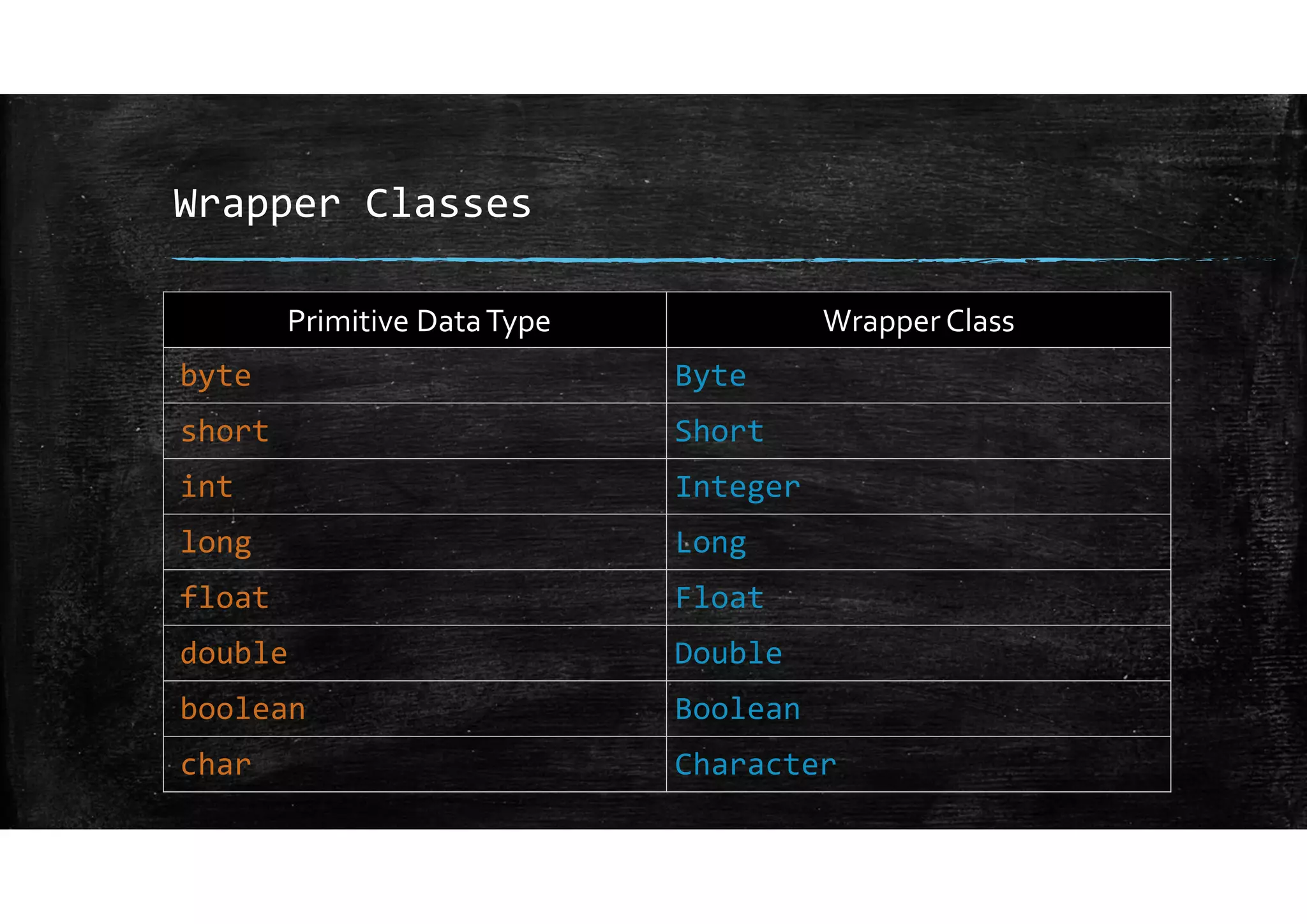
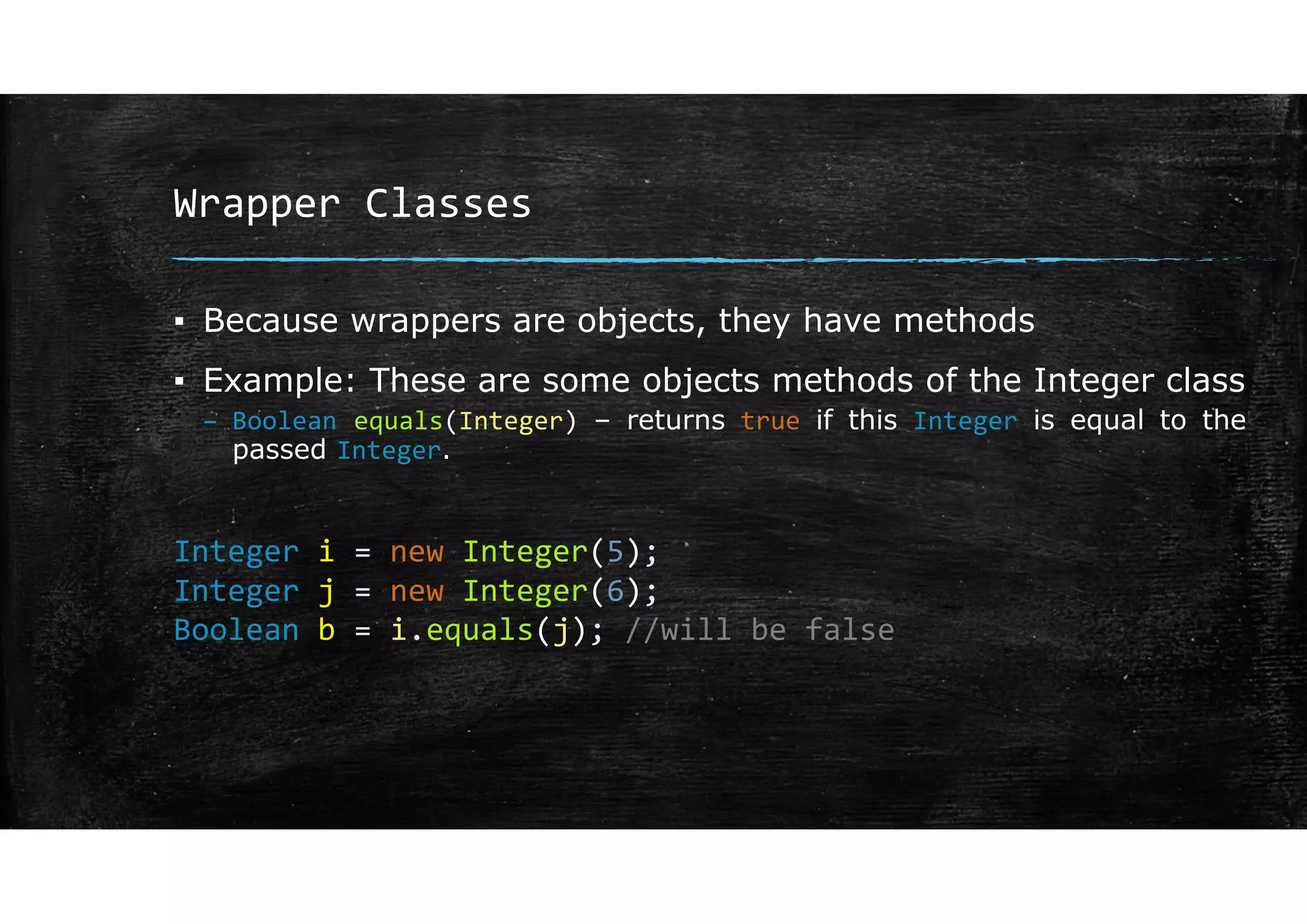
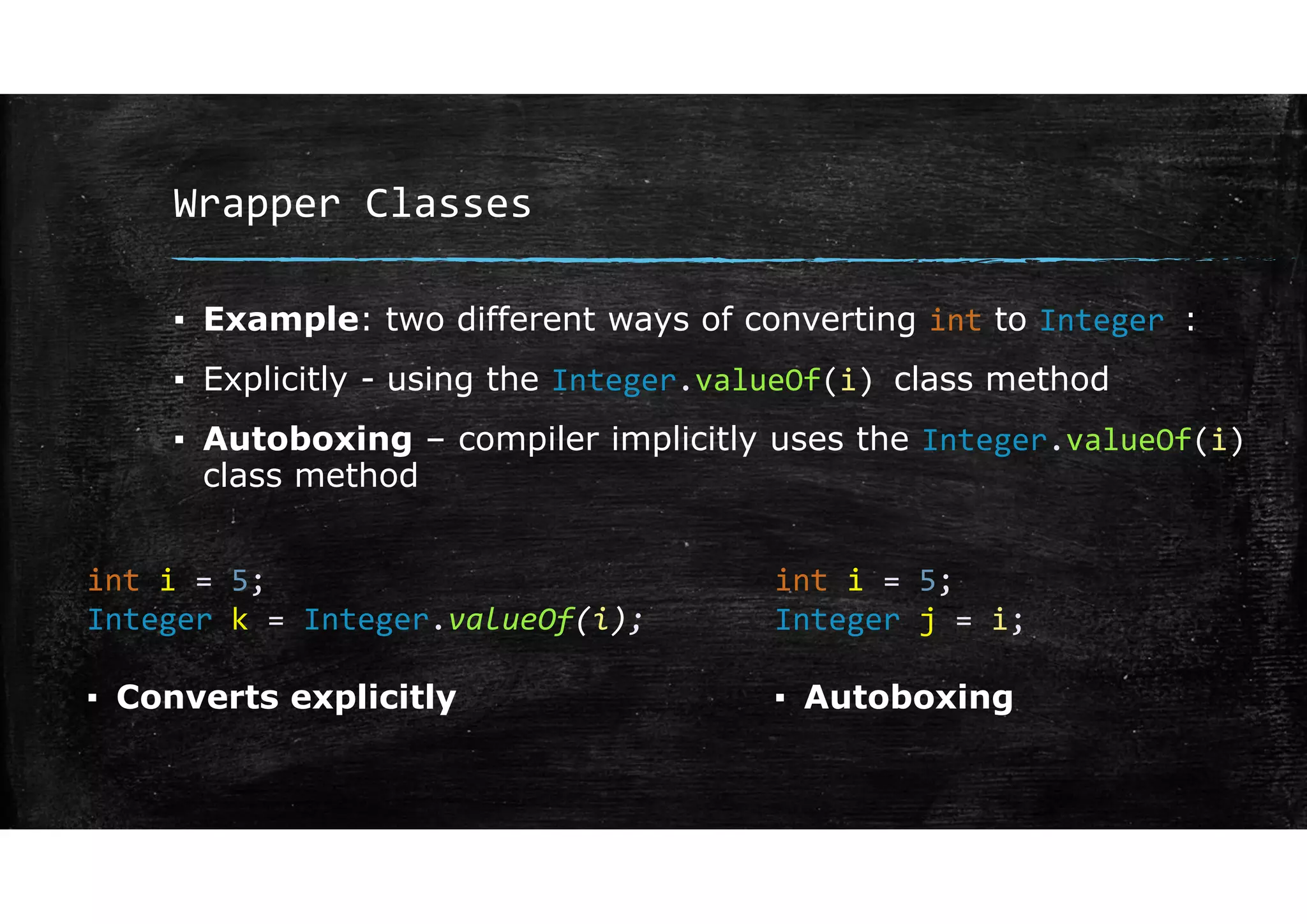
