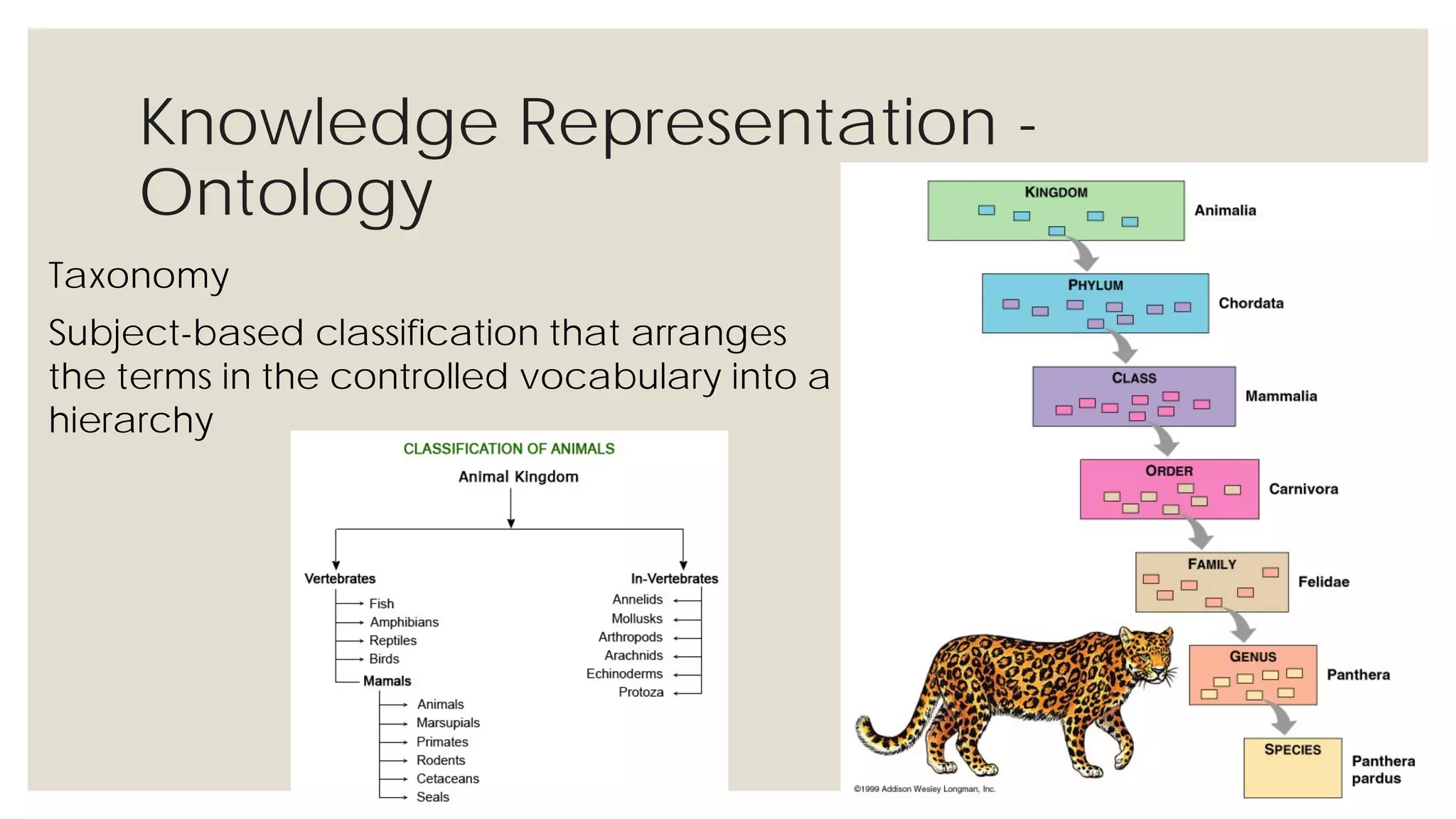
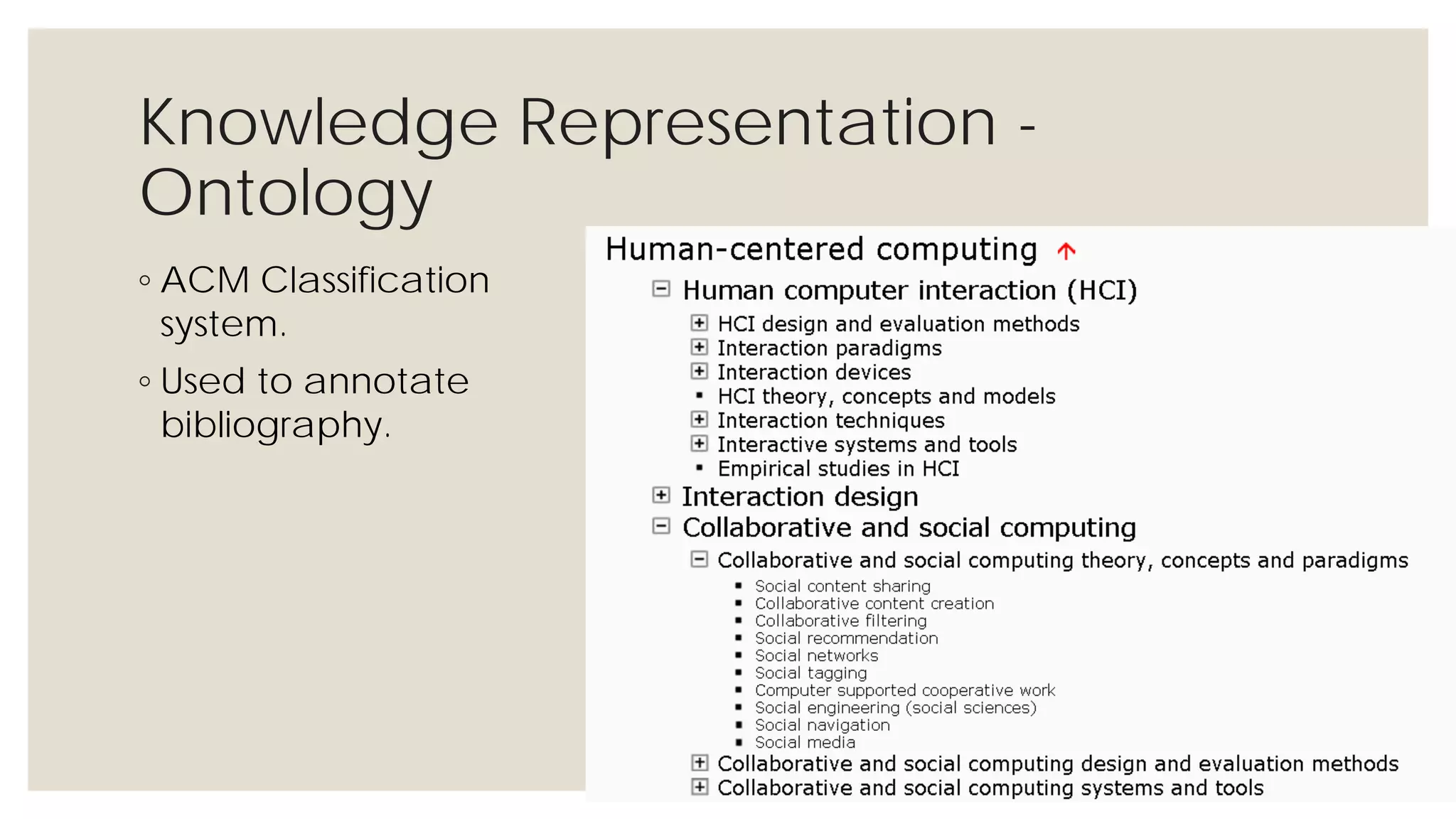
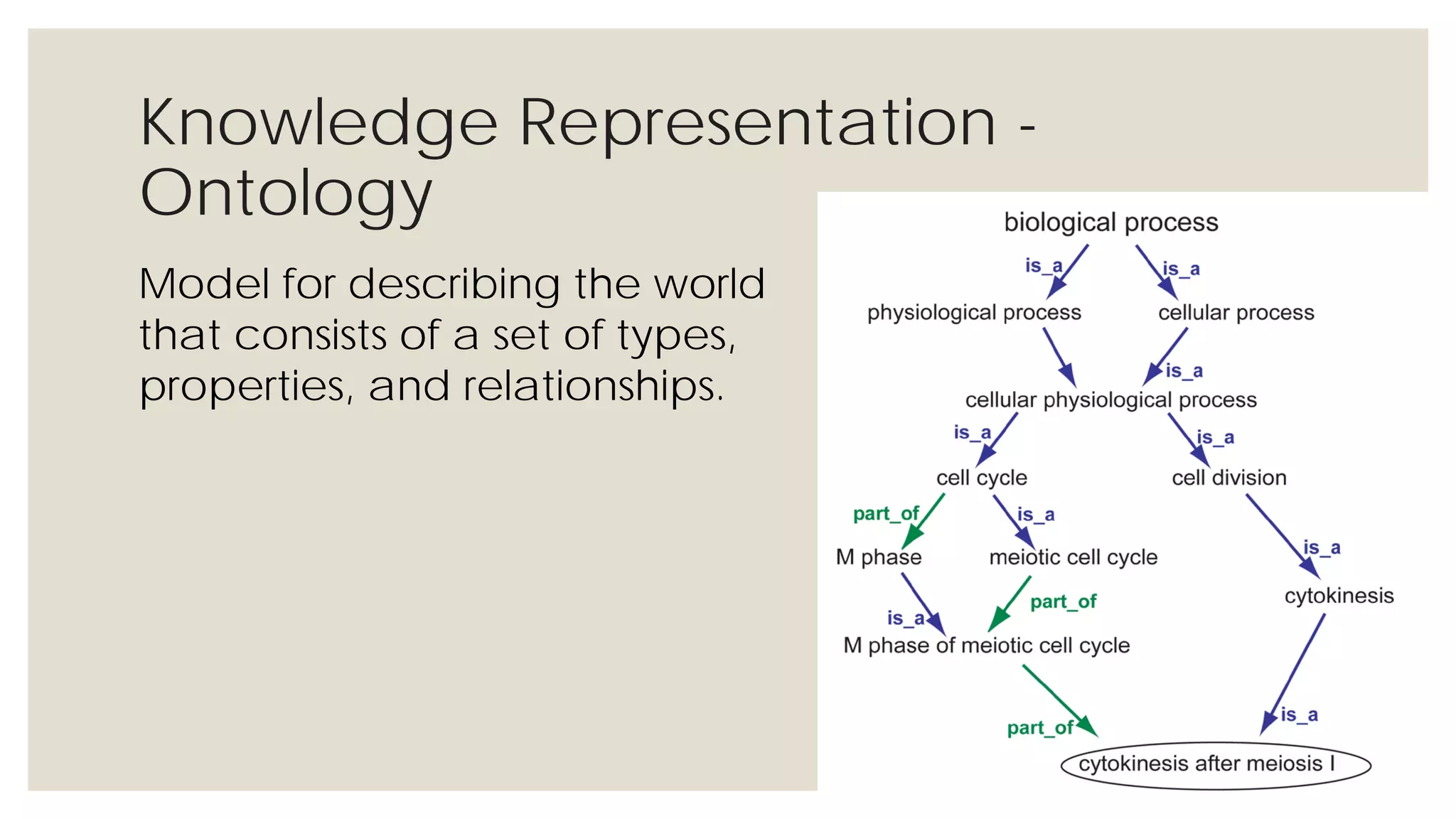
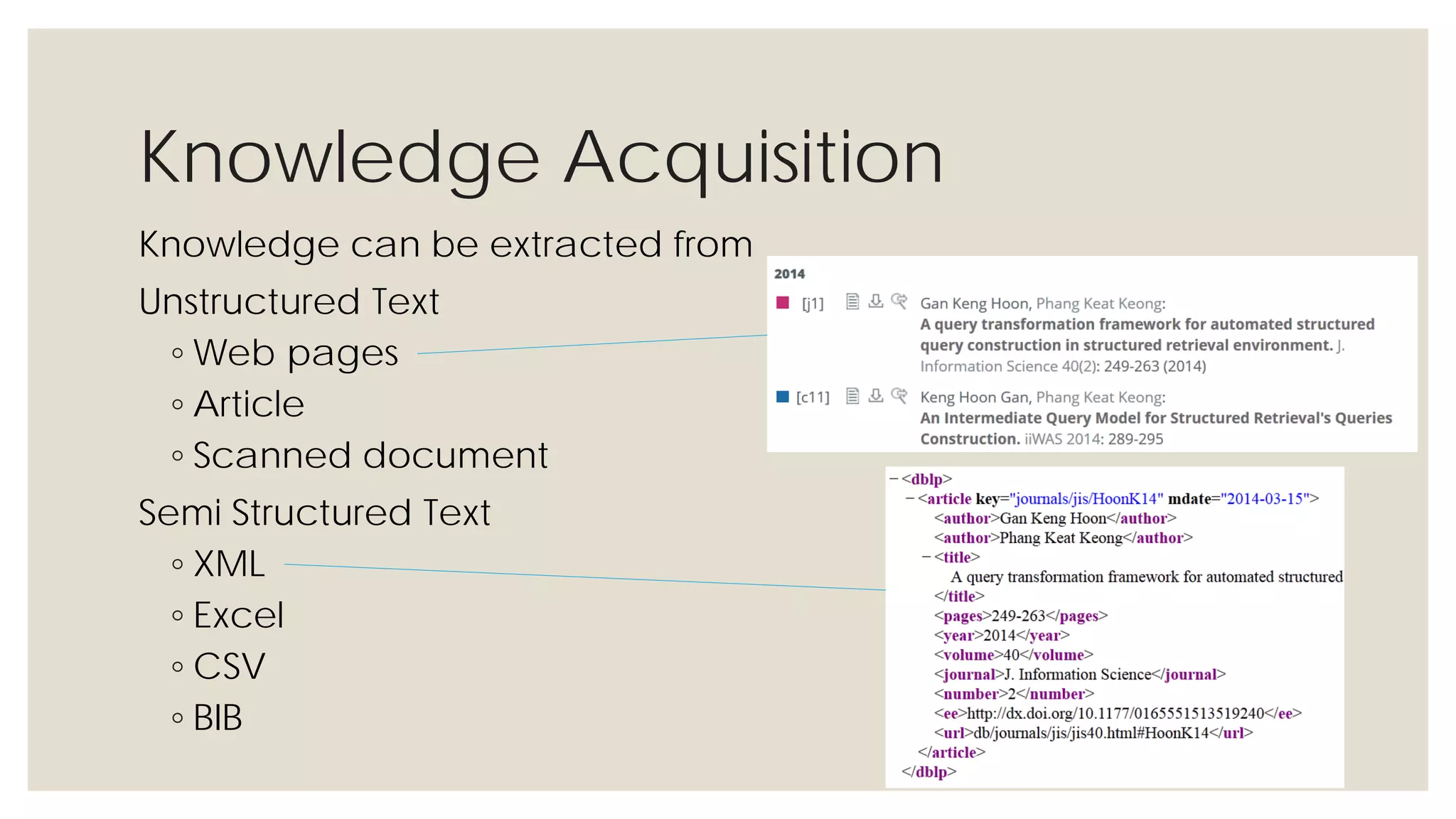
