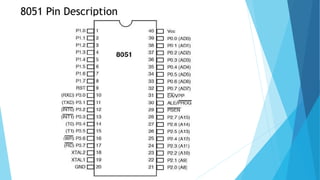
A microcontroller is a small, low-cost microcomputer designed to perform specific tasks in embedded systems. The 8051 microcontroller contains a processor, memory (RAM, ROM), serial ports, peripherals (timers, counters), and is commonly used in devices like microwaves and remote controls. It has 4 I/O ports that can be configured as inputs or outputs, with ports 0 and 2 also used for addressing external memory. The 8051 is an 8-bit microcontroller commonly used in embedded applications due to its low power consumption and cost-effectiveness.