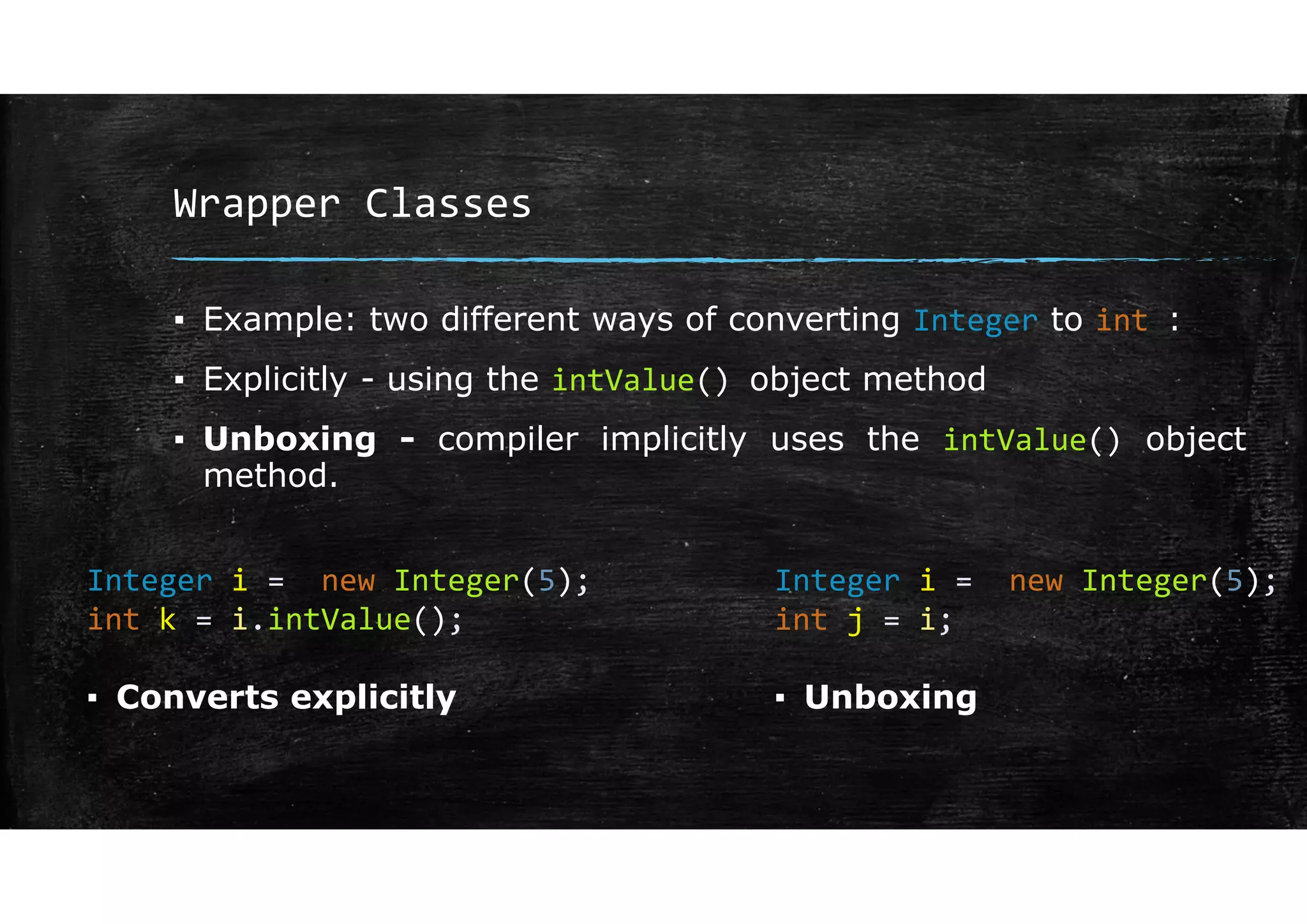
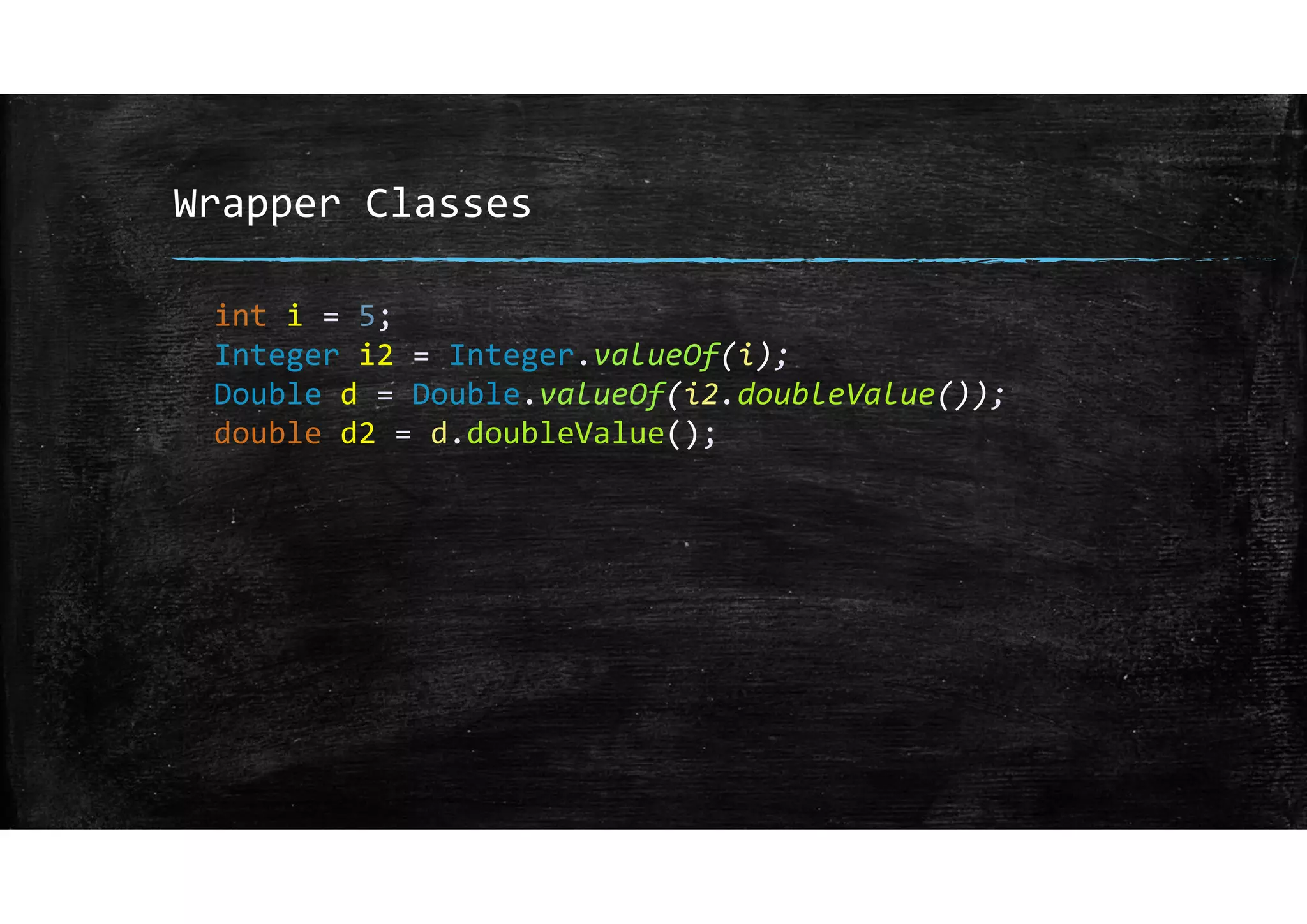
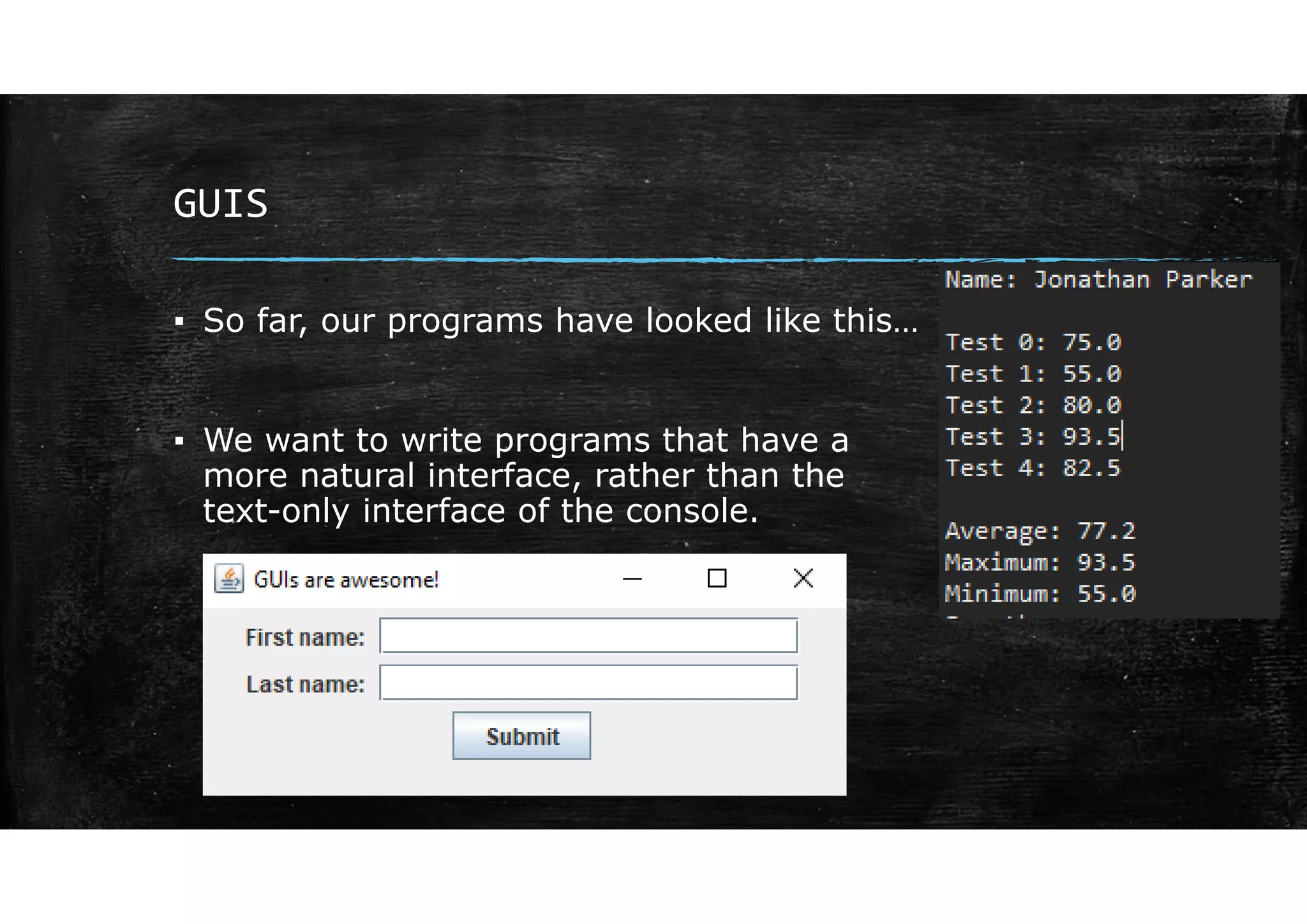