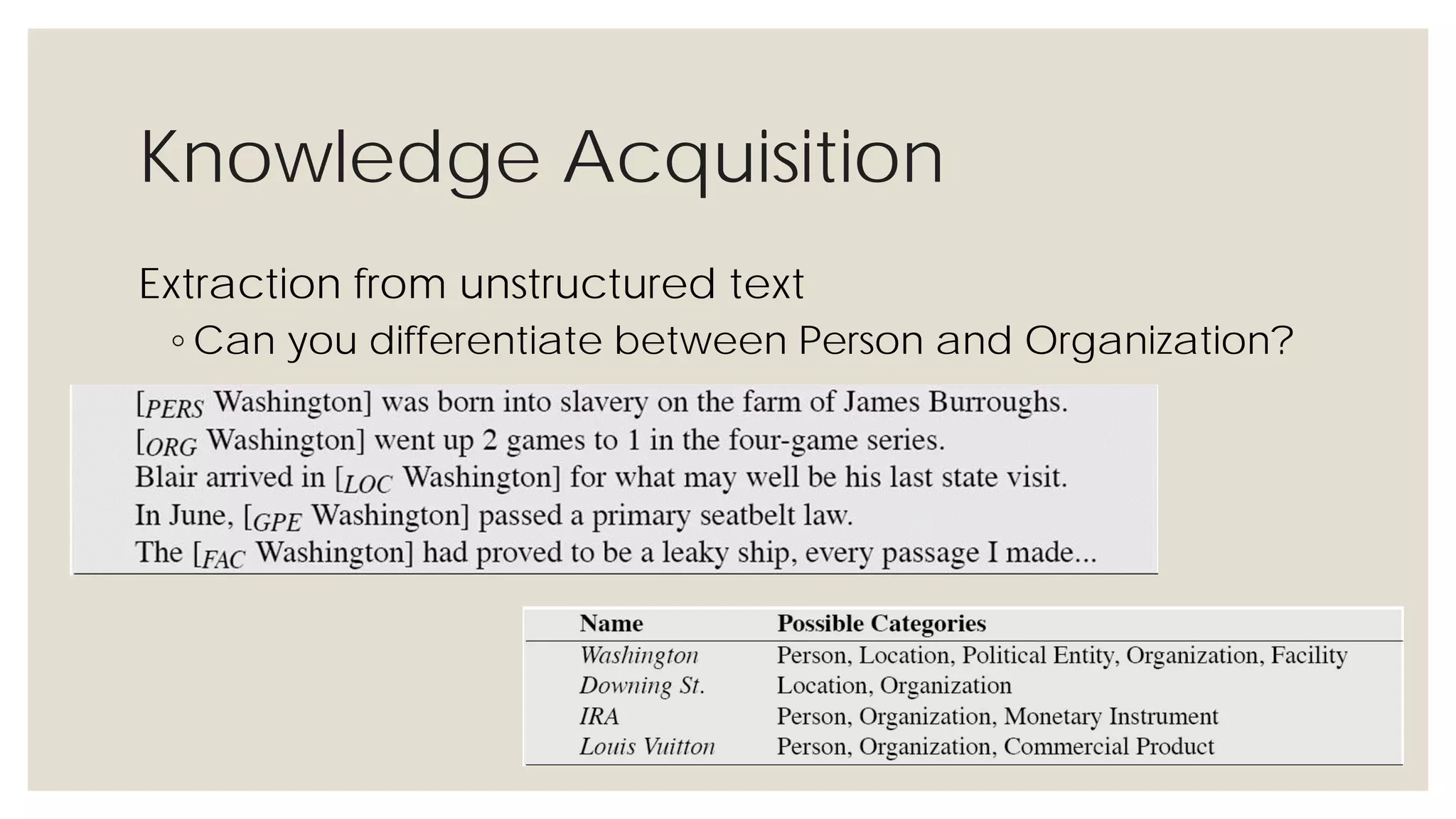
This document provides an overview of knowledge acquisition, representation, and publishing. It defines knowledge and discusses how knowledge can be captured, structured, and shared. Knowledge acquisition involves extracting knowledge from sources, structuring the knowledge, and organizing it for representation. Knowledge representation standards like the Resource Description Framework (RDF) and ontologies provide structured descriptions of knowledge through semantic annotations and metadata. Personal knowledge publishing allows individuals to share their knowledge through various online tools and formats.