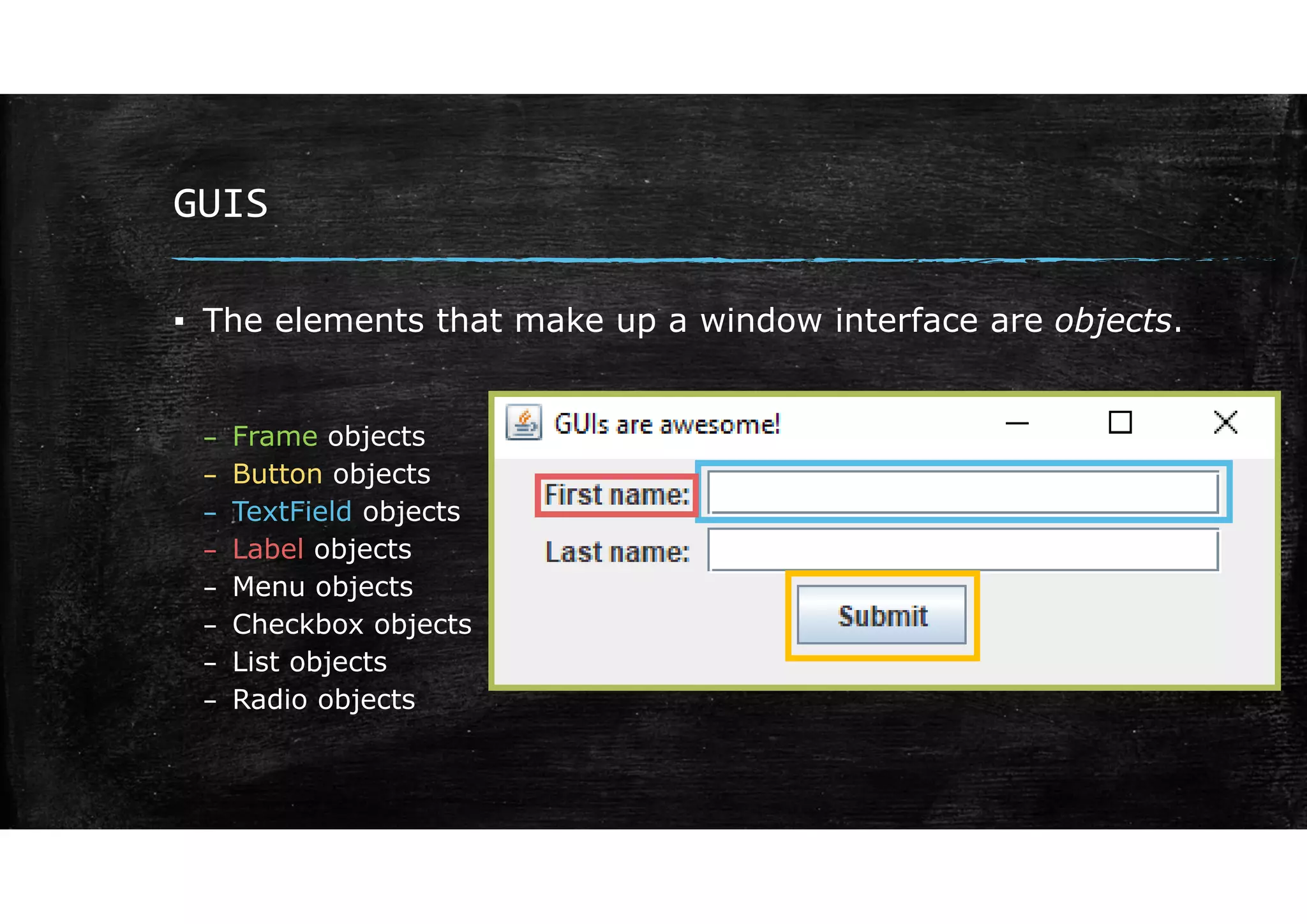
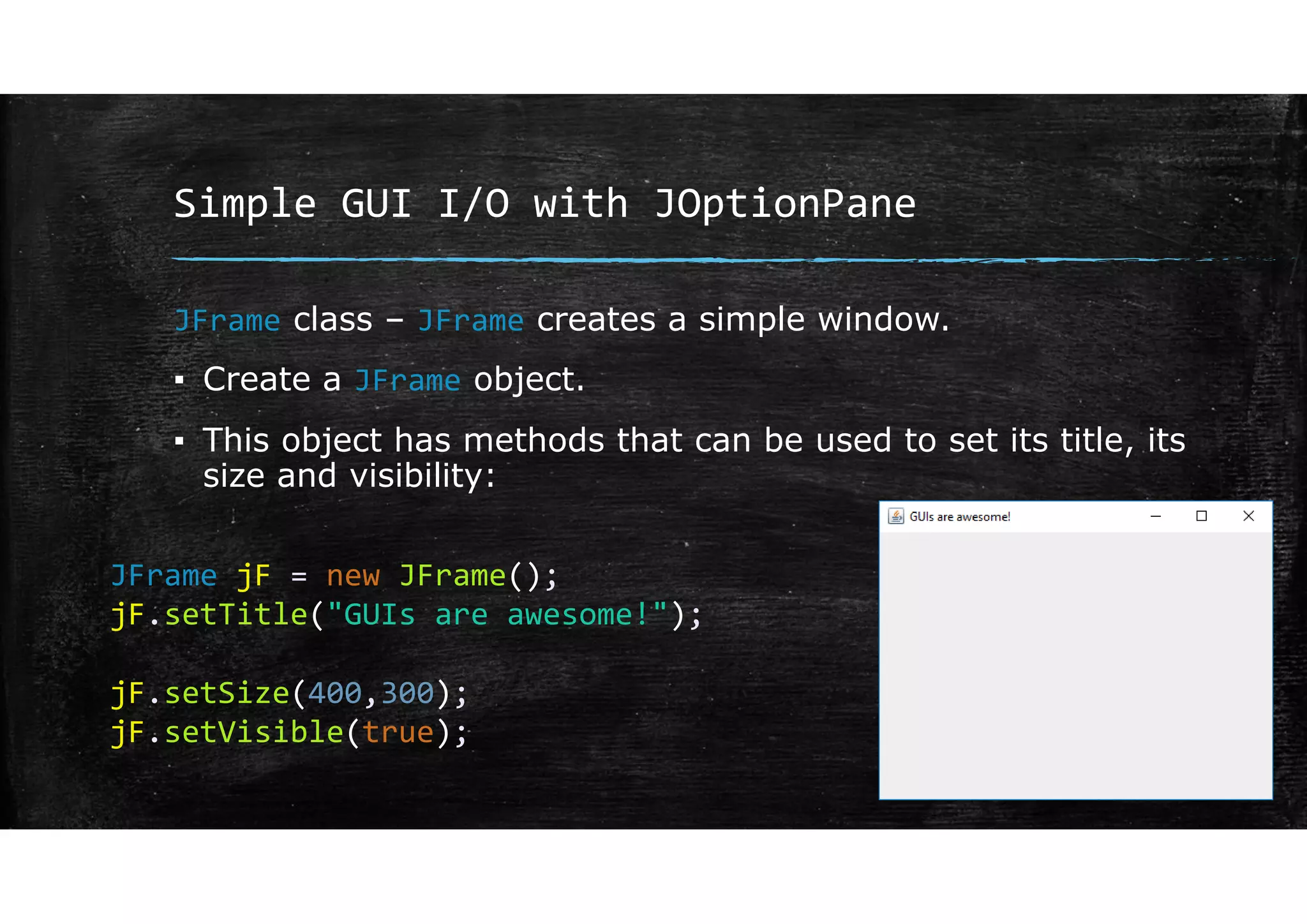
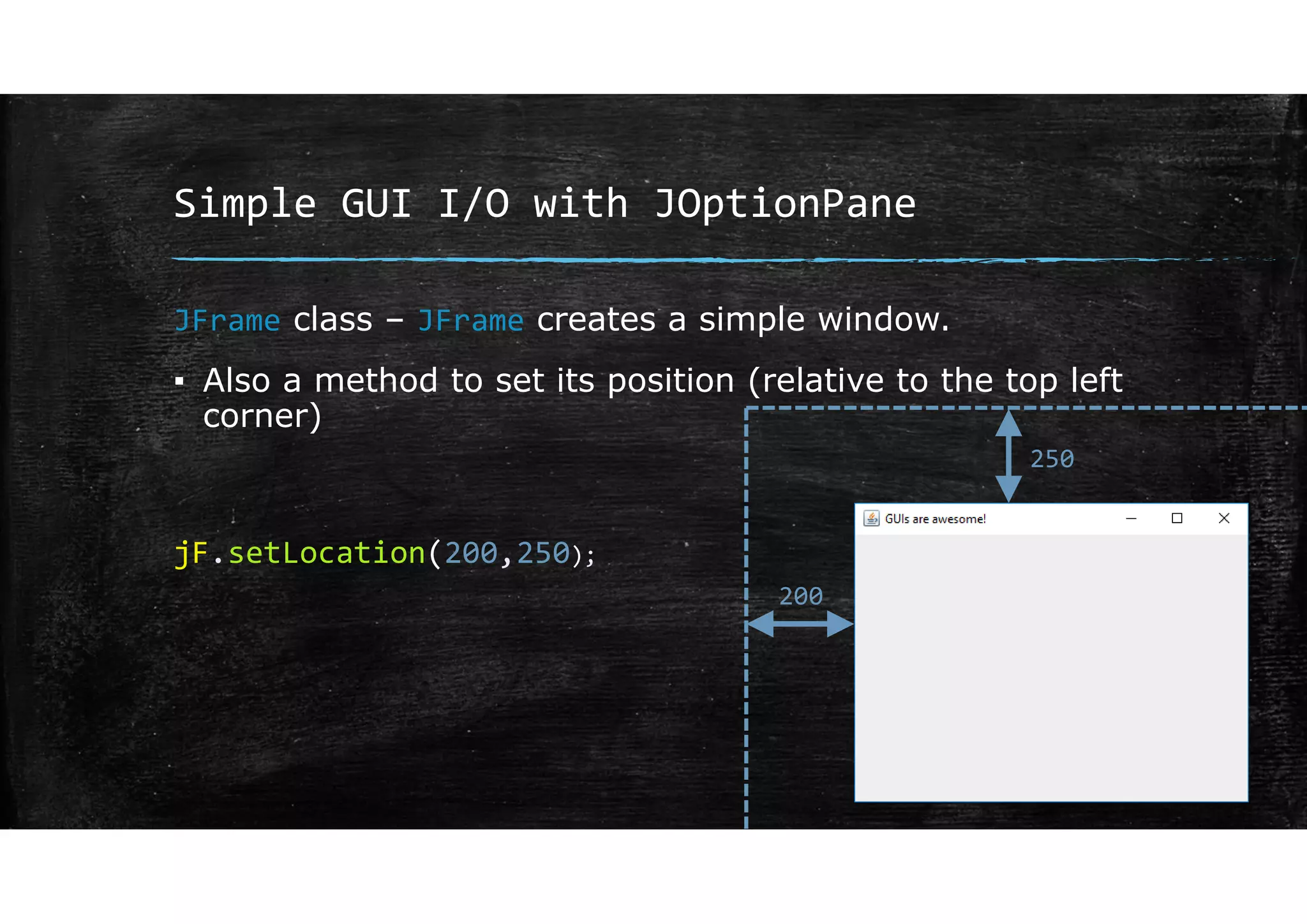
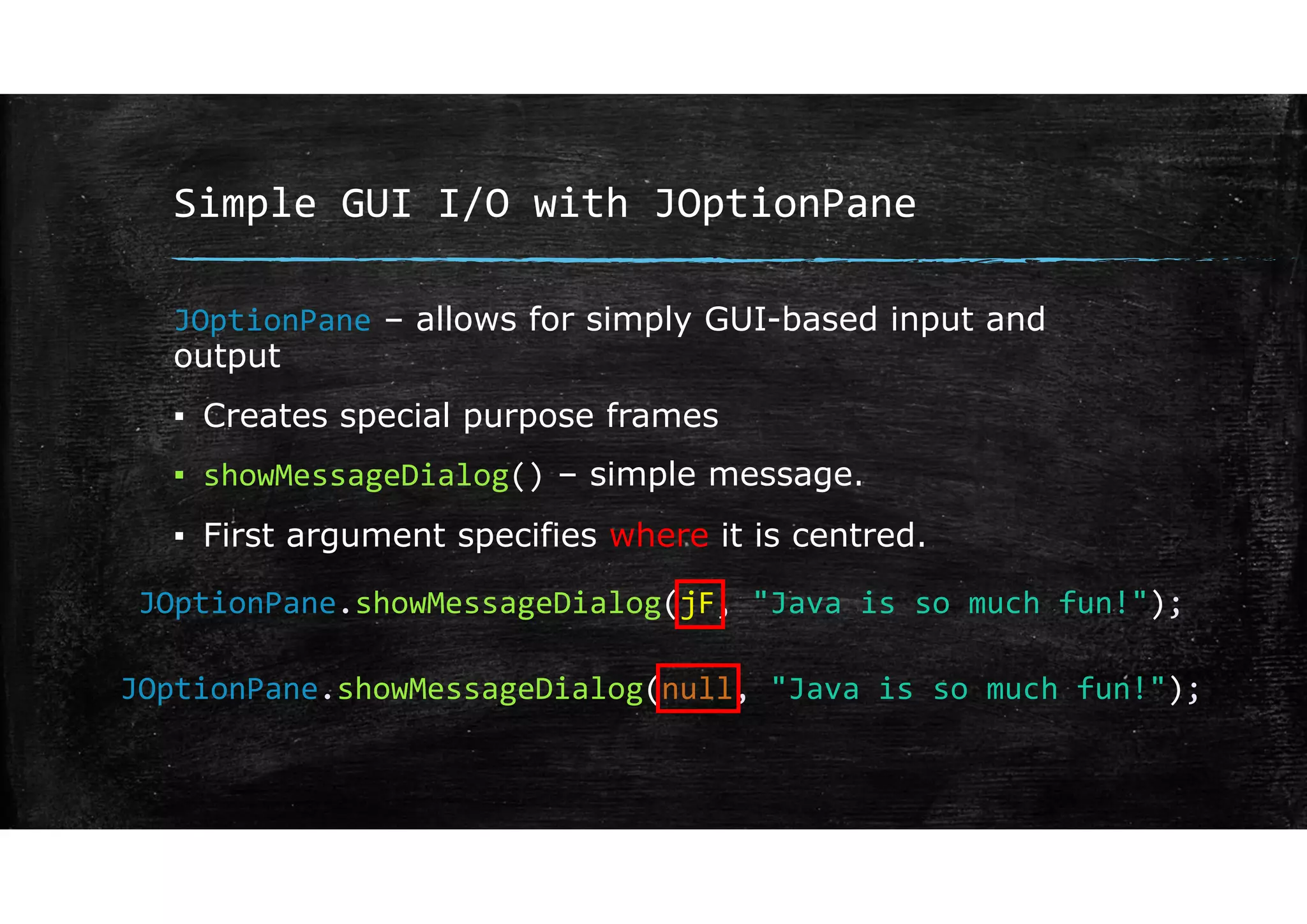
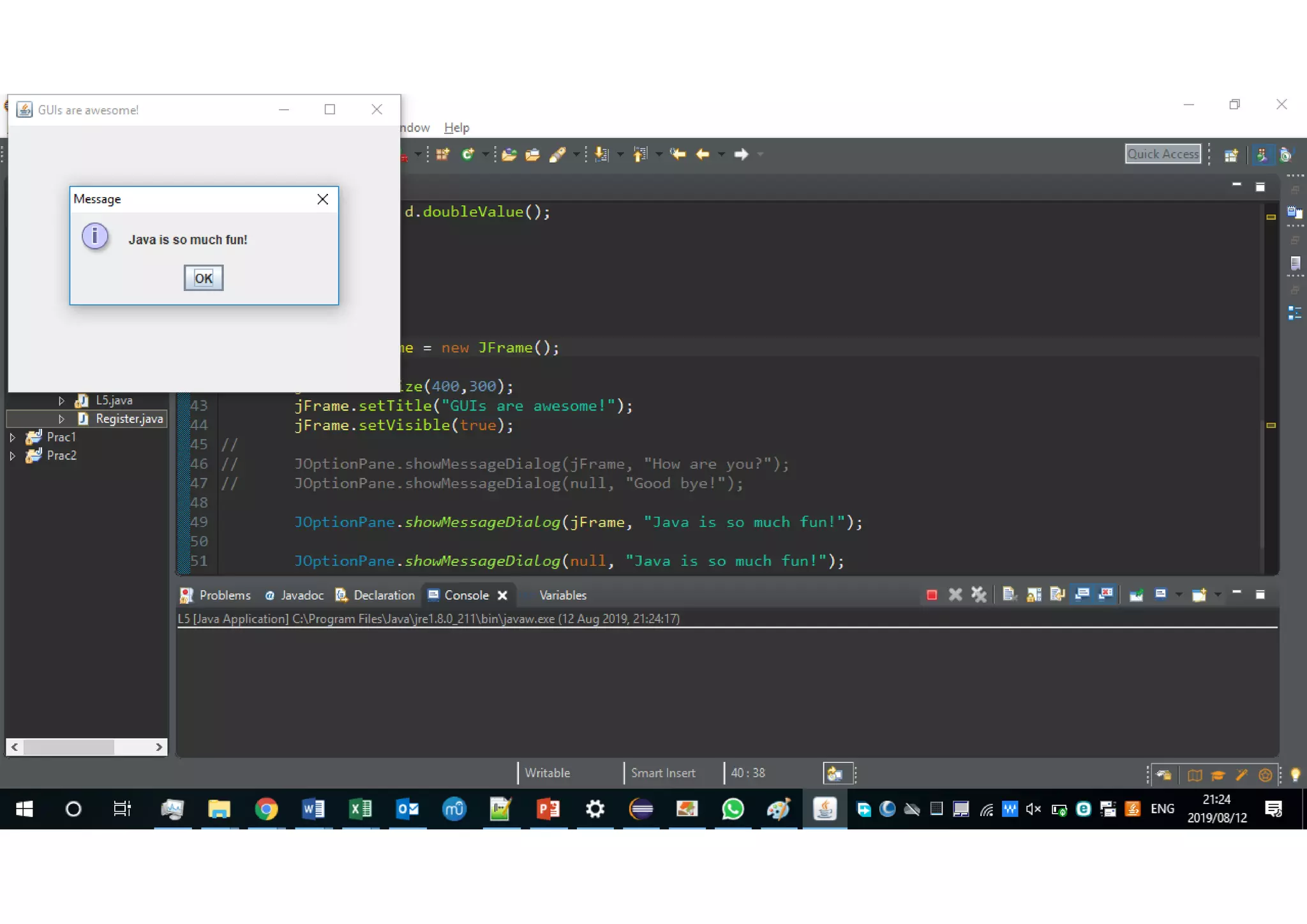
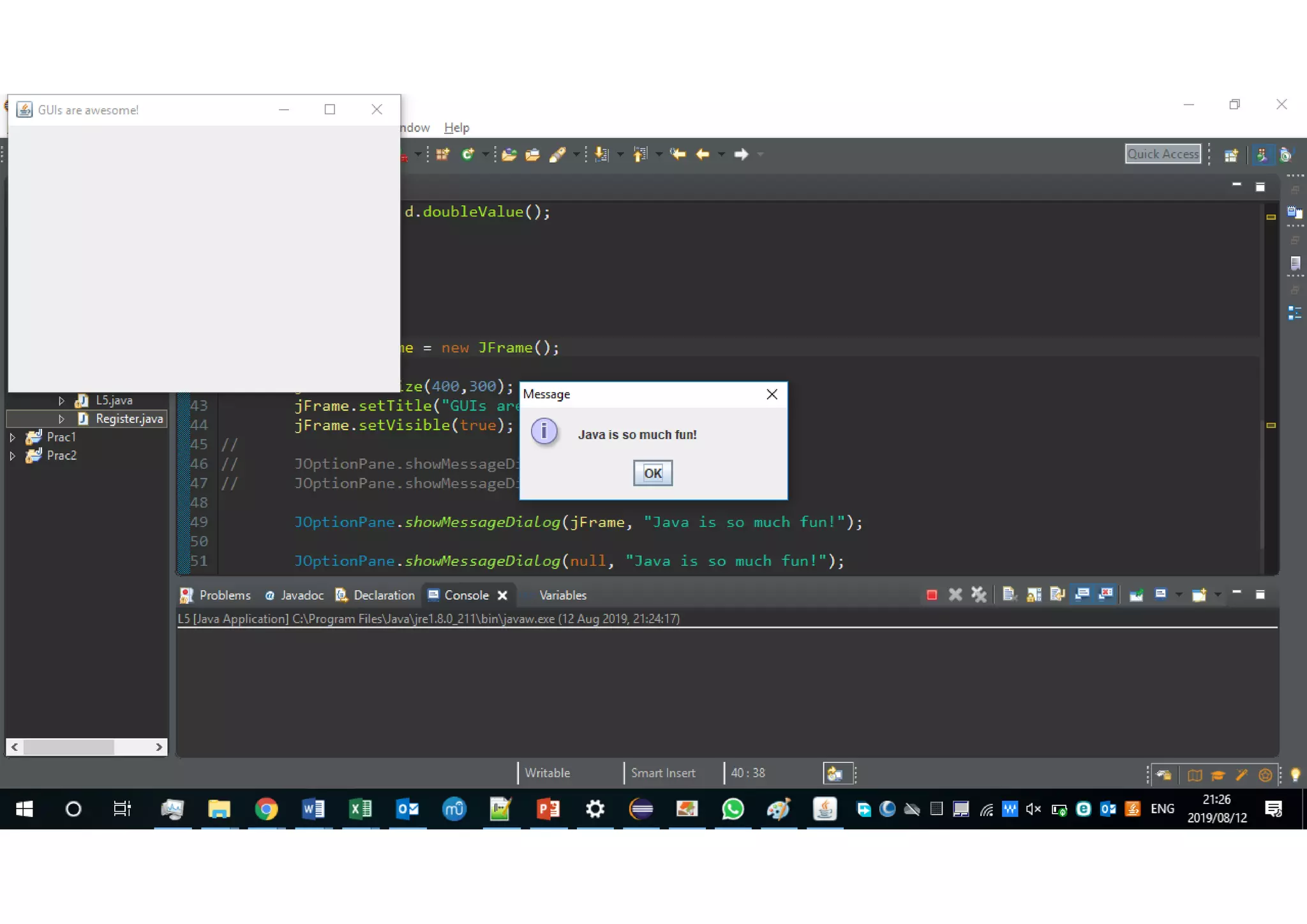
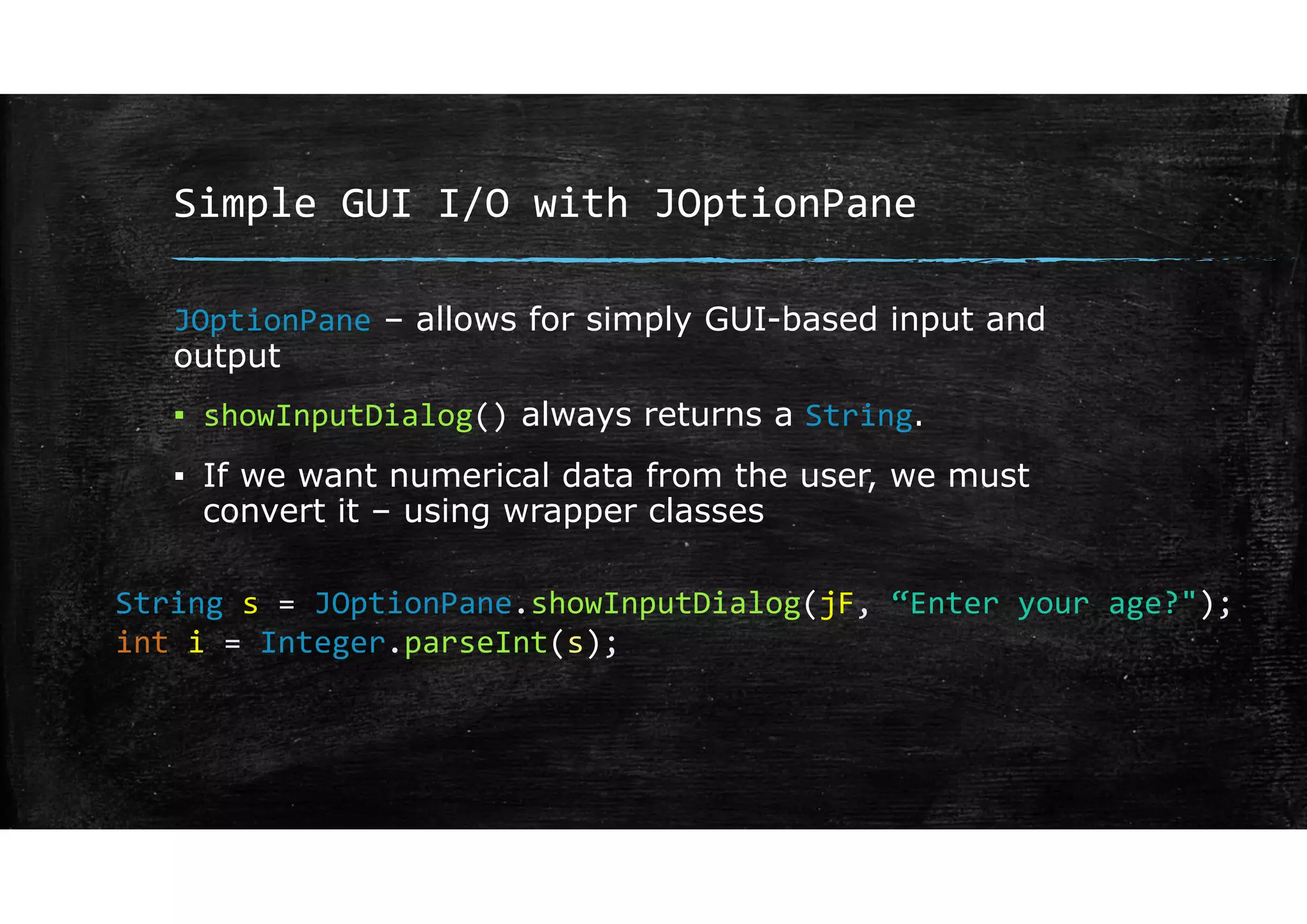
Wrapper classes allow primitive data types like int and double to be used as objects. Each primitive type has a corresponding wrapper class like Integer and Double. Wrapper classes allow primitive values to be passed by reference rather than by value. GUIs can be created using Swing components like JFrame for windows and JOptionPane for simple input/output dialogs. Components are added to the content pane of the JFrame to build the GUI interface.